rvm use ruby-2.5.0@global --create \
&& gem install --no-rdoc --no-ri bundler \
&& gem install --no-rdoc --no-ri rails -v "5.1.2"rails new websvc -d postgresql --skip-yarn --skip-spring \
&& cd websvc \
&& bundle \
&& rails generate scaffold Post title:string content:textFirst, a Dockerfile:
# ./Dockerfile
FROM ruby:2.5.0-alpine
RUN apk add --update \
alpine-sdk \
nodejs \
postgresql-dev \
tzdata
COPY Gemfile* /opt/bundle/
WORKDIR /opt/bundle
RUN bundle install
COPY . /opt/app
WORKDIR /opt/app
ENTRYPOINT ["/bin/ash", "-c"]Also, a .dockerignore:
# ./.dockerignore
tmp/*
log/*
db/*.sqlite3
.git
# ./config/database.yml
default: &default
adapter: postgresql
encoding: unicode
development:
<<: *default
url: <%= ENV['DATABASE_URL'] %>
test:
<<: *default
url: <%= ENV['DATABASE_URL'] %>_test
production:
<<: *default
url: <%= ENV['DATABASE_URL'] %>docker build . -t demo:latestMake sure that a Postgres database named foodb exists on your (Mac) host and
is accessible by a role named foouser:
createuser --createdb foouser \
&& createdb --owner foouser foodbLaunch the server:
docker run -it \
-v $(pwd):/opt/app \
-p 3333:3000 \
-e RAILS_ENV=development \
-e DATABASE_URL=postgresql://foouser@docker.for.mac.host.internal/foodb \
demo:latest "rails db:migrate && rails server -b 0.0.0.0"aws configure set default.region us-east-1Using CloudFormation, we'll create an ECR repository to which we'll push our Docker images:
# image-repository.yml
Resources:
Repository:
Type: AWS::ECR::Repository
Outputs:
RepositoryArn:
Value: !Sub arn:aws:ecr:${AWS::Region}:${AWS::AccountId}:repository/${Repository}
RepositoryUri:
Value: !Sub ${AWS::AccountId}.dkr.ecr.${AWS::Region}.amazonaws.com/${Repository}aws cloudformation deploy \
--stack-name demorepo \
--template-file ./image-repository.ymlOnce the CloudFormation stack containing our ECR repository has been created, we obtain its URI:
export REPOSITORY_URI=$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks \
--stack-name demorepo \
| jq -r '(.Stacks[0].Outputs[] | select(.OutputKey == "RepositoryUri")).OutputValue')eval $(aws ecr get-login --no-include-email)Tag the previously-built image:
docker tag demo:latest ${REPOSITORY_URI}:latestPush the image to the ECR:
docker push ${REPOSITORY_URI}:latestCreate a database (could take 20 minutes):
# database.yml
Parameters:
VpcId:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPC::Id
Description: The VPC which owns the RDS SG
Resources:
RdsWideOpenSecurityGroup:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VpcId
GroupDescription: Accepting traffic from any place
SecurityGroupIngress:
- { CidrIp: 0.0.0.0/0, IpProtocol: -1 }
Tags:
- { Key: Name, Value: demodb-wide-open-sg }
Database:
Type: AWS::RDS::DBInstance
Properties:
AllocatedStorage: 5
BackupRetentionPeriod: 0
DBInstanceClass: db.t2.micro
DBName: foodb
Engine: postgres
EngineVersion: 9.6.5
MasterUsername: foouser
MasterUserPassword: foopassword
PubliclyAccessible: true
VPCSecurityGroups:
- !Ref RdsWideOpenSecurityGroup
Outputs:
DatabaseUrl:
Description: A database connection string
Value:
Fn::Join:
- ""
- - "postgresql://foouser:foopassword"
- "@"
- !GetAtt Database.Endpoint.Address
- ":"
- !GetAtt Database.Endpoint.Port
- "/foodb"Get the default VPC id:
export VPC_ID=$(aws ec2 describe-vpcs \
--filters "Name=isDefault,Values=true" | jq -r '.Vpcs[].VpcId')aws cloudformation deploy \
--stack-name demodb \
--parameter-overrides \
VpcId=${VPC_ID} \
--template-file ./database.ymlAfter that's created, get the database URL from the stack output:
export DATABASE_URL=$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks \
--stack-name demodb \
| jq -r '(.Stacks[0].Outputs[] | select(.OutputKey == "DatabaseUrl")).OutputValue')Get the subnets for this VPC:
export PUBLIC_SUBNETS=$(aws ec2 describe-subnets \
--filters Name=vpc-id,Values=${VPC_ID} \
| jq -r '[([.Subnets[].SubnetId])[0, 2]] | join(",")')Create the cluster (5m26.842s):
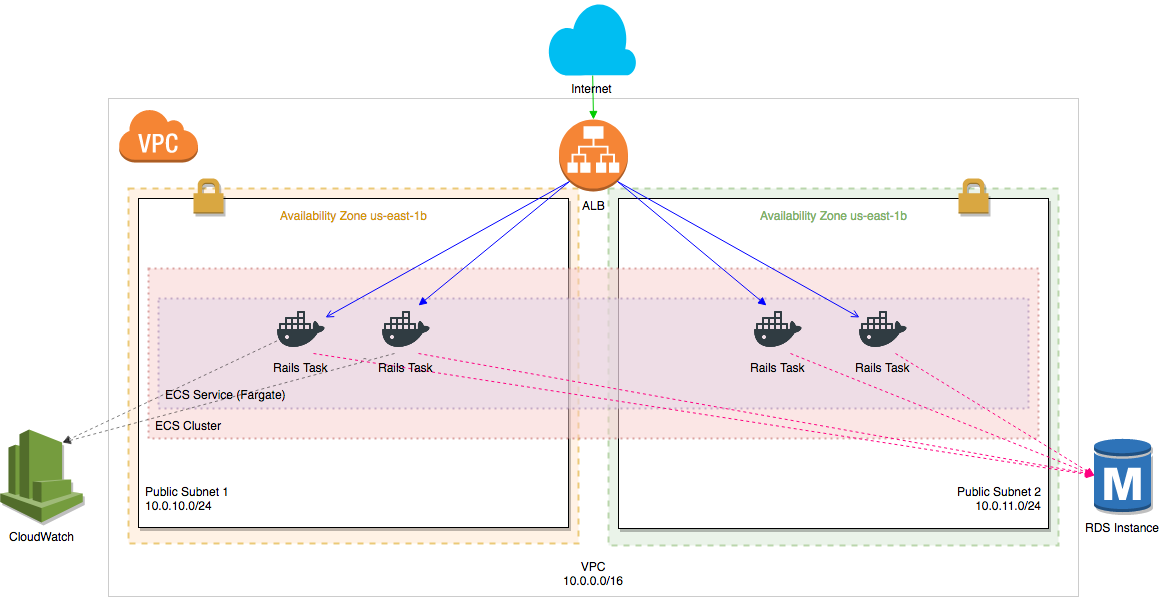
# cluster.yml
Description: >
This template deploys a network load balancer that exposes our ECS service to
the internet
Parameters:
VpcId:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPC::Id
Description: Choose which VPC the Application Load Balancer should be deployed to
PublicSubnets:
Description: Choose which subnets the Application Load Balancer should be deployed to
Type: List<AWS::EC2::Subnet::Id>
DatabaseUrl:
Type: String
DockerImage:
Type: String
Resources:
WideOpenSecurityGroup:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VpcId
GroupDescription: Accepting traffic from any place
SecurityGroupIngress:
- CidrIp: 0.0.0.0/0
IpProtocol: -1
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${AWS::StackName}-wide-open-sg
LoadBalancer:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::LoadBalancer
Properties:
Type: network
Scheme: internet-facing
Name: !Sub ${AWS::StackName}-nlb
Subnets: !Ref PublicSubnets
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${AWS::StackName}-nlb
LoadBalancerListener:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::Listener
Properties:
LoadBalancerArn: !Ref LoadBalancer
Port: 80
Protocol: TCP
DefaultActions:
- Type: forward
TargetGroupArn: !Ref TargetGroup
TargetGroup:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::TargetGroup
Properties:
Name: !Sub ${AWS::StackName}-target-group
VpcId: !Ref VpcId
Port: 3000
Protocol: TCP
TargetType: ip
TargetGroupAttributes:
- Key: deregistration_delay.timeout_seconds
Value: '10'
Cluster:
Type: AWS::ECS::Cluster
Properties:
ClusterName: !Sub ${AWS::StackName}-cluster
Service:
Type: AWS::ECS::Service
DependsOn: LoadBalancerListener
Properties:
Cluster: !Ref Cluster
LaunchType: FARGATE
DesiredCount: 2
DeploymentConfiguration:
MaximumPercent: 150
MinimumHealthyPercent: 100
TaskDefinition: !Ref TaskDefinition
NetworkConfiguration:
AwsvpcConfiguration:
Subnets: !Ref PublicSubnets
AssignPublicIp: ENABLED
SecurityGroups:
- !Ref WideOpenSecurityGroup
LoadBalancers:
- ContainerName: !Sub ${AWS::StackName}-container
ContainerPort: 3000
TargetGroupArn: !Ref TargetGroup
TaskDefinition:
Type: AWS::ECS::TaskDefinition
Properties:
TaskRoleArn: !GetAtt TaskExecutionRole.Arn
ExecutionRoleArn: !GetAtt TaskExecutionRole.Arn
Cpu: 256
Memory: 512
Family: !Sub ${AWS::StackName}-task-family
NetworkMode: awsvpc
RequiresCompatibilities:
- FARGATE
ContainerDefinitions:
- Name: !Sub ${AWS::StackName}-container
Command:
- !Sub "rails db:migrate && rails assets:precompile && rails server -b 0.0.0.0"
Environment:
- Name: RAILS_SERVE_STATIC_FILES
Value: true
- Name: RAILS_LOG_TO_STDOUT
Value: true
- Name: RAILS_ENV
Value: production
- Name: PORT
Value: 3000
- Name: DATABASE_URL
Value: !Ref DatabaseUrl
- Name: SECRET_KEY_BASE
Value: 7db791ebc31366f3fccd67467ed6128f20175ff947c1fe262beb8f28d9466700fda9dbd278cfe7a63d6ace11d282d125a7bfd2d5b813f19d6f23fd46a8d7cdae
Essential: true
Image: !Ref DockerImage
PortMappings:
- ContainerPort: 3000
LogConfiguration:
LogDriver: awslogs
Options:
awslogs-group: !Sub ${AWS::StackName}
awslogs-region: !Ref AWS::Region
awslogs-stream-prefix: ecs
LogGroup:
Type: AWS::Logs::LogGroup
Properties:
LogGroupName: !Sub ${AWS::StackName}
RetentionInDays: 7
TaskExecutionRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- ecs-tasks.amazonaws.com
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
ManagedPolicyArns:
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AmazonECSTaskExecutionRolePolicy
Outputs:
LoadBalancerUrl:
Description: The URL of the NLB
Value: !GetAtt LoadBalancer.DNSNameaws cloudformation deploy \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_IAM \
--stack-name democluster \
--template-file ./cluster.yml \
--parameter-overrides \
DatabaseUrl=${DATABASE_URL} \
VpcId=${VPC_ID} \
PublicSubnets=${PUBLIC_SUBNETS} \
DockerImage=${REPOSITORY_URI}:latestUse stack outputs to get URL of the posts index:
export NLB_DNS_NAME=$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks \
--stack-name democluster \
| jq -r '(.Stacks[0].Outputs[] | select(.OutputKey == "LoadBalancerUrl")).OutputValue')
export POSTS_URL=http://${NLB_DNS_NAME}/postsThen, open the app and create a post:
open ${POSTS_URL}Make requests to the Rails application in a loop:
while true; do echo $(date)-$(curl -s ${POSTS_URL} | grep h1); sleep 1; doneChange the title of the posts index, stage, and commit it:
sed -i -e "s;<h1>.*<\/h1>;<h1>MEOW MEOW HISS<\/h1>;g" websvc/app/views/posts/index.html.erbBuild a new Docker image, tag it, and push it:
docker build . -t demo:latest \
&& docker tag demo:latest ${REPOSITORY_URI}:latest \
&& eval $(aws ecr get-login --no-include-email) \
&& docker push ${REPOSITORY_URI}:latestThen, update the service (~3 minutes for new task to run, 15 for full update):
aws ecs update-service \
--service democluster-service \
--cluster democluster-cluster \
--force-new-deploymentService:
Type: AWS::ECS::Service
Properties:
DesiredCount: 2
DeploymentConfiguration:
MaximumPercent: 150
MinimumHealthyPercent: 100export MIGRATION_TASK_ARN=$(aws ecs run-task \
--launch-type FARGATE \
--network-configuration "awsvpcConfiguration={subnets=[${PUBLIC_SUBNETS}],assignPublicIp=ENABLED}" \
--task-definition democluster-task-family \
--cluster democluster-cluster \
--count 1 \
--overrides '{"containerOverrides": [{"name": "democluster-container", "command": ["rails db:migrate"]}]}' \
--started-by deploy \
| jq -r '.["tasks"][0]["taskArn"]')
aws ecs wait tasks-stopped \
--cluster democluster-cluster \
--tasks ${MIGRATION_TASK_ARN}
export MIGRATION_EXIT_CODE=$(aws ecs describe-tasks \
--cluster democluster-cluster \
--tasks ${MIGRATION_TASK_ARN} | jq -r '.["tasks"][0]["containers"][0]["exitCode"]')
if [ "${MIGRATION_EXIT_CODE}" != "0" ] ; then
# fail build
exit 1
fi