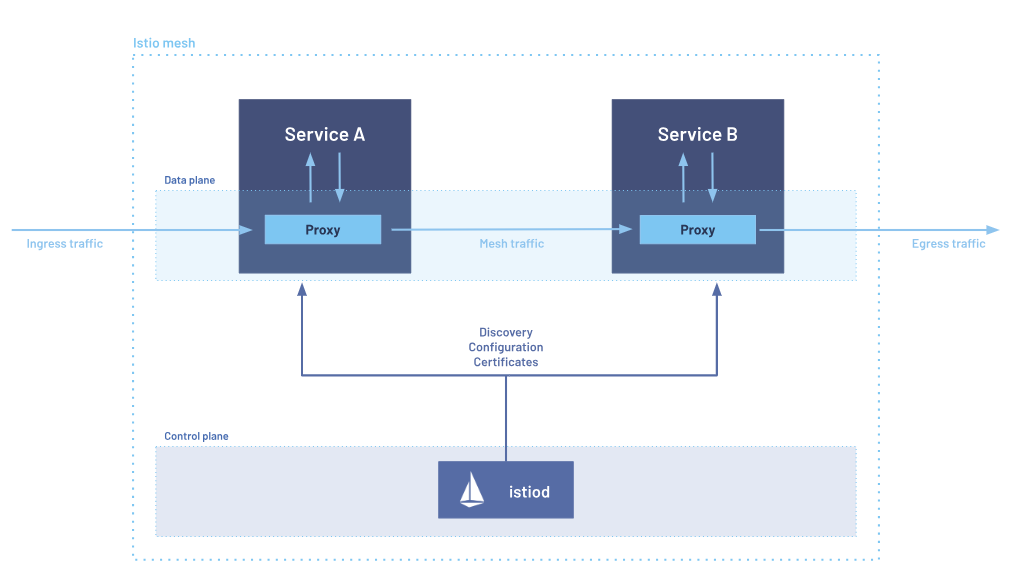
Istio is an open-source service mesh platform that provides a way to manage and secure communication between microservices in a distributed application. It acts as a layer on top of the network infrastructure, offering advanced traffic management, security, and observability features without requiring changes to the application code.
Key features of Istio include:
-
Traffic Management: Istio allows fine-grained control over traffic behavior, including routing, load balancing, and failover. It supports advanced policies like A/B testing, canary releases, and circuit breaking.
-
Security: Istio provides robust security features such as mutual TLS (mTLS) for secure service-to-service communication, authentication, and authorization. It helps enforce policies to protect services from vulnerabilities.
-
Observability: Istio offers tools for monitoring and observing the health of microservices, including metrics, distributed tracing, and logging. This helps in diagnosing issues and understanding system behavior.
-
Policy Enforcement: Istio enables the definition and enforcement of policies for access control, rate limiting, and quotas, helping ensure compliance and resource management.
-
Service Discovery and Load Balancing: Istio integrates with service discovery mechanisms to route traffic based on service availability and health, improving system resilience and reliability.
Istio achieves these capabilities by deploying sidecar proxies (usually Envoy) alongside each service in the mesh. These proxies intercept and manage all network traffic between services, applying the desired policies and configurations.
Start minikube cluster
minikube start --driver=docker --memory=4096 --cpus=4Using Docker desktop Kubernetes
kubectl config use-context docker-desktopInstall metrics server and Skooner dashboard
kubectl apply -f kubernetes-dashboard/metrics-server.yaml
kubectl apply -f kubernetes-dashboard/skooner_dashboard.ymlAccess Skooner dashboard Get service account token to access skooner dashboard
kubectl create token skooner-sa -n defaultIstio can be downloaded from release page or via curl commands
- https://istio.io/latest/about/faq/#install-method-selection
- https://istio.io/latest/docs/setup/getting-started/#download
Install Istio demo profile without gateways and enable sidecar injection
cd istio-1.22.3/
istioctl install -f samples/bookinfo/demo-profile-no-gateways.yaml -y
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabledVerify Istio installation status
istioctl verify-install
istioctl analyzeInstall the Kubernetes Gateway API CRDs
kubectl get crd gateways.gateway.networking.k8s.io &> /dev/null || \
{ kubectl kustomize "github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/config/crd?ref=v1.1.0" | kubectl apply -f -; }Check CRDs
$ kubectl get crds
NAME CREATED AT
authorizationpolicies.security.istio.io 2024-08-03T14:21:56Z
destinationrules.networking.istio.io 2024-08-03T14:21:56Z
envoyfilters.networking.istio.io 2024-08-03T14:21:56Z
gatewayclasses.gateway.networking.k8s.io 2024-08-03T14:24:22Z
gateways.gateway.networking.k8s.io 2024-08-03T14:24:22Z
gateways.networking.istio.io 2024-08-03T14:21:56Z
grpcroutes.gateway.networking.k8s.io 2024-08-03T14:24:22Z
httproutes.gateway.networking.k8s.io 2024-08-03T14:24:23Z
peerauthentications.security.istio.io 2024-08-03T14:21:56Z
proxyconfigs.networking.istio.io 2024-08-03T14:21:56Z
referencegrants.gateway.networking.k8s.io 2024-08-03T14:24:23Z
requestauthentications.security.istio.io 2024-08-03T14:21:56Z
serviceentries.networking.istio.io 2024-08-03T14:21:56Z
sidecars.networking.istio.io 2024-08-03T14:21:56Z
telemetries.telemetry.istio.io 2024-08-03T14:21:56Z
virtualservices.networking.istio.io 2024-08-03T14:21:56Z
wasmplugins.extensions.istio.io 2024-08-03T14:21:56Z
workloadentries.networking.istio.io 2024-08-03T14:21:56Z
workloadgroups.networking.istio.io 2024-08-03T14:21:56ZDeploy the sample application
kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml
kubectl get po,svc,saValidate the application
kubectl exec "$(kubectl get pod -l app=ratings -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')" -c ratings -- curl -sS productpage:9080/productpage | grep -o "<title>.*</title>"
Check gateway class
kubectl get gatewayclass
kubectl describe gatewayclass/istioInstall gateway for BookInfo app
kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/gateway-api/bookinfo-gateway.yaml
kubectl get gateways
kubectl get gateways/bookinfo-gateway -o yamlOpen your browser and navigate to http://localhost:80/productpage to view the Bookinfo application. If you refresh the page, you should see the book reviews and ratings changing as the requests are distributed across the different versions of the reviews service.
Istio integrates with several different telemetry applications. These can help you gain an understanding of the structure of your service mesh, display the topology of the mesh, and analyze the health of your mesh.
kubectl apply -f samples/addons
kubectl rollout status deployment/kiali -n istio-systemAccess the Kiali dashboard.
istioctl dashboard kialiIn the left navigation menu, select Graph and in the Namespace drop down, select default. To see trace data, you must send requests to your service. The number of requests depends on Istio’s sampling rate and can be configured using the Telemetry API. With the default sampling rate of 1%, you need to send at least 100 requests before the first trace is visible. To send 100 requests to the productpage service, use the following command:
for i in $(seq 1 100); do curl -s -o /dev/null "http://$GATEWAY_URL/productpage"; doneor
while true; do curl -s http://localhost:80/productpage > /dev/null; sleep 0.5; doneThe Kiali dashboard shows an overview of your mesh with the relationships between the services in the Bookinfo sample application. It also provides filters to visualize the traffic flow.
Access the jaeger dashboard.
istioctl dashboard jaegerkubectl delete -f samples/bookinfo/gateway-api/bookinfo-gateway.yamlWe will be using istio API for this demo. Install Istio Gateways
istioctl install -f samples/bookinfo/demo-profile-with-gateways.yaml -y
kubectl get po,svc -n istio-systemInstall Ingress Gateway to access the application.
The configurations for Gateway and VirtualService dynamically configures the Istio Ingress Gateway. The Gateway and VirtualService resources are custom resource definitions (CRDs) in Kubernetes. These are high-level abstractions that define how traffic should be managed at the ingress and service levels.
When you apply a Gateway or VirtualService resource to your Kubernetes cluster, Istio's control plane (specifically the Istiod component) picks up these configurations.Istiod then translates these configurations into low-level Envoy configurations that are pushed to the Istio Ingress Gateway (and other Envoy proxies in the mesh).
The Istio Ingress Gateway itself runs an Envoy proxy. It does not have a static config file where you manually apply these settings. Instead, it receives its configuration dynamically from Istiod. The Gateway resource defines which ports the Ingress Gateway should listen on and which hostnames it should handle.
The VirtualService resource defines the routing rules for the incoming traffic, specifying which services within the mesh should handle requests based on path, headers, etc.
kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml
kubectl get gateway.networking.istio.io
Kubectl get vskubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/destination-rule-all.yaml
kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-all-v1.yaml
kubectl get virtualservices -o yamlkubectl delete -f samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-all-v1.yaml
kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-reviews-v3.yaml
kubectl get virtualservices -o yamlkubectl delete -f samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-reviews-v3.yaml
kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-reviews-80-20.yaml
kubectl get virtualservices -o yamlOn the /productpage of the Bookinfo app, log in as user jason. Refresh the browser. What do you see? The star ratings appear next to each review.
kubectl delete -f samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-reviews-80-20.yaml
kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-reviews-test-v2.yamlGet profiles list
istioctl profile listExtract configurations that can run only with istioctl
istioctl profile dump default > default_profile.yml
kubectl apply -f default_profile.yml
istioctl apply -f default_profile.ymlInstall a specific profiles. Default is default profiles
istioctl install
istioctl install --set profile=demo -y
istioctl verify-installExtract configurations that can run with kubectl
istioctl manifest generate --set profile=demo > istio-installation.yaml
kubectl apply -f istio-installation.yamlVerify if all objects/resources are deployed
istioctl verify-install -f istio-installation.yaml
kubectl get all -n istio-systemAnalyze the setup
istioctl analyzeUninstall
istioctl uninstall -y --purge
kubectl delete namespace istio-system
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection-- Architecture v1.4: https://istio.io/v1.4/docs/ops/deployment/architecture
- Architecture(latest): https://istio.io/latest/docs/ops/deployment/architecture/
- Distributed tracing: https://istio.io/latest/docs/tasks/observability/distributed-tracing/overview/
- Gateway API: https://gateway-api.sigs.k8s.io/
- Gateway API implementations: https://gateway-api.sigs.k8s.io/implementations
- Sidecar mode: https://istio.io/latest/docs/setup/getting-started/
- Ambient mode: https://www.cncf.io/blog/2024/03/19/istio-announces-the-beta-release-of-ambient-mode/
- BookInfo app: https://istio.io/latest/docs/examples/bookinfo/
- Gateway API tasks: https://istio.io/latest/docs/tasks/traffic-management/ingress/gateway-api/
- Traffic management: https://istio.io/latest/docs/concepts/traffic-management/
- Virtual services: https://istio.io/latest/docs/concepts/traffic-management/#virtual-services
- Destination rules:https://istio.io/latest/docs/concepts/traffic-management/#destination-rules
- DestinationRule Load balancing options: https://istio.io/latest/docs/concepts/traffic-management/#load-balancing-options
- Request routing: https://istio.io/latest/docs/tasks/traffic-management/request-routing/
- HTTP Match: https://istio.io/latest/docs/concepts/traffic-management/#virtual-service-example
- ConsistentHashLB: https://istio.io/latest/docs/reference/config/networking/destination-rule/#LoadBalancerSettings-ConsistentHashLB