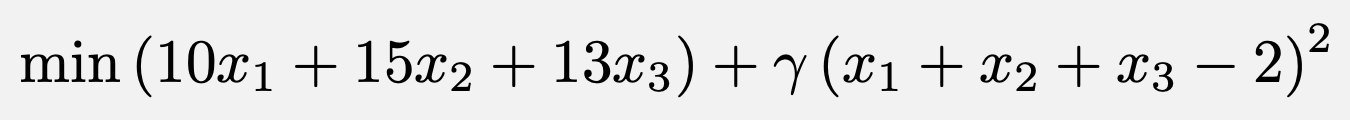Demonstrates what happens when you send a QUBO to the D-Wave QPU
This program takes a 3-variable QUBO function and demonstrates what goes on "behind the scenes" as it runs on the QPU. We see:
- The original QUBO.
- The equivalent Ising form.
- The Ising form embedded onto the QPU architecture using four qubits.
- A scaled version of the embedded Ising form that is the final QMI.
At this point, the problem is run on the D-Wave QPU. When a solution is returned, we see:
- The QMI solution (embedded Ising solution).
- The unembedded Ising solution, with any chain breaks resolved.
- The equivalent unembedded QUBO solution.
Note that we use the default chain strength value in this program (value of 1).
First, run the program as is. Hit return (enter) to continue to the next output as the program runs.
Second, consider the following 3-boxes problem.
Problem:
Pick the pair of boxes with the smallest sum.
As a QUBO, this is written:
Write down your new QUBO, with the Lagrange parameter set to 24.
Third, do the algebra, and write down your new QUBO.
Fourth, in the program for this unit, replace the values on lines 24-29, with the values from your new QUBO.
Fifth, run the program.
Sixth, check through the results, and make sure that you understand them, compared to what you found in the first step.
Released under the Apache License 2.0. See LICENSE file.