A.A. 2019/2020 - Antonio Lategano, Salvatore Visaggi
Table of contents:
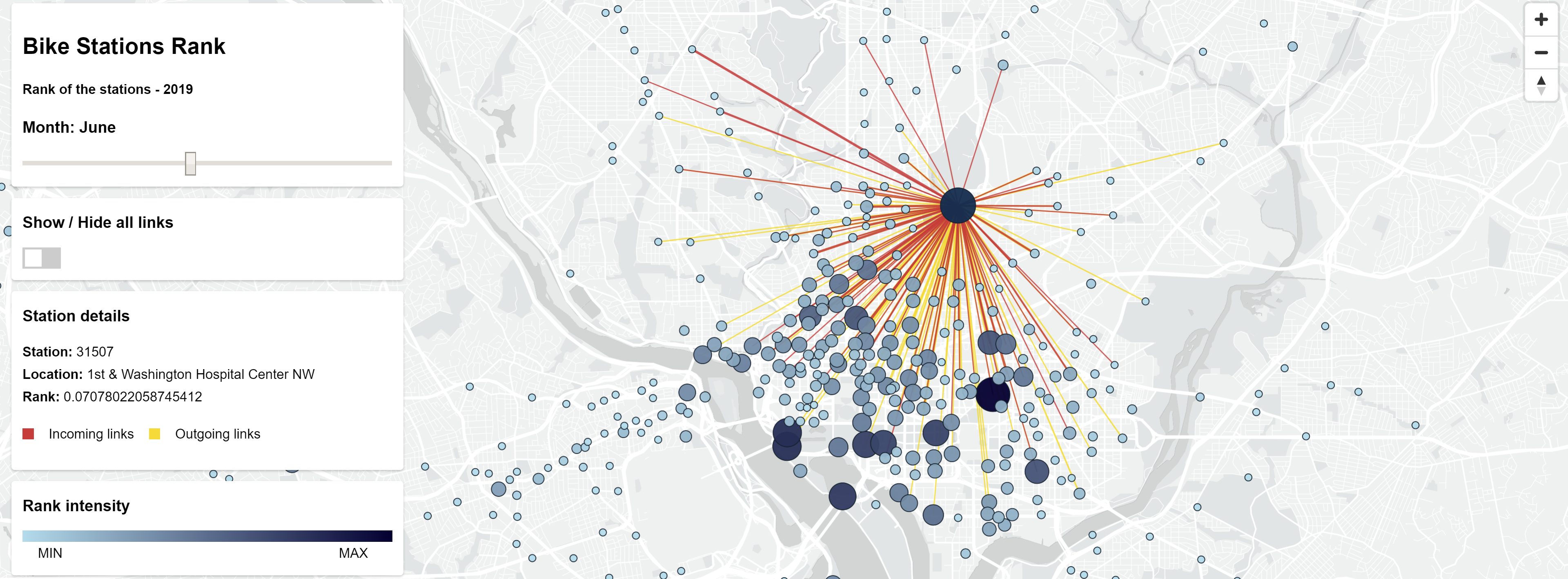
The main purpose of this project is to compute the Weighted PageRank for the bike stations of the
CapitalBikeShare network in Washington DC developing a scala-spark app.
The PageRank of the stations is computed considering the tripdata of the year 2019.
The PageRank algorithm for weighted edges is a modified version of the NetworkX implementation.
The Computation is done on the Google Cloud Platform using the Dataproc and Storage solutions.
A client-server webapp is also developed to run and control the computation on the GCP using the
Nodejs APIs and to show the result on an interactive map using the MapBox GL APIs.
The dataset is divided in 12 files, one for each month of the year 2019.
Each row in a file contains a single trip information, composed by a Start station number, an End station number,
a Start date, an End date and other properties that we have not taken in account.
The files are stored in folder ./data/input/.
A trip from a source to a destination could exist more than one time. During the building of the Graph,
firstly, for each couple source-destionation, the number of times the same couple appears is set as the
weight of that edge.
After, following the formula for the weighted Pagerank, for each station, the weights of the
outgoing edges is normalized such that the sum of outgoing edges is 1.
For each file there are up to 350-400 thousands trips. The number of stations in the graph is 581.
The project consists of a Node.js webapp and a Scala-Spark app.
The Scala-Spark app is the core of the computation: it is developed for computing the PageRank of the stations in
the weighted graph.
The Node.js webapp is a client-server app. The client side runs the requests for the computation and shows the results
on an interactive map. The server side uses the Google Cloud Node.js APIs (Dataproc, Storage) for uploading the files,
running the Scala-Spark app as a Job in a Dataproc cluster and for downloading the results.
Below it is shown the project files and folders structure. It is useful to know for the further steps.
projectScalable
|
├── data
| └── input/[input-files]
|
├── mapViewer
| ├── bin
| | └── www
| ├── public
| | ├── data
| | | ├── demo/[demo-files]
| | | ├── capitalbikeshare-stations.csv
| | | └── result-demo.json
| | ├── js
| | | ├── data.js
| | | ├── gcp-dataproc.js
| | | ├── geoJson.js
| | | ├── map.js
| | | ├── properties.js
| | | └── run.js
| | ├── stylesheets
| | | └── style.css
| | └── index.html
| └── routes
| ├── app.js
| ├── config.json
| ├── package.json
| └── package-lock.json
|
├── project
| └── plugins.sbt
|
├── src/main/scala
| └── pagerank
| ├── package.scala
| ├── GraphBuilder.scala
| ├── Main.scala
| ├── PageRank.scala
| ├── PageRankGraph.scala
| ├── SparkApp.scala
| └── Utils.cala
|
└── build.sbt
- Select or create a Cloud Platform project.
- Enable billing for your project.
- Enable the Google Cloud Dataproc API.
- Enable the Google Cloud Storage API.
- Set up authentication with a service account so you can access the API from your local workstation. Save the JSON key and store it carefully on your local workstation for further use, as explained in Setting up the project.
To create the fat JAR file (i.e. a jar with all the dependencies the program requires)
we used sbt-assembly. To get the fat JAR, run the command below in the root folder of the project
and it will automatically create the projectScalable.jar file in the data folder of the project.
cd projectScalable
sbt assembly
The file config.json is located in the folder projectScalable/mapViewer. This file contains the configuration
values for running the app. The structure of the configuration is shown below.
{
"keyFileName": "",
"gcp": {
"projectId": "",
"location": "",
"bucket": {
"bucketName": "",
"storageClass": ""
},
"cluster": {
"clusterName": "String",
"config": {...}
},
"job": {
"jarFileDir": "",
"jarFileName": "",
"jarArgs": [
"--inputDir",
"--outputDir",
"--numIterations=10",
"--dampingFactor=0.85"
]
}
},
"input": {
"inputPath": "",
"inputLinksFiles": [""]
},
"output": {...}
}
The keyFileName is the path where the key for accessing the Google Cloud APIs is stored
on your local workstation. Set this value before to continue.
The gcp values are used for setting bucket, cluster and job properties on GCP.
Set the value projectId as that your key is associated. Then, set the values
location, bucketName and clusterName as you like, or leave them as they are.
You could change the configuration of the cluster. As default, the cluster is composed of a master and
3 workers with 2 standard CPUs each one.
The Job field contains the properties of the JAR to be uploaded and submitted to Dataproc.
jarFileDir and jarFileName specifies the location of the JAR on your local workstation.
By default, the JAR is placed inside the folder data.
The jarArgs specifies the arguments to be passed to the JAR when launching it.
The arguments to be passed as input to the JAR are:
--inputDir- the argument to use for setting where all the files to process are located on the Bucket.--outputDir- the argument to use for setting where all the output files will be saved on the Bucket.--numIterations- by default is set to10, it is the number of iteration for PageRank algorithm.--dampingFactor- by default is set to0.85, it is the damping factor for PageRank algorithm.--local- by default it is not specified inside thejarArgsarray. When running the JAR on a local machine, it should be added inside the array.
The --inputDir and --outputDir parameters are set dynamically according to the Bucket properties, so it is not
required to change these fields.
Also, you can decide to use the default values for the other arguments, or you can change the values according to
the default settings.
The field input specifies the path and the names of the files to be processed.
By default, the data/input folder contains all the input files named by [year][month]-capitalbikeshare-tripdata.csv.
The field outputspecifies the folders and the properties for downloading and referencing the output of the
computation once it is done on the Cluster. It is not required to modify this field.
The MapViewer app source is located in the mapViewer folder. For installing and running the app, it is required
Node.js to be installed on your local workstation.
For installing the required packages:
cd projectScalable/mapViewer
npm install
After installation, for running the app:
npm start
Before running the project, be sure that you have followed the previous steps:
- The fat JAR has been generated and placed in the folder
dataor it is linked in theconfig.jsonfile. - The key for accessing GCP apis is generated and linked in the
config.jsonfile. - The
projectIdin theconfig.jsonis set as the key associated.
For running the project, run the command npm start in the mapViewer folder.
Once the app is running, you will see a message in the command line: listening on port 3000.
Open a browser with javascript enabled and connect to the server localhost:3000.
Once connected, you will see two buttons: Launch Demo and Launch Job on GCP.
Launch Demo loads the local files and shows few stations on the map as described in the
Demo section.
Launch Job on GCP runs the operations for running the Scala-Spark on a Google Cloud Dataproc Cluster.
The steps done are listed below:
- Initialization of Clients for connecting to Google CLoud APIs.
- Creation of the Bucket.
- Creation of the Cluster with the specified configuration (this may take up to 90s).
- Upload of input files and JAR file to the Bucket.
- Submit of the Job to the cluster.
- Download of the results computed by the Job.
- Launch of the client app for viewing the map.
Each step is excecuted automatically and you will be able to see the progress on the webpage.
Once all the steps are done successfully, an interactive map is shown with the stations and links.
If something goes wrong, an error explanation is shown and the app tries to delete all the allocated resources on
the Google Cloud Platform.
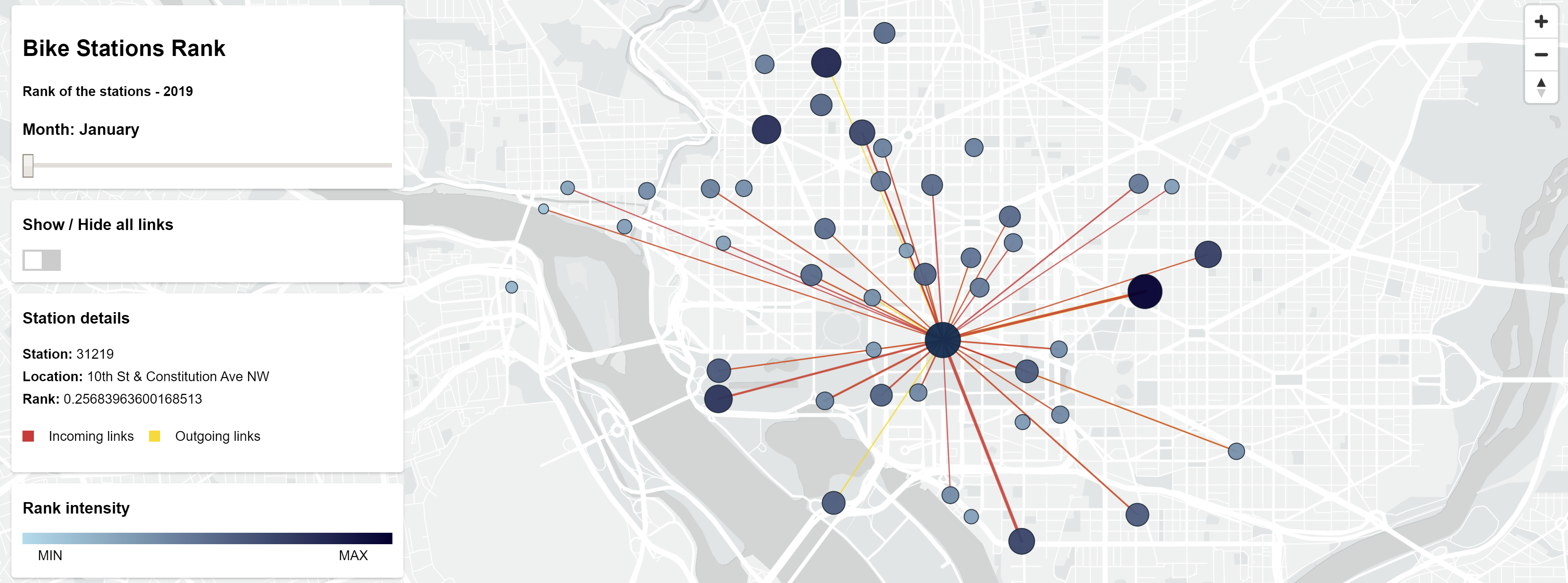
The demo is made for showing an example of the result of computing the PageRank. In the demo it is shown only about 50 stations. The demo is built from a reduced portion of the original dataset, considering only the tripdata of the reduced number of stations.
The result files of the demo are located inside the folder mapViewer/public/data/demo.
To launch the demo, once the Setup is done, simply connect to localhost:3000 on your browser and click on the
launch demo button.
Another way to compute the PageRank using the scala-spark app is through the gcloud command line tool.
After installing and initializating the gcloud sdk, you have to create a Google Cloud project and enable billing and Dataproc API.
gcloud projects create scalable-pagerank
This command allows you to create a new bucket used to store all the data required to the project. It is also used to store the results of the computation (nodes ranks and links).
gsutil mb -p scalable-pagerank -l europe-west3 -c STANDARD gs://scalable-pagerank-bucket/
This below is an example with four nodes: a master and three workers. You are free to
apply changes. Bear in mind that the actual image-version (1.5-debian10) has the
correct version of Scala and Spark. The cluster will be automatically deleted after 15 minutes
to prevent waste of money (max-age).
gcloud dataproc clusters create scalable-pagerank-cluster
--region europe-west3
--subnet default
--zone europe-west3-a
--master-machine-type n1-standard-2
--master-boot-disk-size 30
--num-workers 3
--worker-machine-type n1-standard-2
--worker-boot-disk-size 30
--image-version 1.5-debian10
--max-age=t15m
--project scalable-pagerank
To start the computation you need to upload the executable and the input files to the Bucket.
Input files must be stored all inside the same folder (e.g. gs://scalable-pagerank-bucket/input/).
This because the JAR app takes as input argument
the folder where all the files to be processed are stored, and executes the computation on all the files.
gsutil cp [your_local_path]/projectScalable.jar gs://scalable-pagerank-bucket/
gsutil cp [your_local_path]/[year][month]-capitalbikeshare-tripdata.csv gs://scalable-pagerank-bucket/input/
For the JAR args see JarArgs. This command submits a spark job on the Cluster specified.
gcloud dataproc jobs submit spark
--cluster scalable-pagerank-cluster
--jar gs://scalable-pagerank-bucket/projectScalable.jar --
--inputDir=gs://scalable-pagerank-bucket/input/
--outputDir=gs://scalable-pagerank-bucket/output/
The cluster is automatically deleted after 15 minutes to prevent waste of money. If you want to delete it before (and delete also the bucket) use the following comamnds.
gcloud dataproc clusters delete scalable-pagerank-cluster
gsutil rm -r gs://scalable-pagerank-bucket/