This repository hosts the original code published along with the article in Nature and my experiments (if any) with it.
- This codebase is not written by me (only the "+ my tweaks" part) and I am not employed by DeepMind.
- This implementation is rather old and there are far more efficient algorithms for reinforcement learning available. If you are interested in applying RL to your problem have a look at Keras-RL or rllab instead.
Tested on Ubuntu 14.04 with nVidia GTX 970:
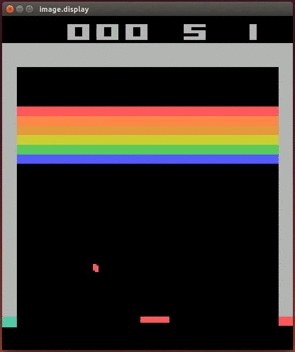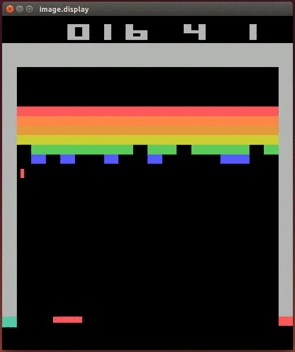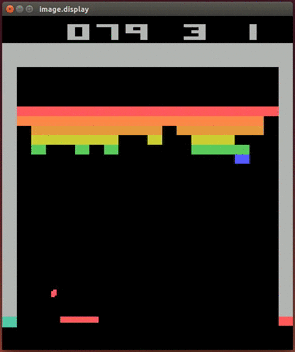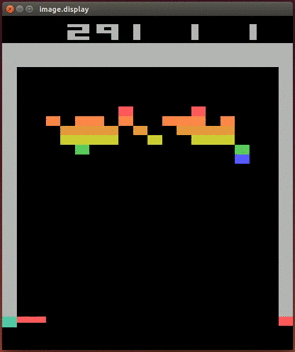
More videos on YouTube Playlist: Deepmind DQN Playing
This project contains the source code of DQN 3.0, a Lua-based deep reinforcement learning architecture, necessary to reproduce the experiments described in the paper "Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning", Nature 518, 529–533 (26 February 2015) doi:10.1038/nature14236.
To replicate the experiment results, a number of dependencies need to be installed, namely:
- LuaJIT and Torch 7.0
- nngraph
- Xitari (fork of the Arcade Learning Environment (Bellemare et al., 2013))
- AleWrap (a lua interface to Xitari) An install script for these dependencies is provided.
Two run scripts are provided: run_cpu and run_gpu. As the names imply, the former trains the DQN network using regular CPUs, while the latter uses GPUs (CUDA), which typically results in a significant speed-up.
The installation requires Linux with apt-get.
Note: In order to run the GPU version of DQN, you should additionally have the NVIDIA® CUDA® (version 5.5 or later) toolkit installed prior to the Torch installation below. This can be downloaded from https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit and installation instructions can be found in http://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-getting-started-guide-for-linux
To train DQN on Atari games, the following components must be installed:
- LuaJIT and Torch 7.0
- nngraph
- Xitari
- AleWrap
To install all of the above in a subdirectory called 'torch', it should be enough to run
./install_dependencies.sh
from the base directory of the package.
Note: The above install script will install the following packages via apt-get: build-essential, gcc, g++, cmake, curl, libreadline-dev, git-core, libjpeg-dev, libpng-dev, ncurses-dev, imagemagick, unzip
Prior to running DQN on a game, you should copy its ROM in the 'roms' subdirectory. It should then be sufficient to run the script
./run_cpu <game name>
Or, if GPU support is enabled,
./run_gpu <game name>
Note: On a system with more than one GPU, DQN training can be launched on a specified GPU by setting the environment variable GPU_ID, e.g. by
GPU_ID=2 ./run_gpu <game name>
If GPU_ID is not specified, the first available GPU (ID 0) will be used by default.
Once you have a snapshot of a network you can run
./test_gpu <game name> <snapshopt filename>
to make it play one game and store the .gif under gifs. For example
./test_gpu breakout DQN3_0_1_breakout_FULL_Y.t7
Options to DQN are set within run_cpu (respectively, run_gpu). You may, for example, want to change the frequency at which information is output to stdout by setting 'prog_freq' to a different value.