PolyPoint is a system for using ultra-wideband RF time-of-flight ranging to perform indoor localization. It incorporates the DecaWave DW1000 for UWB packet transmission and timestamping into a solder-on module that provides node-to-node ranges over an I2C interface.
The name PolyPoint comes from the use of many polygons and shapes in the prototype design and the desire to pinpoint where users are with the system.
When cloning this repository, be absolutely sure to do
git clone --recursive https://github.com/lab11/polypoint.git
so that you get the submodules as well. All of the supporting libraries and build tools are in submodules for the various hardware platforms used in this project.
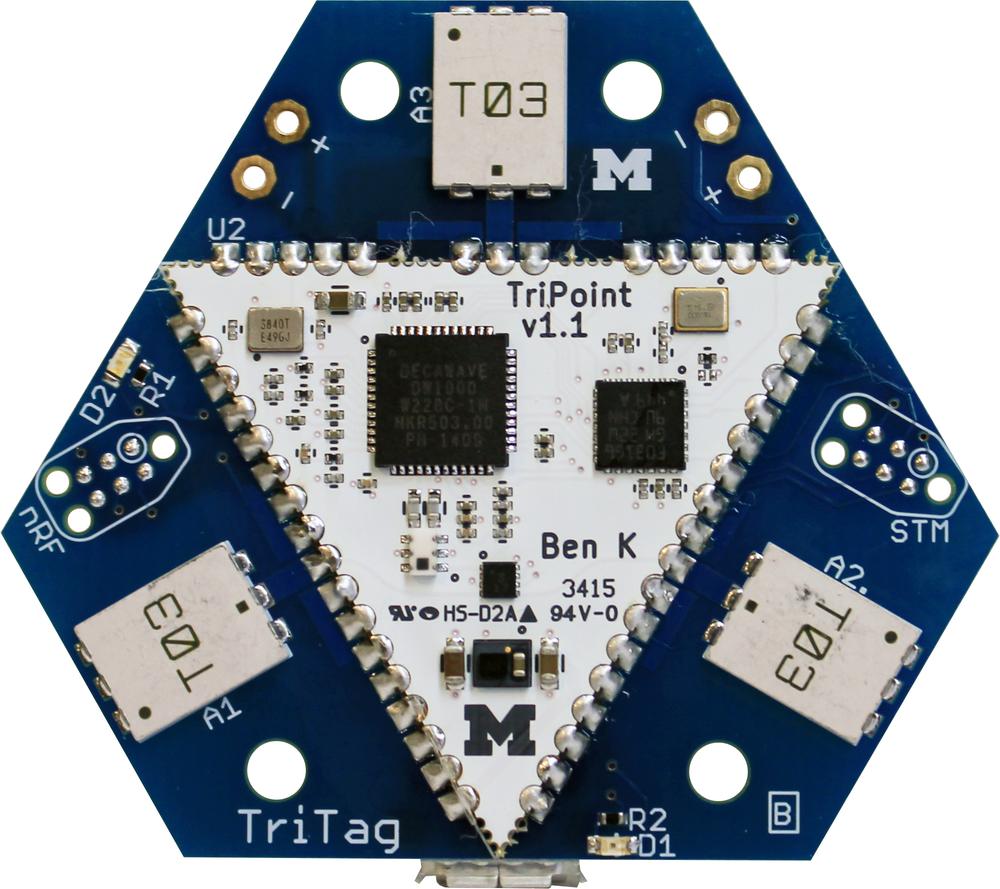
The PolyPoint system is composed of several hardware pieces. At the core is the TriPoint module which is a 1.25" on a side triangle that encompasses all of the core ranging hardware and software. TriPoint has castellated edges and can be soldered on to a carrier board, effectively as a ranging IC. TriTag is one such carrier board designed to be the tag in the ranging system. It includes the UWB antennas and a Bluetooth Low Energy radio plus a battery charging circuit. TriTag is able to provide ranges to a mobile phone application.
TriPoint includes the following components:
- DecaWave DW1000 UWB radio
- STM32F031G6U6 MCU
- RF switch
The MCU contains all the necessary code to run the DW1000 and the ranging protocol.
TriTag includes:
- The TriPoint module
- 3 UWB antennas
- nRF51822 BLE radio
- 3.3 V LDO
- Li-ion battery charger
TriTag is designed to be the tag to be localized in the system and connected to a smartphone.
TriDev is a breakout and testing board for the TriPoint module. It contains the same BLE hardware as TriTag, but also adds an FTDI chip for issuing I2C commands over USB.
PolyPoint contains many software layers that run at various levels of the system.
The core firmware that makes the drop-in TriPoint module work includes all of the logic to implement two way ToF ranging on top of the DecaWave DW1000 UWB radio. The firmware architecture supports multiple "applications", or ranging algorithms, that can be selected at runtime.
The TriTag code implements a BLE application that uses the TriPoint module as an I2C device and prov a BLE service. It puts the TriTag hardware into TAG mode and provides ranges over a BLE characteristic.
The tools in the /phone directory interact with TriTag and read data
across the BLE interface.
The PolyPoint project has led to two academic publications, and an invited talk at HotWireless'16. If you are interested in the theory behind the ranging protocol, please check out our publications:
- SurePoint: Exploiting Ultra Wideband Flooding and Diversity to Provide Robust, Scalable, High-Fidelity Indoor Localization. Benjamin Kempke, Pat Pannuto, Bradford Campbell, and Prabal Dutta. Proceedings of the 14th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems (SenSys’16).
- PolyPoint: Guiding Indoor Quadrotors with Ultra-Wideband Localization. Benjamin Kempke, Pat Pannuto, and Prabal Dutta. 2015 ACM Workshop on Hot Topics in Wireless (HotWireless’15).
If you use PolyPoint or its derivatives, please use the following citation:
@inproceedings{kempke16surepoint,
title = {{SurePoint}: Exploiting Ultra Wideband Flooding and Diversity to Provide Robust, Scalable, High-Fidelity Indoor Localization},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 14th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems},
series = {SenSys'16},
year = {2016},
month = {11},
location = {Stanford, CA, USA},
conference-url = {http://sensys.acm.org/2016/},
author = {Kempke, Benjamin and Pannuto, Pat and Campbell, Bradford and Dutta, Prabal},
}