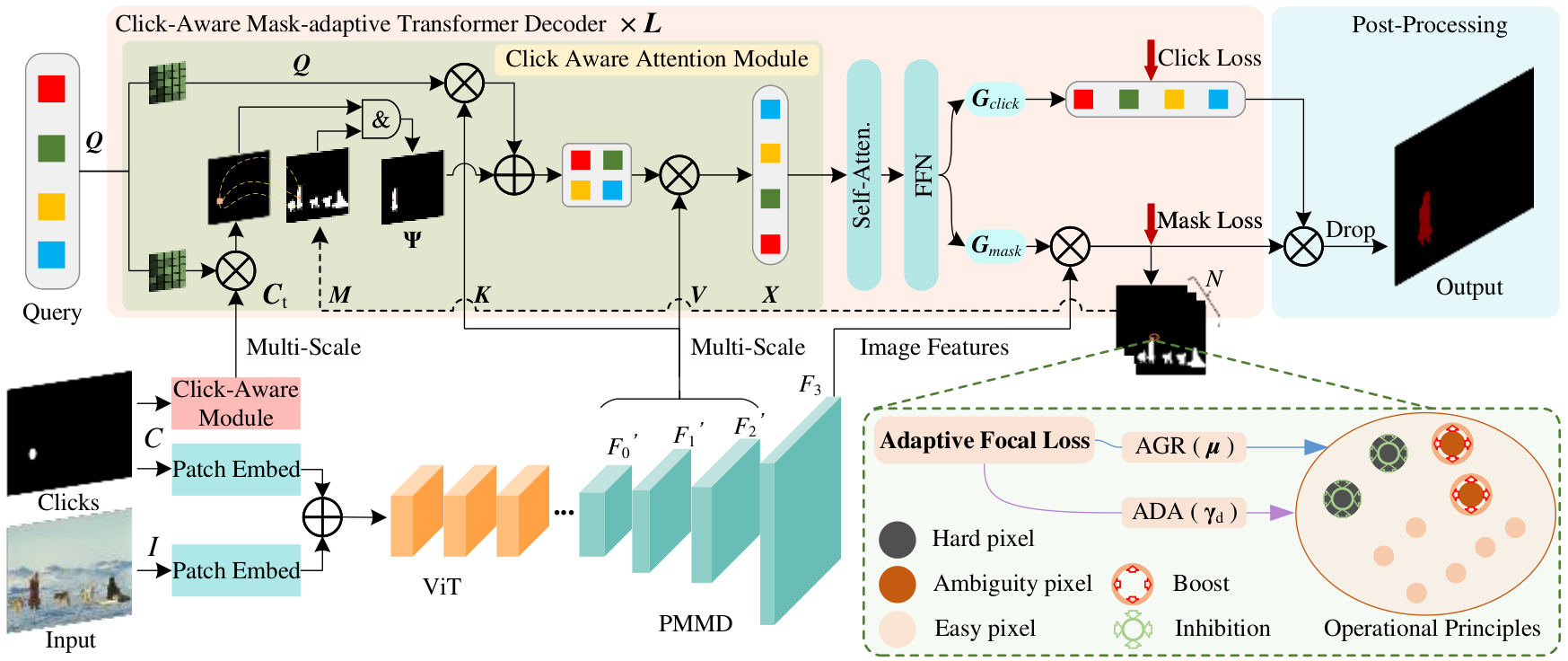
Interactive Image Segmentation (IIS) has emerged as a promising technique for decreasing annotation time. Substantial progress has been made in pre- and post-processing for IIS, but the critical issue of interaction ambiguity that notably hinders segmentation quality, has been under-researched. To address this, we introduce ADAPTIVECLICK – a clicks-aware transformer incorporating an adaptive focal loss, which tackles annotation inconsistencies with tools for mask- and pixel-level ambiguity resolution. To the best of our knowledge, AdaptiveClick is the first transformer-based, mask-adaptive segmentation framework for IIS. The key ingredient of our method is the Clicks-aware Mask-adaptive Transformer Decoder (CAMD), which enhances interaction between clicks and image features. Additionally, AdaptiveClick enables pixel-adaptive differentiation of hard and easy samples in the decision space, independent of their varying distributions. This is primarily achieved by optimizing a generalized Adaptive Focal Loss (AFL) with a theoretical guarantee, where two adaptive coefficients control the ratio of gradient values for hard and easy pixels. Our analysis reveals that the commonly used Focal and BCE losses can be considered special cases of the proposed AFL loss. With a plain ViT backbone, extensive experimental results on nine datasets demonstrate the superiority of AdaptiveClick compared to state-of-the-art methods.
Training and evaluation environment: Python 3.9.7, PyTorch 1.13.1, Ubuntu 20.4, CUDA 11.7. Run the following command to install required packages.
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
After preparing the required environment, run the following command to compile CUDA kernel for MSDeformAttn.
cd isegm/model/modeling/mask2former_helper/ops
sh make.sh
Before evaluation, please download the datasets and models, and then configure the path in configs/base_configuration.yaml.
Use the following code to evaluate the base model.
python scripts/evaluate_model.py NoBRS \
--gpu=0 \
--checkpoint=./weights/adaptiveclick_base448_sbd.pth \
--eval-mode=cvpr \
--datasets=GrabCut,Berkeley,DAVIS,PascalVOC,SBD,ssTEM,BraTS,OAIZIB
Before training, please download the MAE pretrained weights (click to download: ViT-Base).
Use the following code to train a base model on SBD ataset:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3 \
python train.py models/iter_mask/adaptiveclick_base448_sbd_itermask.py \
--batch-size=48 \
--ngpus=4
AdaptiveClick models: Google Drive
BraTS and OAI-ZIB datasets: SimpleClick Github
Other datasets: RITM Github
def sigmoid_adaptive_focal_loss(inputs, targets, num_masks, epsilon: float = 0.5, gamma: float = 2,
delta: float = 0.4, alpha: float = 1.0, eps: float = 1e-12):
"""
Args:
inputs: A float tensor of arbitrary shape.
The predictions for each example.
targets: A float tensor with the same shape as inputs. Stores the binary
classification label for each element in inputs
(0 for the negative class and 1 for the positive class).
epsilon: (optional) Weighting factor in range (0,1) to balance
positive vs negative examples. Default = -1 (no weighting).
gamma: Exponent of the modulating factor (1 - p_t) to
balance easy vs hard examples.
delta: A Factor in range (0,1) to estimate the gap between the term of ∇B
and the gradient term of bce loss.
alpha: A coefficient of poly loss.
eps: Term added to the denominator to improve numerical stability.
Returns:
Loss tensor
"""
prob = inputs.sigmoid()
ce_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(inputs, targets, reduction="none")
p_t = prob * targets + (1 - prob) * (1 - targets)
one_hot = targets > 0.5
with torch.no_grad():
p_sum = torch.sum(torch.where(one_hot, p_t, 0), dim=-1, keepdim=True)
ps_sum = torch.sum(torch.where(one_hot, 1, 0), dim=-1, keepdim=True)
gamma = gamma + (1 - (p_sum / (ps_sum + eps)))
beta = (1 - p_t) ** gamma
with torch.no_grad():
sw_sum = torch.sum(torch.ones(p_t.shape, device=p_t.device), dim=-1, keepdim=True)
beta_sum = (1 + delta * gamma) * torch.sum(beta, dim=-1, keepdim=True) + eps
mult = sw_sum / beta_sum
loss = mult * ce_loss * beta + alpha * (1 - p_t) ** (gamma + 1)
if epsilon >= 0:
epsilon_t = epsilon * targets + (1 - epsilon) * (1 - targets)
loss = epsilon_t * loss
return loss.mean(1).sum() / num_masksThe code is released under the MIT License. It is a short, permissive software license. Basically, you can do whatever you want as long as you include the original copyright and license notice in any copy of the software/source.
- 2023.05.03 Init repository.
- 2023.06.09 Release code and checkpoints.
@article{lin2024adaptiveclick,
title={AdaptiveClick: Click-Aware Transformer With Adaptive Focal Loss for Interactive Image Segmentation},
author={Lin, Jiacheng and Chen, Jiajun and Yang, Kailun and Roitberg, Alina and Li, Siyu and Li, Zhiyong and Li, Shutao},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems},
year={2024},
publisher={IEEE}
}Our project is developed based on RITM, SimpleClick and Mask2Former. Thanks for their excellence works.