-
PostgreSQL Database
Tested withPostgres 12underWSL2. -
Filled out configuration
The fileconfig.template.jsonis a template file for the configuration. In order to take effect rename the file toconfig.json.
Following parameters can be tweaked:Name Function client:base-urlURL of the server which the client communicates to client:logger-configFilename of the client logging configuration, leave untouched if not sure server:portPort on which the server listens to clients server:dbPostgres database config consisting of the fields user,password,ipandportserver:logger-configFilename of the server logging configuration, leave untouched if not sure server:mapquest-api-keyYour private key to the MapQuest API, find more about here server:routes-pathPath in which the route information images are stored server:exports-pathPath in which the tour export pdfs are stored
dotnet build --configuration Release
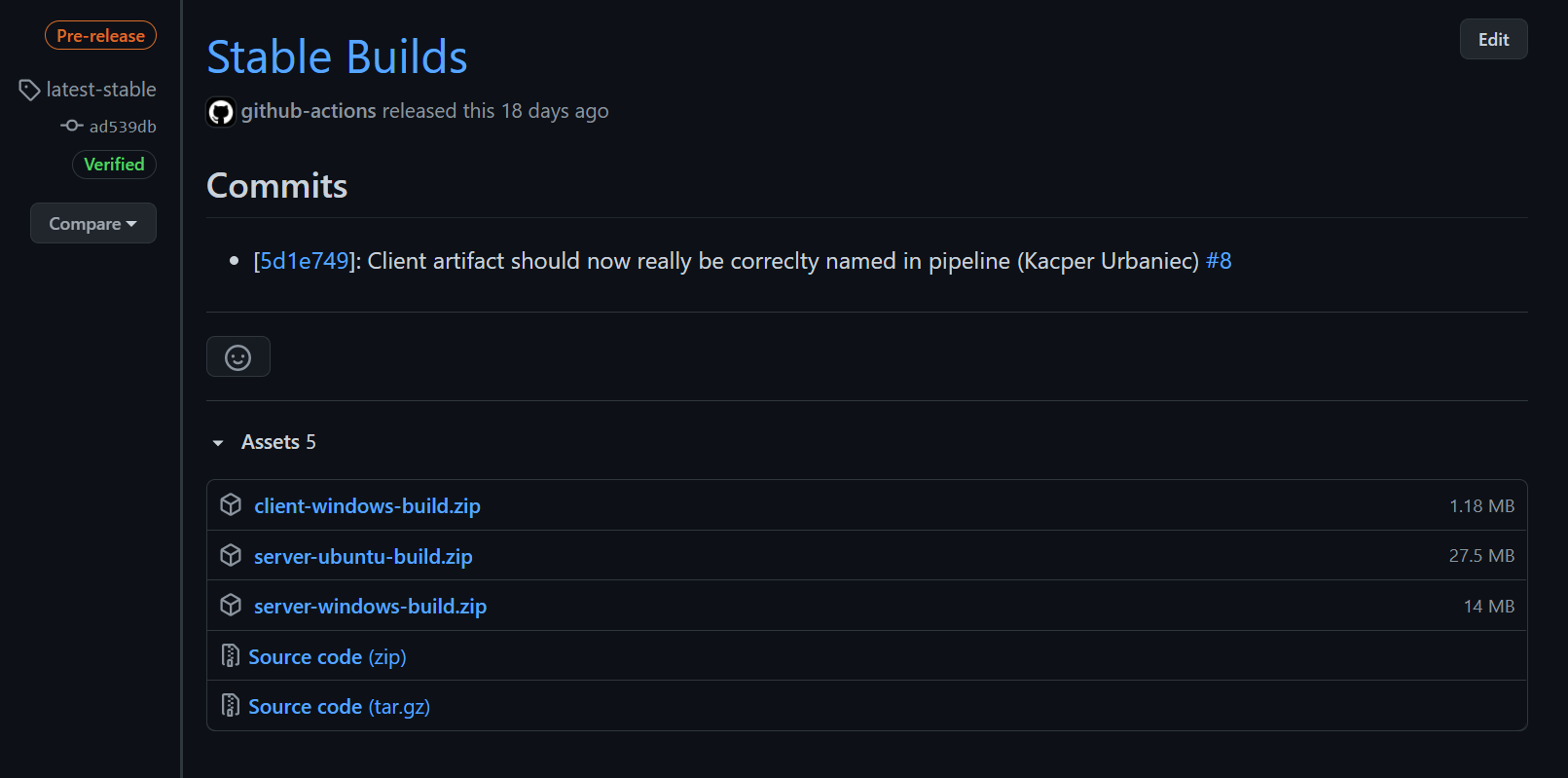
Pre-build artefacts can be found here
Run Tour-Planner server
dotnet run --project .\Server\Server\Server.csproj
Run Tour-Planner server
dotnet run --project .\Client\Client\Client.csproj
Run unit tests
dotnet test
Tour-Planner is based on a Client-Server architecture where the server does all the heavy lifting like data management and persistence and the client is a simple thin-client that communicates with the server through REST-calls. This makes it possible to add or swap out client applications without touching the core business rules in the server.
Both server and client feature internally a layered architecture:
- Services Layer
The server does not have a view or anything similar. Its utmost functionality is to provide access to the offered tour-planner services. This is done through REST-endpoints which are defined internally in theControllerspackage in theTourControllerclass. Each valid request is passed to the Business Layer and returned via a corresponding HTTP-Response. - Business Layer
The Business Layer implements the core functionality and encapsulates all relevant logic. It is defined in theBLpackage and consists of theTourPlannerServerclass which performs the functionality through mostly internal calls to the Data Access Layer. - Data Access Layer
The server has three interfaces in theDALpackage for different data access methods:IDataManagement
Interface used for CRUD operations for the Tour models. Concrete implementation is thePostgresDbclass.IMapApi
Interface used to interact with a Map API. Concrete implementation is theMapQuestApiclass.IExportHanlder
Interface that describes a way to create a printable document. Concrete implementation is thePdfExportHandlerclass.
-
Presentation Layer
In comparison to the server the client has a typical GUI which the user can interact with. The Views are defined in theViewspackage, corresponding ViewModels are found in theViewModelspackage. Events from the Views typically trigger a Command in the ViewModels which calls the Business Layer when core functionality is affected. -
Business Layer
The Business Layer gives clients access to core functionality which in the current implementation means that the client asks the server to perform it and return the response back to the client. It is defined in theLogic.BLpackage in theTourPlannerClientclass. -
Data Access Layer
The client has three interfaces in theLogic.DALpackage for different data access methods:ITourApi
Interface that describes methods to interact with the server. Concrete implementation is theTourApiclass.IImportExportHandler
Interfaces that defines serialization & deserialization of Tours with files. Concrete implementation is theDataHandlerclass.IFilter
Interfaces that defines a way to filter objects. Concrete implementation is theGeneralFilterclass.
Each project uses the same definition for the Tour data model which is found in its own Solution called Model.
The client application uses WPF for visual representation. It is very basic and styling is minimal, nonetheless it features more modern features like a responsive design.
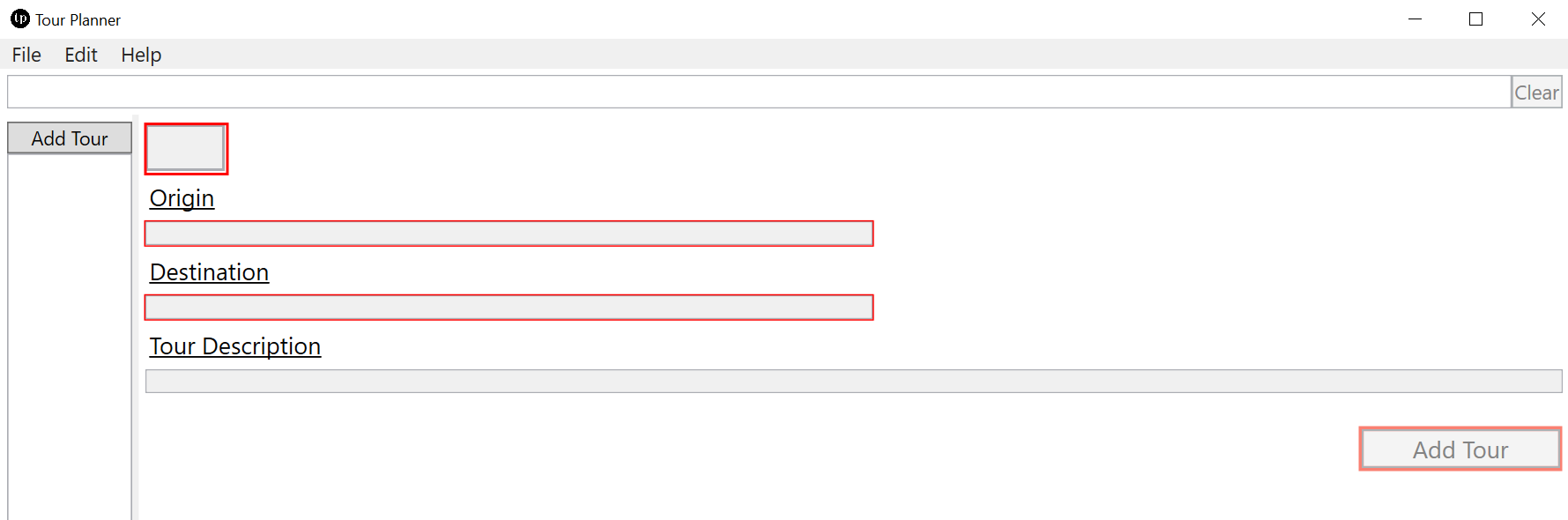
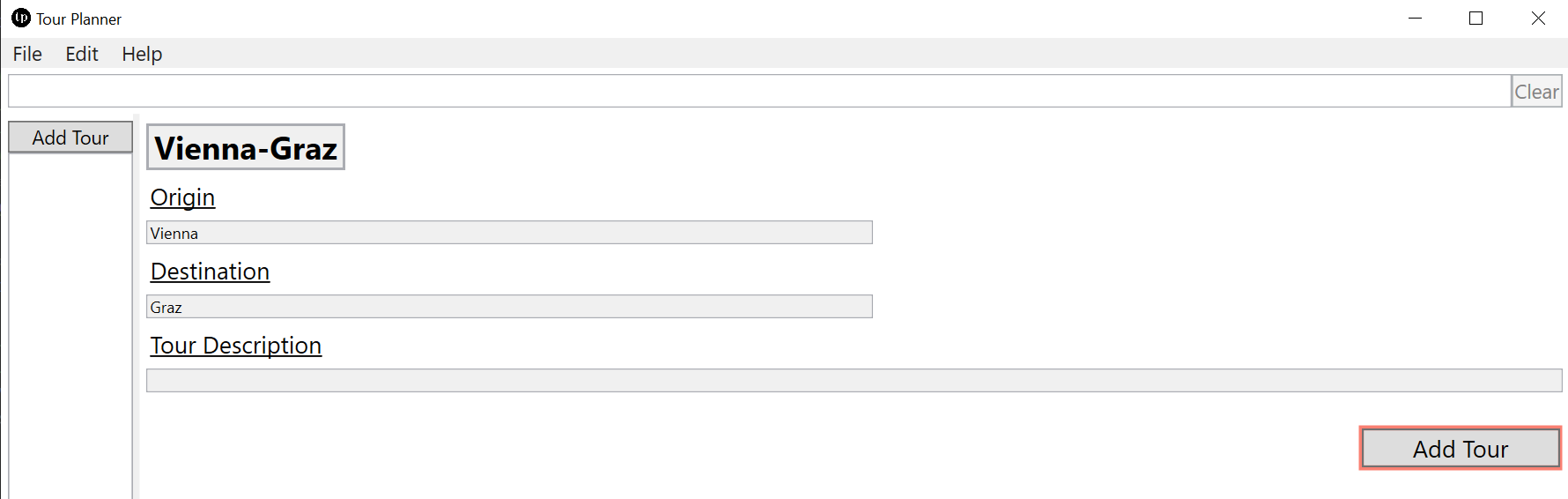
Tour addition is simple, the UI shows which fields are necessary or not and allows only further processing if all fields are filled.
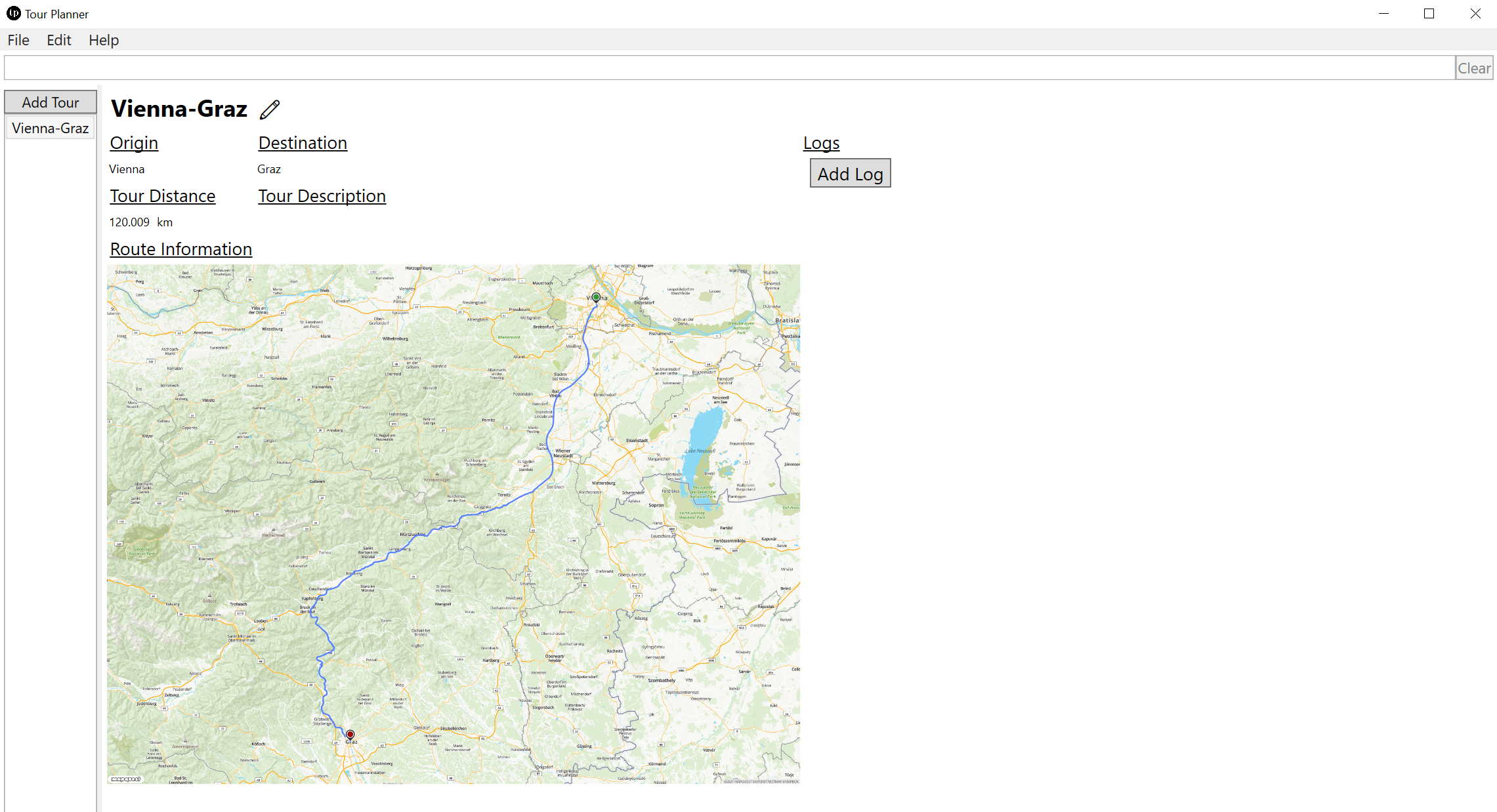
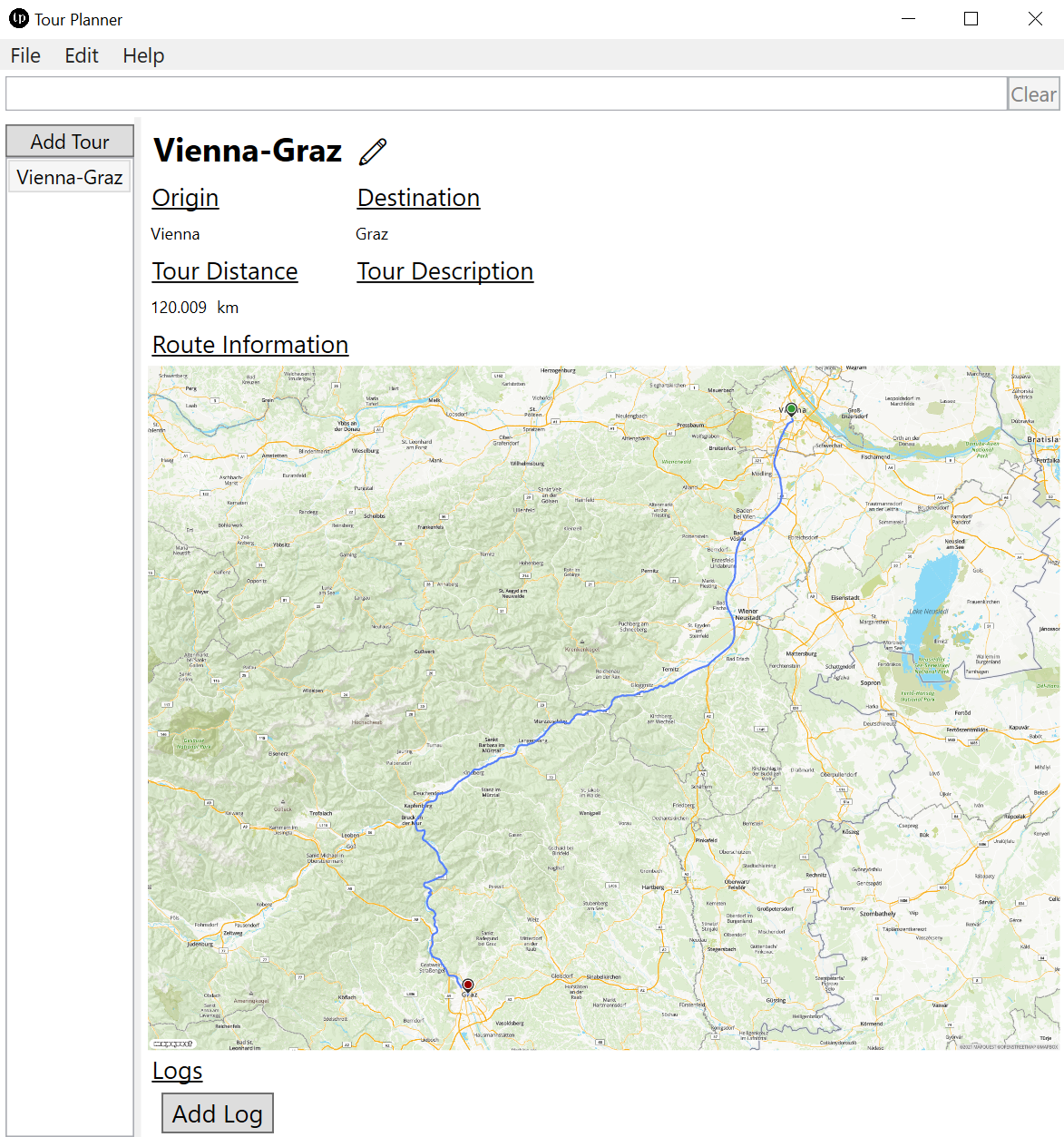
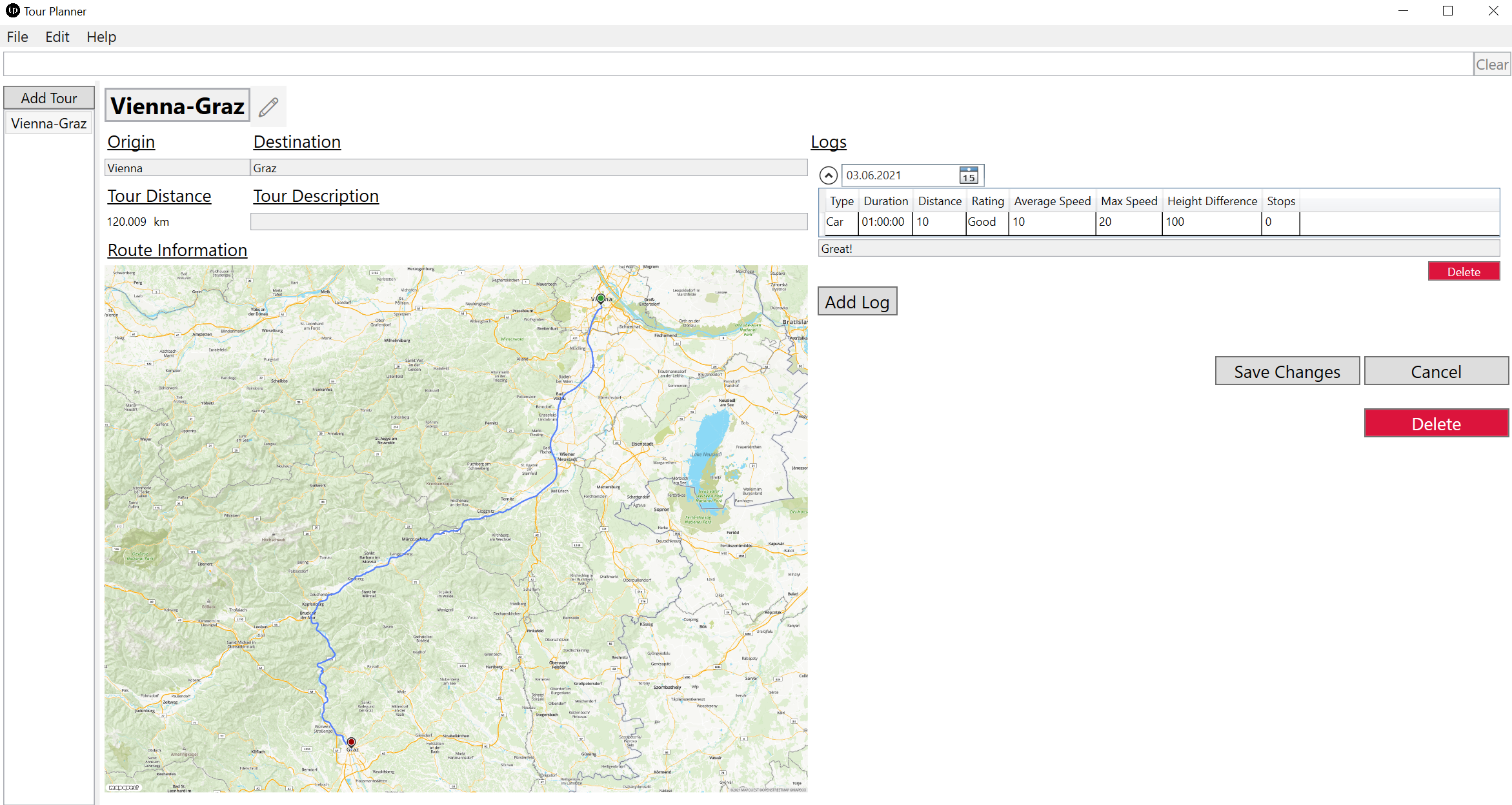
The tour info page is the most sophisticated part of the UI. It features a responsive design which adapts to the width of the application window as seen in the next two images.
The info page is also used to update existing tours or adding new tour logs. To do so one must press the pencil ✏️ button next to the tour title to enter edit mode. When updating the origin and/or the destination of the tour the distance and route information image will be updated accordingly. One can add as many tour logs as one wants and also update and delete them in edit mode.
After editing, changes can be saved or discarded. One can also delete the whole tour and all corresponding tour logs.
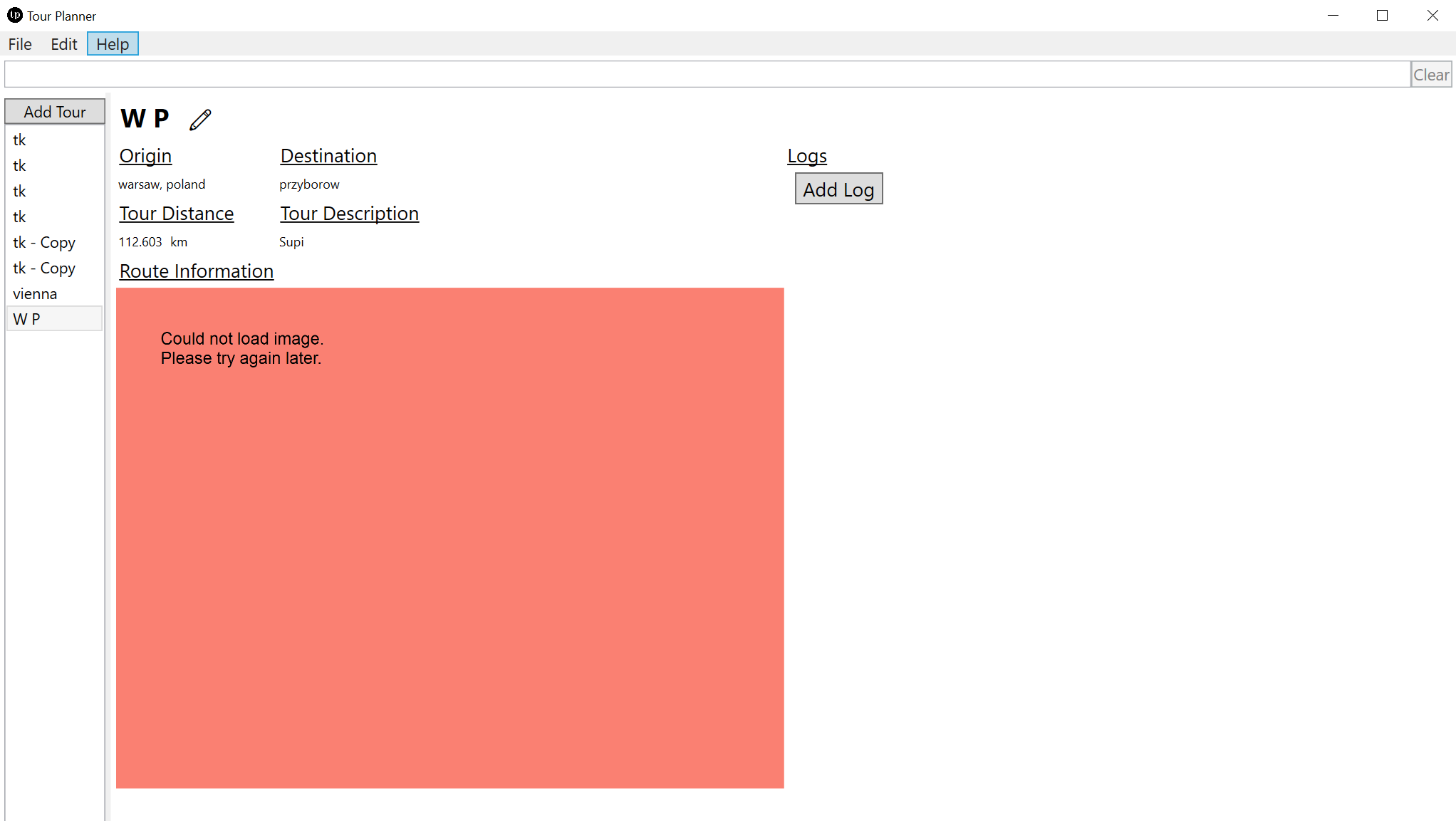
When a route information image cannot be loaded (poor network conditions or the server lost the corresponding image) the client will display an internally generated Bitmap image.
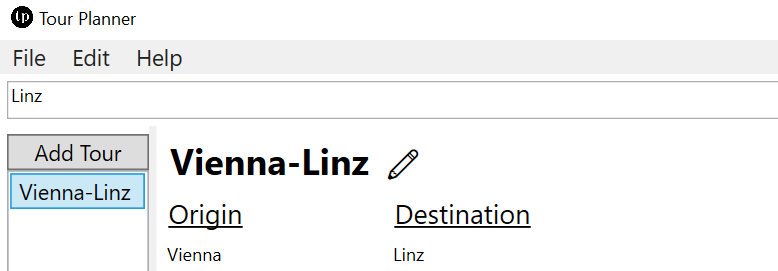
At the top one can find a search bar that searches the given keyword in all fields of tours and tour logs.
Here for example the search filter finds an corresponding match in the title of one tour.
List of some import libraries used throughout the project:
Webservice_Lib
REST-server & Dependency Injection used in the server, based on last semesters Webservice project which can be used now as a librarySystem.WindowswithPresentationFramework
WPF Framework for UI of the clientNpgsql
Postgres Database Access in the serverMicrosoft.Extensions.LoggingwithLog4Net
Used for Logging in the server & clientMicrosoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection
Dependency Injection used in the client
-
MVVM
Event driven programming of user interfaces which are separated inView,ViewModelandModelcomponents. -
Mediator Pattern
Communication between objects through a mediator. The objects do not communicate together directly but instead rely on the mediator. Used for communication betweenViewModels.
Unit tests are written with the help of the Nunit Framework and are separated in client tests and server tests.
TourPlannerServerTest
Tests the Business Layer of the server, especially validation rules (Tourfrom field cannot be empty and so on). Uses predefined classes that are used as substitutes instead of the concreteDALclasses.PdfExportHandlerTest
Checks if pdf export is working correctly (creating files for validTours). This seems rather unnecessary but it provided very useful because the used pdf generation libraryQuestPDFrelied on another dependency which was not designed for Linux. Adding a reference to the valid Linux dependency when building the server on Linux fixed the problem.
TourWrapperTest
Tests the ViewModel which wraps the tour model and is used for binding. This is important because the Wrapper can save but also discard changes on the model. Only the underlying model is send to the server for CRUD operations so it needs to be guaranteed that it is always in a valid state.TourLogWrapperTest
Same asTourWrapperTestbut for tour log models and not tours.DataHandlerTest
Tests the Import/Export of tours through the Business Layer and asserts that data is correctly serialized/deserialized.GeneralFilterTest
Tests the Filter of tours (used in the View for theObservableCollection) and checks if search keywords are found in tour or tour log properties.
The project uses Github Actions for testing & building of artefacts. If one pushes to the main or development branch the pipeline is triggered and executed.
On the releases page one can find the latest builds. There one can find always two releases, the latest stable or latest development builds.
The project implements an optional bonus feature: a REST-server that is responsible for data management and persistence.
Estimated time spent: ~ 65 - 75 h
https://github.com/kurbaniec/SWE2-Tour-Planner
Most encountered problems were WPF-related. This was my first WPF project so I had to get used to the fundamentals of it and how layout/styling is achieved.
Some examples:
- Responsive Design
Implemented with aWrapPaneland twoGrids inside it. The width of theGrids is capped through a customWidthConverterclass which reads the screen size and window size of the application and translates it accordingly. - Scrolling
The logs in the tour info page are realized with aListViewwhich has an internalScrollViewerby default. But it can be removed so theScrollViewerof the page can work correctly. DataGridwith one item
Each log in the tour info page is represented through aDataGridin anExpander. ButDataGrids typically do not support one single item. The solution is a customItemSourceConverterthat takes an item and returns a plain List with only the item in it.