This readme has the following sections.
- The New Stack (TNS) observability app
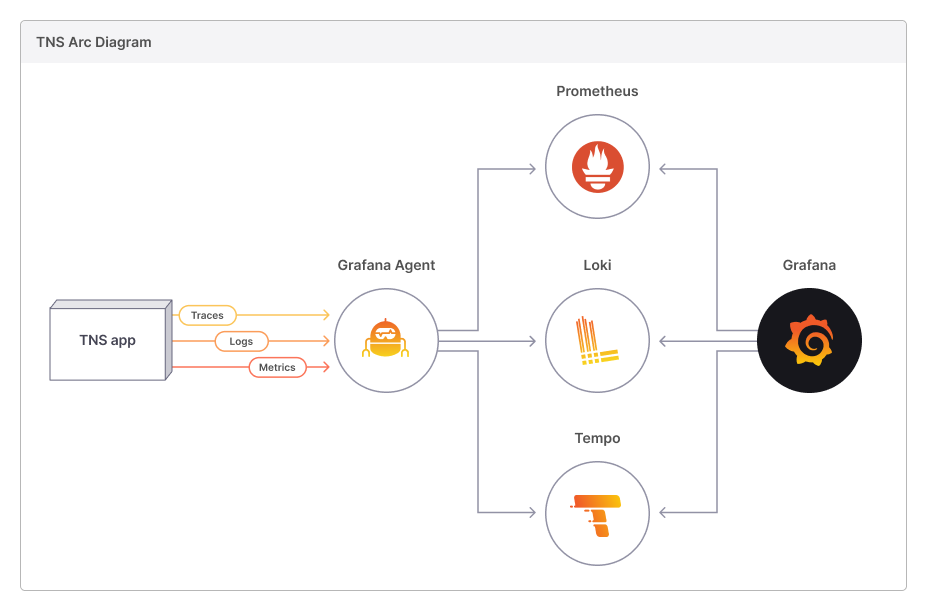
The New Stack (TNS) is a simple three-tier demo application, fully instrumented with the 3 pillars of observability: metrics, logs, and traces. It offers an insight on what a modern observability stack looks like and experience what it's like to pivot among different types of observability data.
The TNS app is an example three-tier web app built by Weaveworks. It consists of a data layer, application logic layer, and load-balancing layer. To learn more about it, see How To Detect, Map and Monitor Docker Containers with Weave Scope from Weaveworks.
The instrumentation for the TNS app is as follows:
-
Metrics: Each tier of the TNS app exposes metrics on /metrics endpoints, which are scraped by the Grafana Agent. Additionally, these metrics are additionally tagged with exemplar information. The Grafana Agent then writes these metrics to a Prometheus (with remote-read enabled) for storage. [While the Prometheus could scrape metrics from the TNS App directly, the demo is configured to make the Agent the central point through which metrics, logs, and traces are collected. The Prometheus can be substituted for any backend which accepts Prometheus remote write, such as Thanos or Cortex.]
-
Logs: Each tier of the TNS app writes logs to standard output or standard error. It is captured by Kubernetes, which are then collected by the Grafana Agent. Finally, the Agent forwards them to Loki for storage.
-
Traces: Each tier of the TNS app sends traces in Jaeger format to the Grafana Agent, which then converts them to OTel format and forwards them to Tempo for storage. Visualization: A Grafana instance configured to talk to the Prometheus, Loki, and Tempo instances makes it possible to query and visualize the metrics, logs, and traces data.
If you are running the full metrics, logs and traces stack locally, install and configure all of the following software applications.
If you wish to only deploy the TNS app to an existing K8s cluster using the app-only option, install and configure kubectl, tanka, and jsonnet-bundler.
Verify you have Docker installed. For download and installation instructions, click here.
To run the TNS demo, you need a Kubernetes cluster. The cluster creation script uses k3d which runs as a single node cluster inside Docker. The specific version to use depends on your operating system:
- For Ubuntu 20.04 and lower, use (https://github.com/rancher/k3d/releases/tag/v3.2.0).
- For Ubuntu 21.10 and higher (which has cgroups v2 enabled by default, and k8s fails to start thinking cgroups are not available), use (https://github.com/rancher/k3d/releases/tag/v5.0.0)
Note: Ensure that your Docker daemon has a minimum of 2.5 GB of total memory available for all pods in this deployment to be scheduled.
You can also run the TNS demo without Kubernetes. Click here for more information.
The TNS demo uses kubectl to interact with the Kubernetes clusters. Click here for kubectl installation instructions.
Tanka uses the Jsonnet language to interact with Kubernetes, via the kubectl tool. Click here for installation instructions.
When you install the TNS demo application, it will create a tanka directory in your TNS checkout. This directory contains all of the Jsonnet resources used to install this demo.
To find out more about Tanka, see https://tanka.dev.
The Jsonnet bundler download Jsonnet dependencies. Click here for download instructions.
After downloading the library:
- Rename the downloaded binary to
jband move it to a location specified in$PATH, for example,/usr/local/bin. - Verify that the binary is executable:
$ chmod +x /usr/local/bin/jb
These instructions assume that you are using a local k3d. If you plan to use a Kubernetes cluster other than a local k3d one, you will need to modify these instructions for your setup.
-
Clone the TNS repository.
$ git clone https://github.com/grafana/tns $ cd tns -
Install K3D cluster.
$ ./create-k3d-cluster $ export KUBECONFIG=$(k3d kubeconfig write tns)
If you see an error similar to
permission denied while trying to connect to the Docker daemon socket at unix:///var/run/docker.sock, then add yourself to thedockergroup. This will ensure that you are able to run Docker without using thesudocommand.$ sudo usermod -aG docker <username>
Logout and then login again for the changes to take effect.
-
Install TNS demo application:
$ ./install
-
Confirm
yeswhen prompted. You will be prompted four times during the installation.Wait for the installation to finish. It can take over ten minutes for everything to download and then start up.
-
Verify the status of your cluster by running this command.
$ kubectl get pods -A
If all the pods are listed as either
runningorcompleted, your cluster is ready for use. -
Access TNS using the URL http://localhost:8080/.
Note: If you need to re-do this process to get everything running, you can run k3d cluster delete tns to delete the cluster, then run ./create-k3d-cluster and re-start the process.
If you already have a K8s cluster and cloud metrics, logs, and traces services available to you, use the app-only option to deploy only the instrumented TNS app to a Kubernetes cluster.
A tutorial using this method will soon be available in Grafana Cloud's docs.
-
Get Kubernetes context
$ kubectl config get-contexts
Note down the context you'd like to use to deploy the app.
-
Deploy the app
$ ./install CONTEXT_YOU_NOTED app-only
-
Confirm
yeswhen prompted. -
Verify the status of your cluster by running this command.
$ kubectl get pods -n tns-cloud
If all the pods are listed as either
running, your app is ready for use.
The following instructions will help you go from metrics to logs to traces.
- Open the TNS dashboard.
- Zoom in on a section of a panel with failed requests.
- From the panel drop-down, click Explore.
- In the Explore view, go to the data source drop-down and select Loki.
- Choose a logline with a traceID of Tempo.
The following instructions will help you go from metrics to logs to traces.
- In Grafana, go to the Explore view.
- From the data source drop-down and select Prometheus.
- Run the following query.
histogram_quantile(.99, sum(rate(tns_request_duration_seconds_bucket{}[1m])) by (le)) - Click on an exemplar data.
- Click on the log icon on a span line to view the log details.
- In Grafana, go to the Explore view.
- From the data source drop-down and select Loki.
- Run the following query.
{job="tns/app"} | logfmt | level="info" | status>=500 and status <=599 and duration > 50ms - Choose a logline with a traceID of Tempo.
To disable your cluster, run this command:
$ k3d cluster stop tnsTo re-enable the cluster, run this command:
$ k3d cluster start tnsTo remove your cluster, run this command:
$ k3d cluster delete tns
$ rm -rf tankaIssue: 404 error when trying to load Tempo traces.
Solution: Your Jaeger agent is likely not running correctly. Check that all pods were successfully scheduled.
- Run
maketo compile the code and tag new images in your local Docker image registry, after you have modified the source code of the TNS demo application, - Instruct
k3dto pull the new images on a pod restart (and not use the image from it's local cache):k3d image import -c tns grafana/tns-app && k3d image import -c tns grafana/tns-db && k3d image import -c tns grafana/tns-loadgen. - Kill relevant pod(s) by running the following command:
kubectl delete pod app-69db48747b-s6qq6 --namespace=tns.
- Update the manifests by running the following tanka command:
tk apply --force environments/<ENV>/main.jsonnet. - Update Grafana, for example, when changing dashboards by running the following tanka command:
tk apply --force environments/default/main.jsonnet.