openyurtio/openyurt
English | 简体中文
 What is NEW! What is NEW! |
|---|
| September 26th, 2021. OpenYurt v0.5.0 is RELEASED! Please check the CHANGELOG for details. |
| August 6th, 2021. OpenYurt v0.4.1 is RELEASED! Please check the CHANGELOG for details. |
| March 21th, 2021. OpenYurt v0.4.0 is RELEASED! Please check the CHANGELOG for details. |
| January 8th, 2021. OpenYurt v0.3.0 is RELEASED! Please check the CHANGELOG for details. |
| August 30th, 2020. OpenYurt v0.2.0 is RELEASED! Please check the CHANGELOG for details. |
| May 29th, 2020. OpenYurt v0.1.0-beta.1 is RELEASED! Please check the CHANGELOG for details. |
OpenYurt(official website: https://openyurt.io) is now hosted by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation(CNCF) as a Sandbox Level Project. It is built based on native Kubernetes and aims to extend it to support edge computing seamlessly. In a nutshell, OpenYurt enables users to manage applications that run in the edge infrastructure as if they were run in the cloud infrastructure.
OpenYurt is suitable for common edge computing use cases whose requirements include:
- Minimizing the network traffic over long distances between cloud control plane and edge nodes.
- Resolving the network bandwidth or reliability limitations.
- Processing data remotely to reduce latency.
- Providing a better security model to handle sensitive data.
- Manage edge resources and edge applications in the cloud control plane.
OpenYurt has the following advantages over state of the art edge solutions.
- Kubernetes native. It preserves full Kubernetes API compatibility. All Kubernetes native workloads, services, operators, plugins are supported.
- Seamless conversion. It provides a tool to make a Kubernetes cluster "edge" ready. The resource and maintenance overheads from OpenYurt components are low.
- Node autonomy. It provides various mechanisms to tolerate unstable or disconnected cloud-edge networking. Applications running in the edge nodes are not affected even if the nodes are disconnected to the cloud.
- Cloud platform agnostic. OpenYurt can be easily deployed in any public cloud Kubernetes services.
- Edge Device Management. It integrates with EdgeX Foundry platform and uses Kubernetes CRDs to manage edge devices.
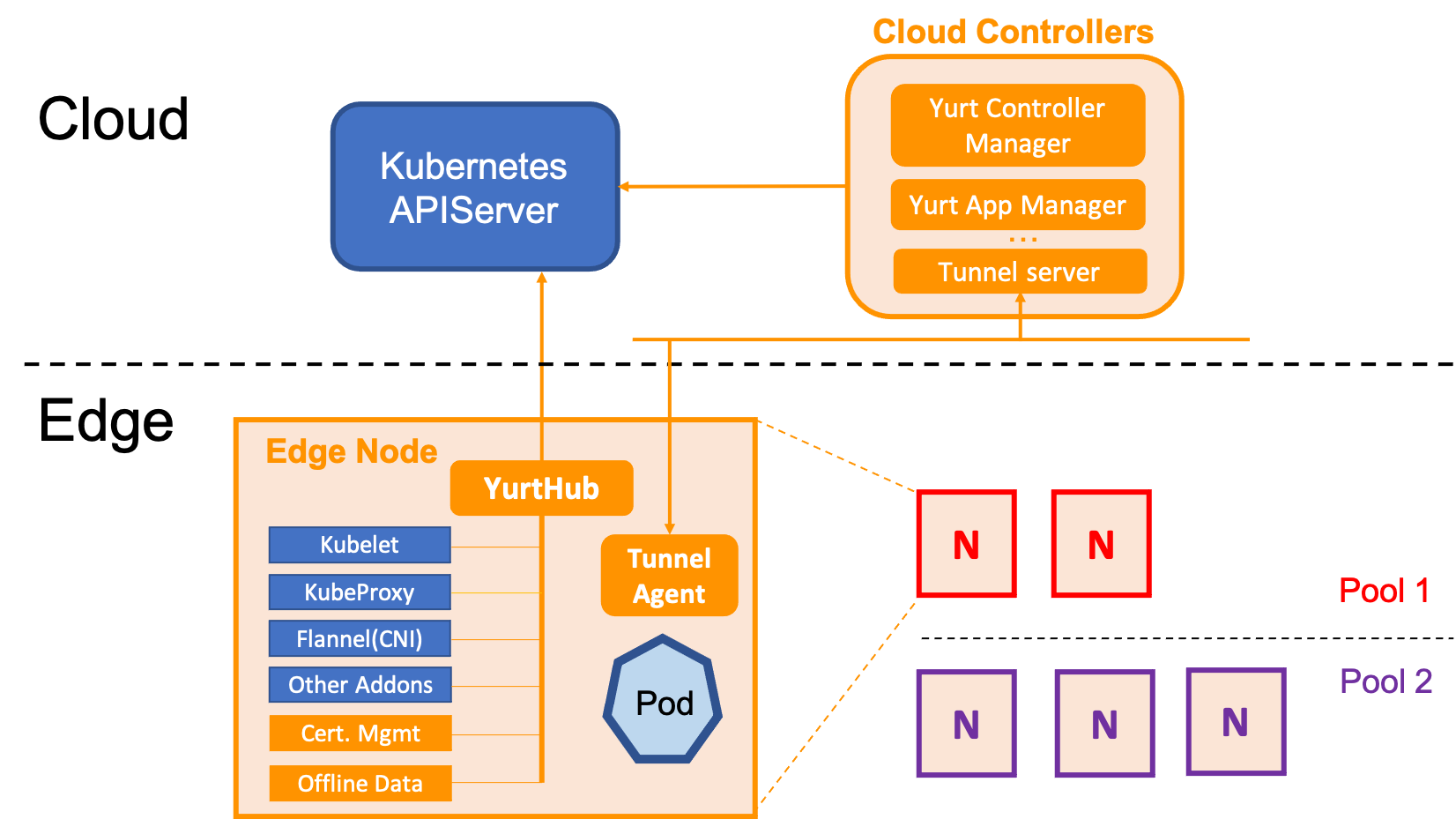
Architecture
OpenYurt follows a classic edge application architecture design -
a centralized Kubernetes control plane residing in the cloud site, which
manages multiple edge nodes residing in the edge site. Each edge node has moderate compute resources available in order to
to run a number of edge applications plus the required node daemons. The edge nodes in a cluster can span
multiple physical regions. The terms region and Pool are used interchangeably in OpenYurt.
As illustrated in above figure, the core OpenYurt components consist of:
- YurtHub: A node daemon that serves as a proxy for the outbound traffic from the Kubernetes node daemons (Kubelet, Kubeproxy, CNI plugins and so on). It caches the states of all the resources that the Kubernetes node daemons might access in the edge node's local storage. In case the edge node is disconnected to the cloud, YurtHub can recover the states when the node restarts.
- Yurt controller manager: It manages a node controller for different edge computing use cases. For example,
the Pods in the nodes that are in the
autonomymode will not be evicted from APIServer even if the node heartbeats are missing. - Yurt app manager: It manages two CRD resources introduced in OpenYurt: NodePool and UnitedDeployment. The former provides a convenient management experience for a pool of nodes within the same region or site. The latter defines a new edge application management methodology of using per node pool workload.
- Yurt tunnel (server/agent):
TunnelServerconnects with theTunnelAgentdaemon running in each edge node via a reverse proxy to establish a secure network access between the cloud site control plane and the edge nodes that are connected to the intranet.
In addition, OpenYurt also includes auxiliary controllers for integration and customization purposes.
- Node resource manager: It manages edge node resources other than CPU/Memory of OpenYurt cluster in a unified manner. It currently supports managing LVM, QuotaPath and Pmem Memory. Please refer to node-resource-manager for more details.
- Yurt-edgex-manager: It manages EdgeX Foundry software suite lifecycle such as create, delete, update in OpenYurt cluster. Please refer to yurt-edgex-manager for more details.
- Yurt-device-controller: It uses Kubernetes custom resources to manage edge devices hosted by the existing edge computing platforms, such as EdgeX Foundry. Please refer to yurt-device-controller for more details.
Before you begin
Resource and system requirements
Getting started
OpenYurt supports Kubernetes versions up to 1.18. Using higher Kubernetes versions may cause compatibility issues.
You can setup the OpenYurt cluster manually, but we recommend to start
OpenYurt by using the yurtctl command line tool. To quickly build and install yurtctl,
assuming the build system has golang 1.13+ and bash installed, you can simply do the following:
git clone https://github.com/openyurtio/openyurt.git
cd openyurt
make build WHAT=cmd/yurtctlThe yurtctl binary can be found at _output/bin. To convert an existing Kubernetes cluster to an OpenYurt cluster,
the following simple command line can be used(support kubernetes clusters that managed by minikube, kubeadm, kind):
_output/bin/yurtctl convert --provider [minikube|kubeadm|kind]To uninstall OpenYurt and revert back to the original Kubernetes cluster settings, you can run the following command:
_output/bin/yurtctl revertTo create OpenYurt cluster, you can run the following command:
_output/bin/yurtctl initTo join nodes to OpenYurt, you can run the following command:
_output/bin/yurtctl joinTo reset nodes of OpenYurt, you can run the following command:
_output/bin/yurtctl resetPlease check yurtctl tutorial for more details.
Usage
We provider detailed tutorials to demonstrate how to use OpenYurt to manage edge applications.
Roadmap
Community
Contributing
If you are willing to be a contributor for OpenYurt project, please refer to our CONTRIBUTING document for details. We have also prepared a developer guide to help the code contributors.
Meeting
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| APAC Friendly Community meeting | Bi-weekly APAC (Starting Sep 2, 2020), Wednesday 11:00AM GMT+8 |
| Meeting link APAC Friendly meeting | https://us02web.zoom.us/j/82828315928?pwd=SVVxek01T2Z0SVYraktCcDV4RmZlUT09 |
| Meeting notes | Notes and agenda |
| Meeting recordings | OpenYurt bilibili Channel |
Contact
If you have any questions or want to contribute, you are welcome to communicate most things via GitHub issues or pull requests. Other active communication channels:
- Mailing List: https://groups.google.com/g/openyurt/
- Slack: channel
- Dingtalk Group (钉钉讨论群)
License
OpenYurt is under the Apache 2.0 license. See the LICENSE file for details. Certain implementations in OpenYurt rely on the existing code from Kubernetes and the credits go to the original Kubernetes authors.