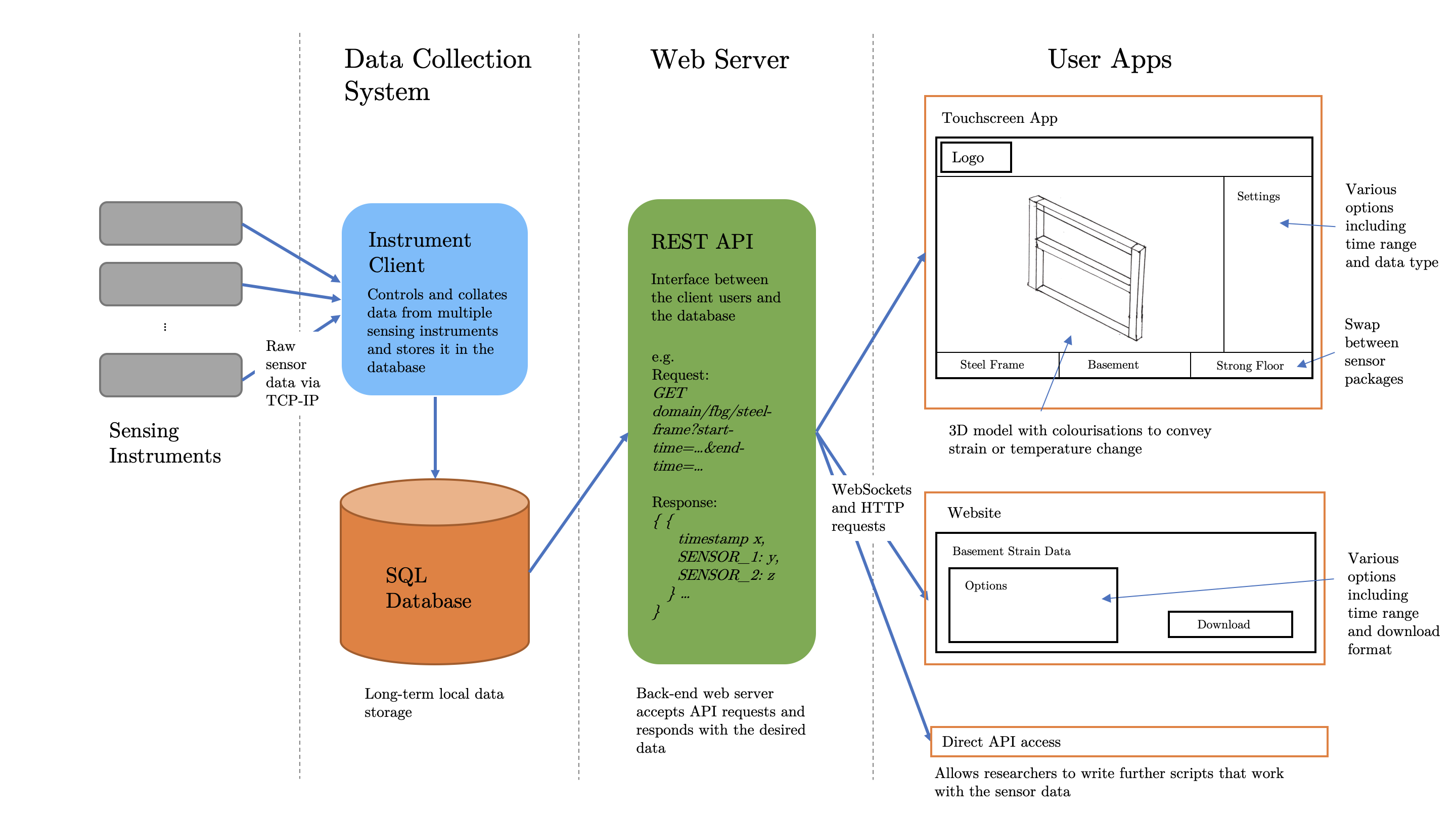
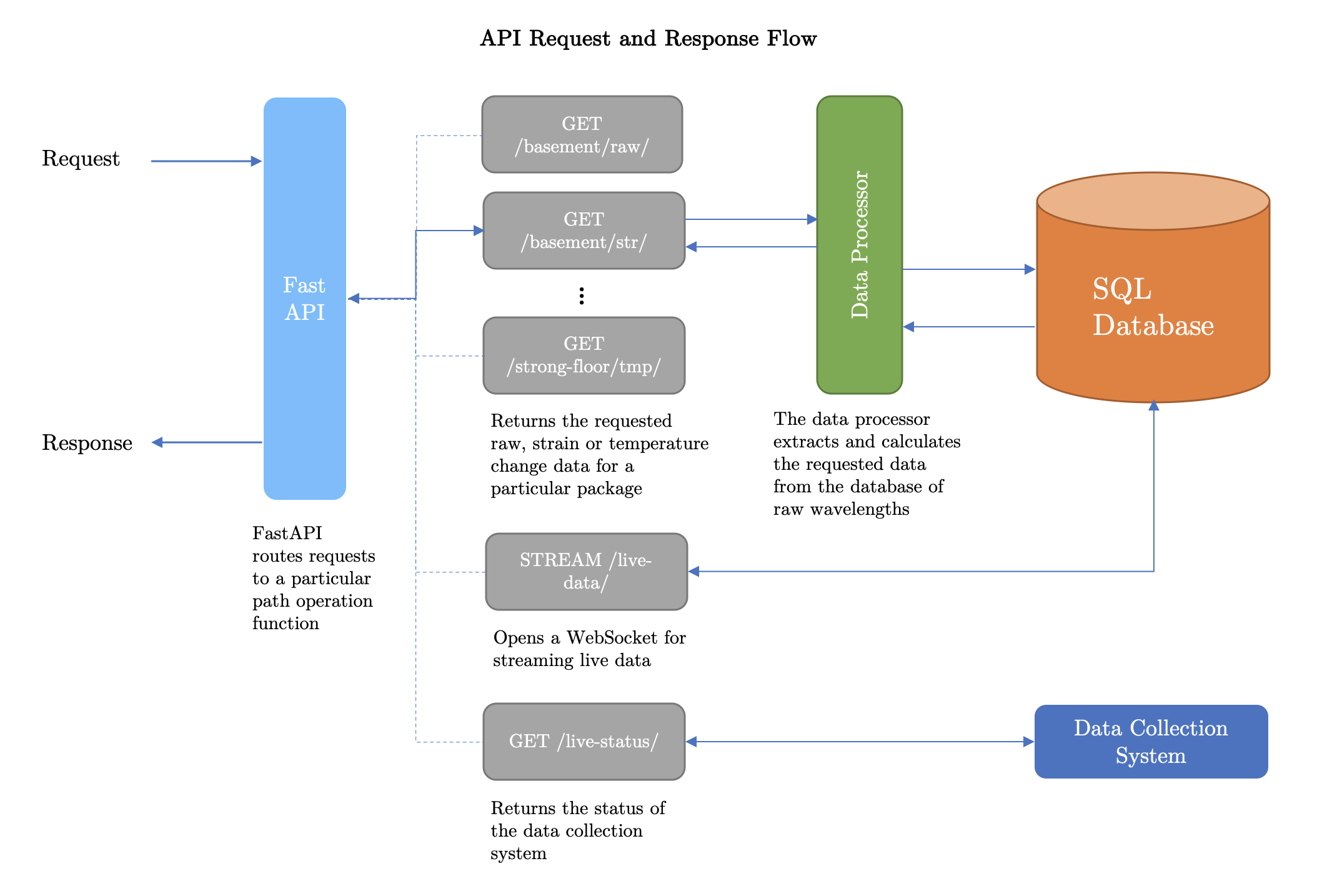
This is a monitoring system and user interface for the new Civil Engineering building in West Cambridge, developed as part of a fourth year CUED project. The system is designed to autonomously record data from the building's FBG sensors, distribute this data via a web API, and allow a user to download and visualise it in various frontend clients.
The Data Collection System is a Python package which connects to and records sensor data from a variety of optical instruments. At the moment only a single si255 optical instrument is enabled. It features a graphical user interface from which the user can connect to this optical instrument, see various status information, upload a particular configuration and start/stop recording.
Please note that the si255 instrument obtains the time from the server when it connects. The computer must therefore be set to the Etc/UTC timezone to ensure the instrument time is also always UTC.
source venv/bin/activate # Activate virtual environment
pip install -r backend/requirements.txt -f https://extras.wxpython.org/wxPython4/extras/linux/gtk3/ubuntu-16.04
export PYTHONPATH=`pwd`/backend
export DATABASE_URL=postgresql+psycopg2://postgres:<password>@localhost/nrfisdb
source venv/bin/activate # Activate virtual environment
python -m data_collection_system
Substitute in the database password, currently known to Lawrence Berry and Paul Fidler.
To run against a local test database substitute in your own DATABASE_URL. This environment variable can also be set automatically by placing it in your bash profile e.g. ~.profile.
export PYTHONPATH=`pwd`
export DATABASE_URL="sqlite:///./backend/data_collection_system/tests/.test.db"
source venv/bin/activate # Activate virtual environment
pytest backend/data_collection_system
The Web Server is a Python FastAPI application which allows users to access past sensor data via a REST API and accompanying website. The API can be accessed from within the Enginering network (either a wired connection in the department, on the CUED WiFi network, or on the Engineering VPN) at: http://129.169.72.175, and the website at: http://129.169.72.175/docs. The website lists all available endpoints and provides an interface for fetching and downloading data. There is also a WebSocket endpoint for streaming real-time data at up to 10Hz: ws://129.169.72.175/fbg/live-data/?data-type=<raw/str/tmp>.
sudo docker build -t web_server_image -f backend/web_server/Dockerfile ./backend
export DATABASE_URL=postgresql+psycopg2://postgres:<password>@127.0.0.1/nrfisdb
cd backend
uvicorn web_server.main:app --reload
Substitute in the database password, currently known to Lawrence Berry and Paul Fidler.
To run against a local test database substitute in your own DATABASE_URL. This environment variable can also be set automatically by placing it in your bash profile e.g. ~.profile.
sudo docker run -d --name web_server_container -p 80:80 --restart always --network="host" -v ~/nrfis/backend/data_collection_system/var:/var --env DATABASE_URL=postgresql+psycopg2://postgres:<password>@127.0.0.1/nrfisdb web_server_image
Substitute in the database password, currently known to Lawrence Berry and Paul Fidler.
export DATABASE_URL="sqlite:///./backend/web_server/tests/.test.db"
source venv/bin/activate # Activate virtual environment
pytest backend/web_server
The App is a Javascript React Native iOS and Android app which allows users to visualise FBG sensor data on 3D models of the building and through graphical plots.
cd frontend/app
npm install
cd frontend/app
expo start
The app can then be tested on the iOS simulator on a Mac, or on a real iOS or Android device by installing the Expo app and following the QR link in the terminal and Expo web interface.
The app can be published by running:
cd frontend/app
expo publish
This will upload the latest build to Expo, which will automatically be installed by users as an OTA update the next time they open either the Expo app or the standalone build.
A standalone version of the app, independent of the Expo client, can be built using:
cd frontend/app
expo build:android
This will build a .apk file using the Expo build service, which can then be distributed and installed on Android. Publishing updates as above will update this standalone app the next time the user opens it. You can also build for iOS, though distribution of standalone iOS apps is limited without an Apple developer license.
Download the app for Android here. You may need to enable the installation of apps from unknown sources. Note that the app requires you to be connected to the Engineering department VPN to work. Instructions for setting this up are available here.
Note that the app can currently only be downloaded on Android. The iOS version is restricted to local development, though if necessary an Apple license could be purchased to distribute it via the app store or via TestFlight.
The server can be accessed remotely via SSH by proxying through the Engineering department gate as follows:
ssh -J <crsid>@gate.eng.cam.ac.uk -D 8080 nrfis@129.169.72.175
The -D 8080 flag binds the server to local port 8080. This allows you to view the website in the Firefox web browser without connecting to the Engineering VPN by setting Firefox's proxy access settings to SOCKS host: 127.0.0.1, port: 8080.
To connect to the database when SSH'ed into the server or running a local terminal:
psql -U postgres -h 127.0.0.1 nrfisdb
This connects to the nrfisdb database as the postgres user.
During the course of my project, I've collated a great deal of documentation regarding the Micron Optics optical instruments and the building's FBG sensors, including their locations, calculation formulas and calibrated coefficients (metadata). These are held in a private Google Drive due to uncertainty over copyright material. Please contact Lawrence Berry or Paul Fidler if you wish to gain access to this information.