CRISPR-DAV is a pipeline to analyze amplicon-based NGS data of CRISPR clones in a high throughput manner. In the pipeline, BWA alignment and ABRA realignment are performed to detect insertion and deletion. The realignment with ABRA was found to have improved detection of large indels. A simplified measurement on a read level, % indel reads, was defined to evaluate NHEJ (Non-Homologous End Joining) efficiency. Homology Directed Repair (HDR) efficiency was assessed in the pipeline as well. Resutls are presented in a comprehensive set of charts and an interactive alignment view. The charts are also helpful to explain potential issues related to read quality, non-specific amplification and sample swapping.
For more details, please check our manuscript https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx518.
The pipeline can be run via a docker container or a physical install. Please see Install-and-Run for instructions.
Results are presented in an HTML report, which looks like this:
The various sections are described below:
Brief information about the amplicon and CRISPR target.
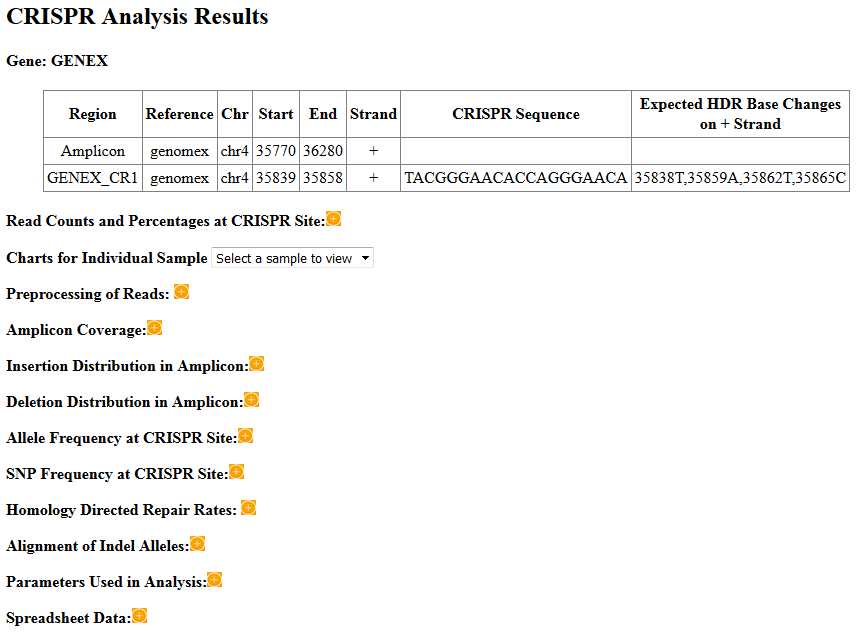
The count plot shows the number of reads (wild type, indel, and inframe indel) at the CRISPR site. The reads must span the sgRNA sequence region. Reads that only overlap with the sgRNA sequence partially are ignored. Wild type reads refer to reads that have no insertions or deletions (indel) in the sgRNA region. Indel reads have insertion and/or deletion of at least one base inside the sgRNA region. The deleted sequence can extend continously beyound the sgRNA region. Inframe indel reads are those indel reads that have net indel lengths as multiples of 3 and thus do not cause frame shift in translation.
The percentage plot shows the percentage of read types with regard to total reads (WT reads + indel reads).
This section shows a group of charts for a particular sample chosen from a dropdown menu.
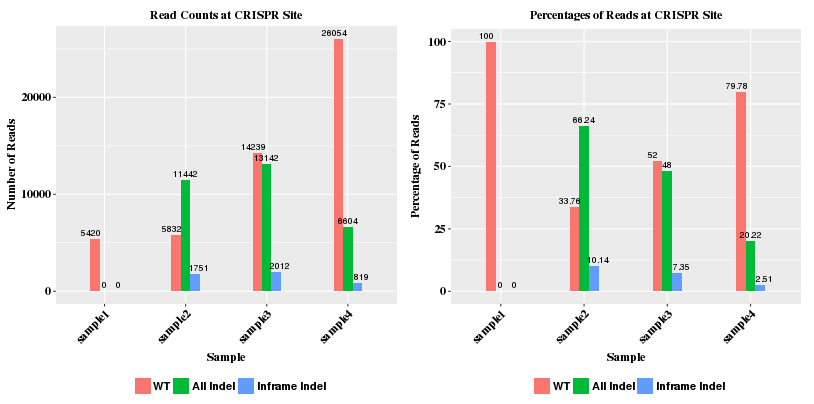
The first plot shows counting of reads at various stages: raw reads, quality reads, reads mapped to genome, and reads mapped to amplicon. The second plot shows the numbers of reads on different chromosomes. If reads are mapped to multiple chromosomes, that usually indicates non-specific amplifiction of the reads in the sample.
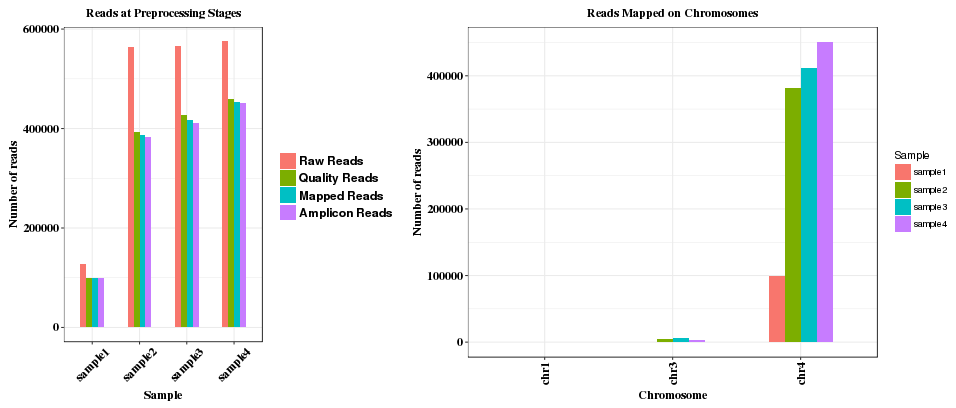
The plot shows the read depth in the amplicon range, with grey bar indicating the location of the CRISPR sgRNA region. Read depth at each position is the sum of reads aligned and reads with deletion at the position.
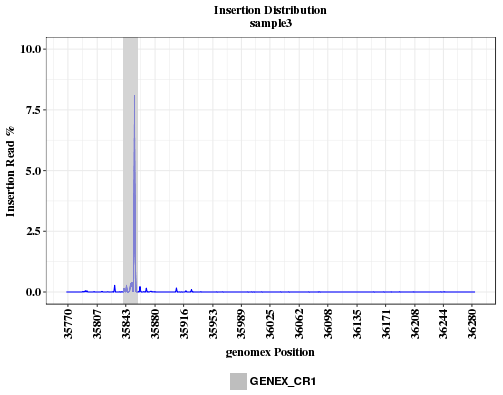
The plot shows the insertion rates across the amplicon range. Insertion rate is calculated as reads with insertion divided by read depth (aligned+deleted). If the insertion is caused by CRISPR, the insertion peak should overlap with the location of CRISRP site. If the peak is far away from the CRISPR site, the sgRNA sequence or coordinates provided may be incorrect, or the sample was swapped with another that has a different guide.
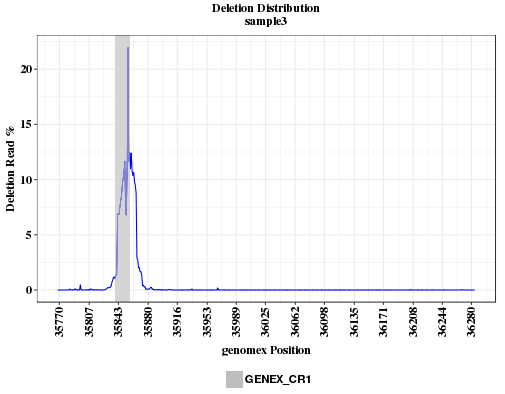
The plot shows the deletion rates across the amplicon range. Deletion rate is calculated as reads with deletion divided by read depth (aligned+deleted). If the deletion is caused by CRISPR, the peak should overlap with the location of CRISRP site. If the peak is far away from the CRISPR site, the sgRNA sequence or coordinates provided may be incorrect, or the sample was swapped with another that has a different guide.
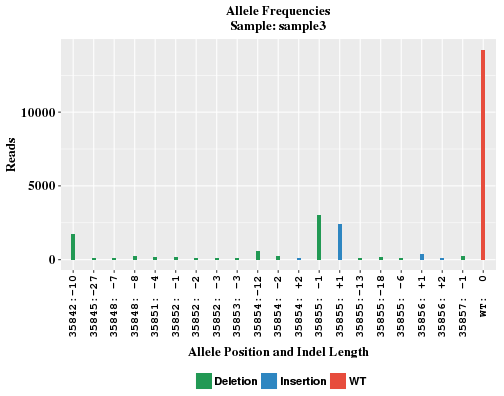
The plot shows the locations and frequencies of the top-abundance indel alleles, and frequency of WT (non-indel) reads. The X-axis indicates the allele position and a net length change as a result of insertion and deletion. WT read has indel length of 0. If allele position is p, for insertion, the inserted bases occur between p and p+1; for deletion, the deleted bases range from p to (p + indel length - 1).
In control sample where no CRISPR is introduced, there is often no significant number of indel reads. Without several indel alleles, the WT bar will look awefully wide in the plot. In order to maintain similar bar width comparable to other samples, sham alleles of zero reads are added to the plot and labeled like "any:+n" and "any:-n" in X-axis.
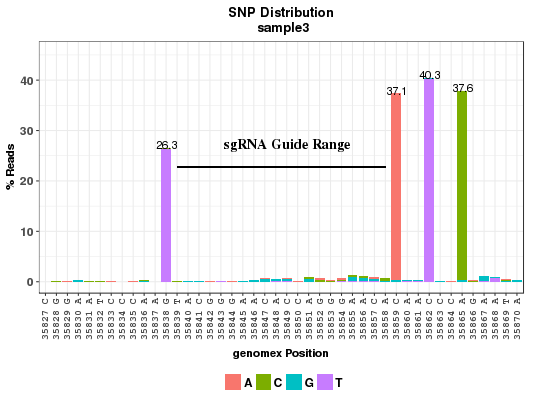
The plot shows the point mutation rates in and around a CRISPR site. The X-axis shows the position and reference base on positive strand; Y-axis shows the percentage of reads with the mutant bases which are color coded. SNP rate is calculated as reads with point mutations divided by total aligned reads at the position. Reads with deletion at the position are not included in the total. The sgRNA sequence region is marked with a horizontal line. The number of bases on the sides of the guide to display is determined by the parameter wing_length in the conf.txt file. Please note that not every read is necessarily long enough to cover all the positions in the plot. Neighboring positions may not show on the same read.
The chart is similar to the "SNP Frequency at CRISPR Site" chart (See previous section). The differences are: (1) The coordinates are restricted to HDR/sgRNA region which covers all bases of intended HDR mutations and sgRNA region. (2) All positions in the chart are on same read. As a result, the SNP rates were deemed more accurate.
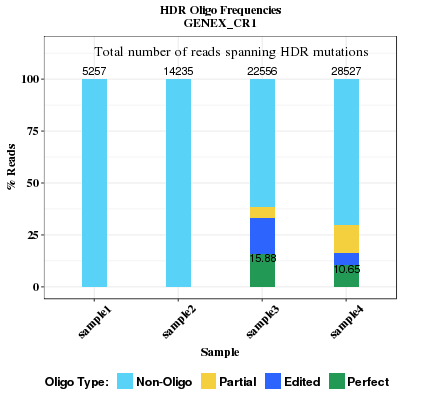
This plot compares the HDR rates across all samples. Read seqences in HDR/sgRNA region are categorized into four types: Non-Oligo, Partial, Edited, Perfect. The rate of perfect repair is labelled in the plot bars if it's greater than 0.1%.
- Non-Oligo: None of the intended base changes occurs, regardless of indel.
- Partial Oligo: Some but not all intended base changes occur, and no indel.
- Edited Oligo: One or more intended base changes occur, and there is indel(s).
- Perfect Oligo: All intended base changes occur, but no indel. Percentage value of perfect oligo is shown inside the bar.
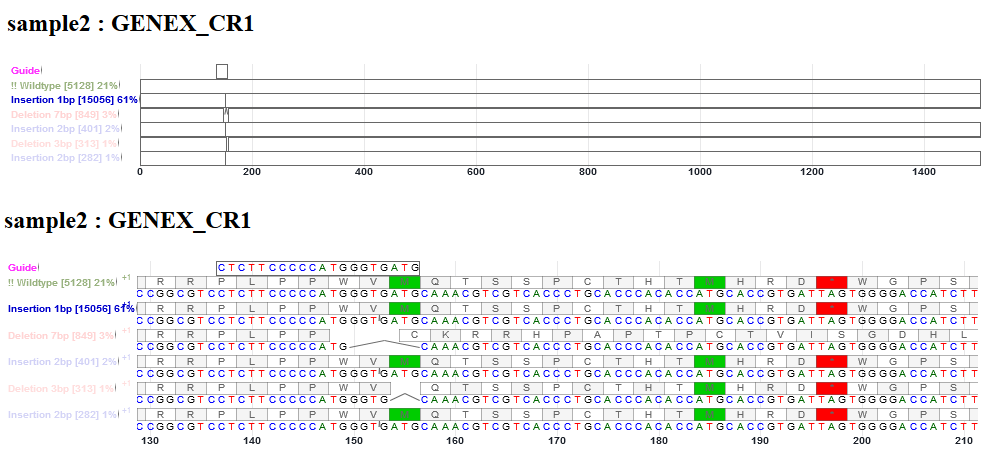
This is an interactive alignment view of the CDS (coding sequence) of sgRNA guide, WT (non-indel), and indel alleles in the gene. The frequencies of WT, deletion and insert reads are shown. Point mutations in reads were not represented here. The CDS sequences before and after indels were reconstructed from reference CDS. The view is enabled with Canvas Xpress (http://canvasxpress.org/html/index.html). The bars can be zoomed in and out, and moved to the left and right. Intronic bases, if present in sgRNA sequence or deleted bases, will not be drawn. Deletion is shown as an arc line connecting neighboring bases. Insertion is shown as a small tick mark between two bases. The inserted bases are shown in the pop up window.
This section appears only when (1) the parameter refGene is specified in conf.txt and the gene of interest can be found in the refGene file; or (2) an amplicon sequence is used as reference in lieu of genome, and codon start location is specified, assuming continuous translation.
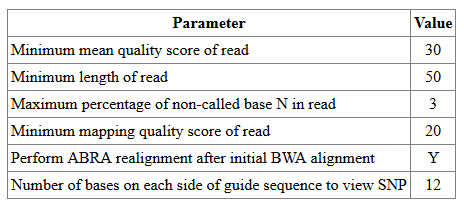
This shows the parameters used for read filtering, realignment, and SNP plot region.
This section lists the Excel files for download. Most of the plots were drawn based on the data in the spreadsheets.
For questions and bugs, please contact xuning.wang@bms.com.