This is an UNOFFICIAL Chainer related tool. This tool helps you to find forward, backward and update part from profiling details when you use NVIDIA Visual Profiler (https://developer.nvidia.com/nvidia-visual-profiler / https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/profiler-users-guide/index.html) or NVIDIA Nsight Systems (https://developer.nvidia.com/nsight-systems / https://docs.nvidia.com/nsight-systems/#nsight_systems/2019.3.1-x86/01-overview.htm). As a result, you can improve your workload more efficiently.
- Change your code according to example codes below
- Run your code via
nvprof(eg.nvprof -o prof.nvvp python main.py ...) - Load
prof.nvvpto NVIDIA Visual Profilernvvp - Enjoy your profiling and accelerating!
Additional option, --profile-child-processes, makes it to track all child processes.
In addition, the profiler adds each process ID into the file name by using %p like prof%p.nvvp.
- Change your code according to example codes below
- Run your code via
nsys(eg.nsys profile --trace cuda,cublas,cudnn,nvtx,osrt python3 train.py ...) - Load
report1.qdstrmto NVIDIA Nsight Systems GUI - Let's analyze your bottleneck
Adding 2 lines is all you need. First, import a function. Second, call it.
optimizer = chainer.optimizers.Adam(alpha=0.001)
optimizer.setup(model)from chainer_profutil import create_marked_profile_optimizer
optimizer = create_marked_profile_optimizer(
chainer.optimizers.Adam(alpha=0.001), sync=True, sync_level=2)
optimizer.setup(model)When you use ChainerMN's create_multi_node_optimizer(), you need to give an instance returned from create_multi_node_optimizer() to create_marked_profile_optimizer() as follows.
optimizer = create_marked_profile_optimizer(
chainermn.create_multi_node_optimizer(
chainer.optimizers.MomentumSGD(lr=0.01, momentum=0.9),
comm),
sync=False)
optimizer.setup(model)A training script usually runs training procedure at multiple epochs.
But, the size of nvprof output becomes large if the training runs for long hours.
Therefore, we strongly recommend that you add an additional option to your code corresponding to the number of iterations. If this iteration option is given, then a script stops by the given iteration instaed of epochs. By this change, we can get relatively small profiling output and operate it by NVIDIA Visual Profiler.
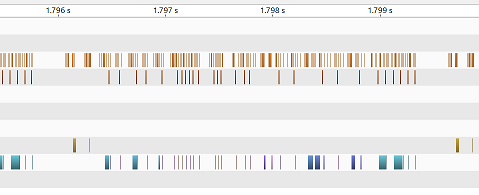
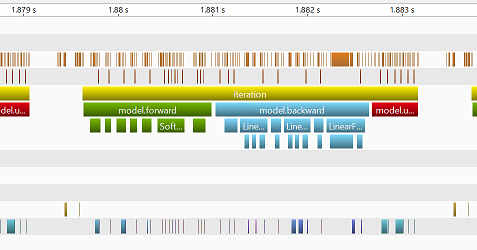
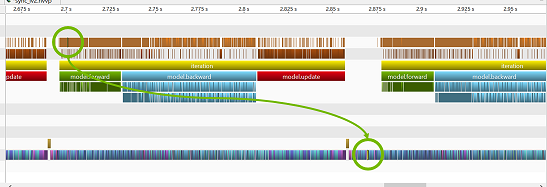
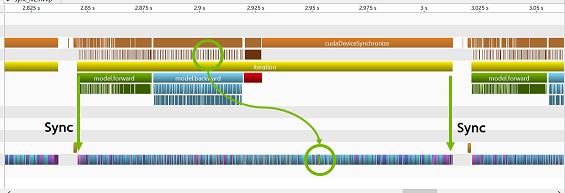
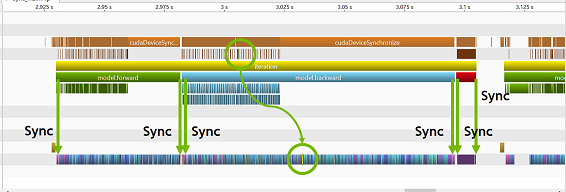
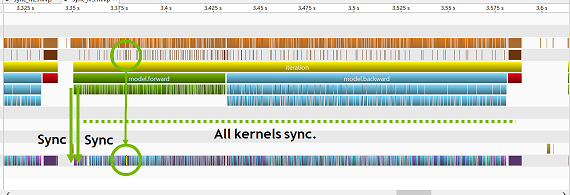
This tool has 3 synchronization levels and sync/async switch. Each level corresponds to each marker.
When you disable synchronize mode (ie., sync=False), then all markers don't synchronize all GPU kernels as below.
When you enable synchronize mode (ie., sync=True), then some markers synchronize corresponding GPU kernels and other markers are asynchronous.
At level 1 (ie., sync_level=1), highest marker only synchronizes at the being and end of 1 iteration.
At level 2 (ie., sync_level=2), forward/backward/update markers synchronize at the begin and end of corresponding kernels.
On level 3 (ie., sync_level=3), all markers synchronize corresponding kernels.