This project consists of a backend API developed using FastAPI for a simplified version of a digital book collection.
It's called MADR (Mader), a Portuguese acronym for "Meu Acervo Digital de Romances" (My Digital Collection of Romances), and it allows user registration and all CRUD operations for both authors and books.
It is built using the FastAPI framework, with Pydantic responsible for data validation. It uses a PostgreSQL database, and SQLAlchemy is used for ORM, with Alembic handling database migrations during the development process.
JWT (JSON Web Token) is used as a Bearer token for authorization and authentication in API operations, such as creating, updating, and deleting records. The JWT is included in the Authorization header of HTTP requests as a Bearer token.
The tests have 100% coverage in the src folder using pytest and pytest-cov. It also uses factory-boy to handle massive creation of models, freezegun to test token expiration, and testcontainers to build a PostgreSQL instance during tests.
It is possible to run it locally using Docker Compose, which creates all the tables in PostgreSQL. A CI routine was also implemented using GitHub Actions.
The API has 4 main routes:
The /auth route is used for user login and generates the access token responsible for authorizing and authenticating some of the CRUD operations. It is also possible to refresh the token, which is set to last 60 minutes by default.
The /user route is used to create a user and manage the account. It is possible to delete and update the account, as it verifies if the user has the authorization.
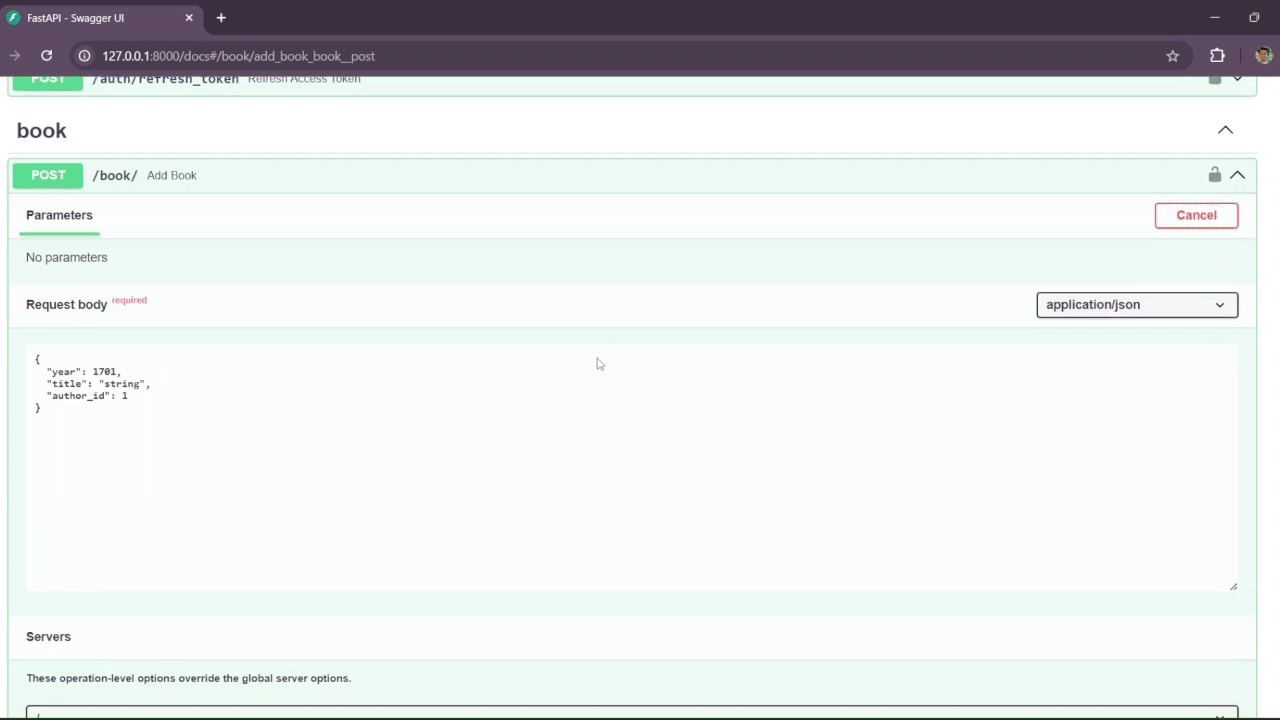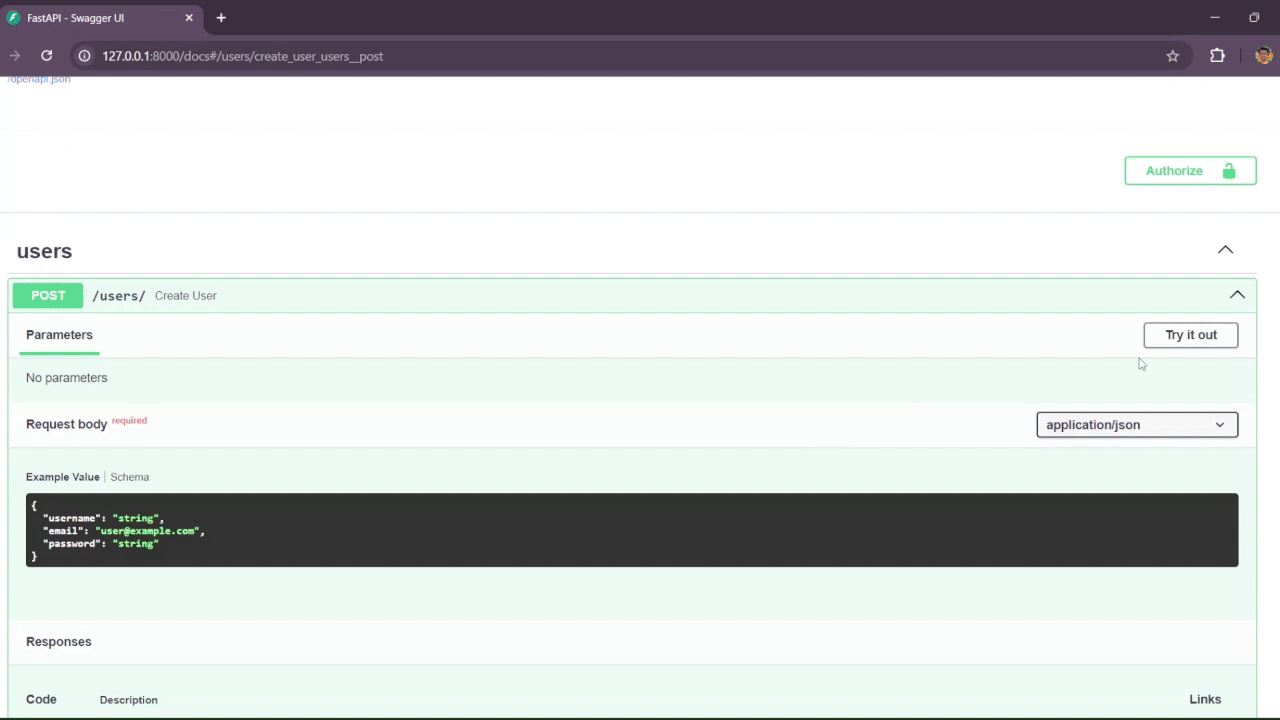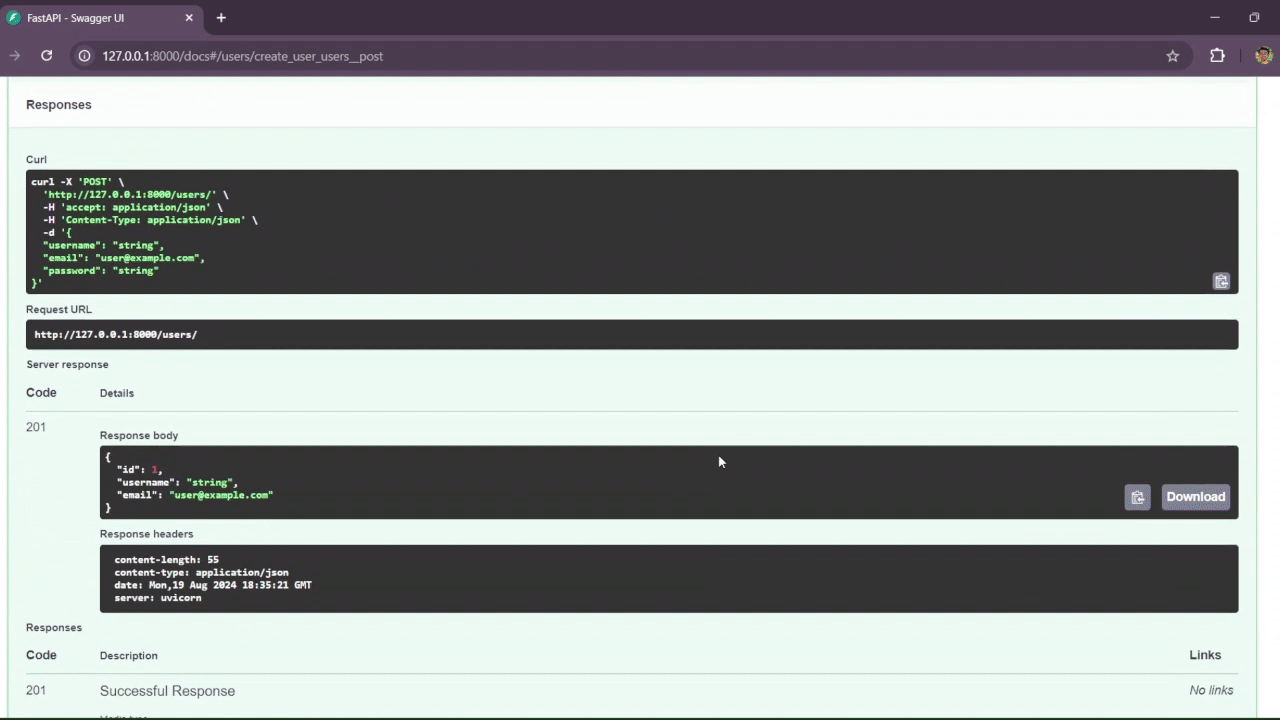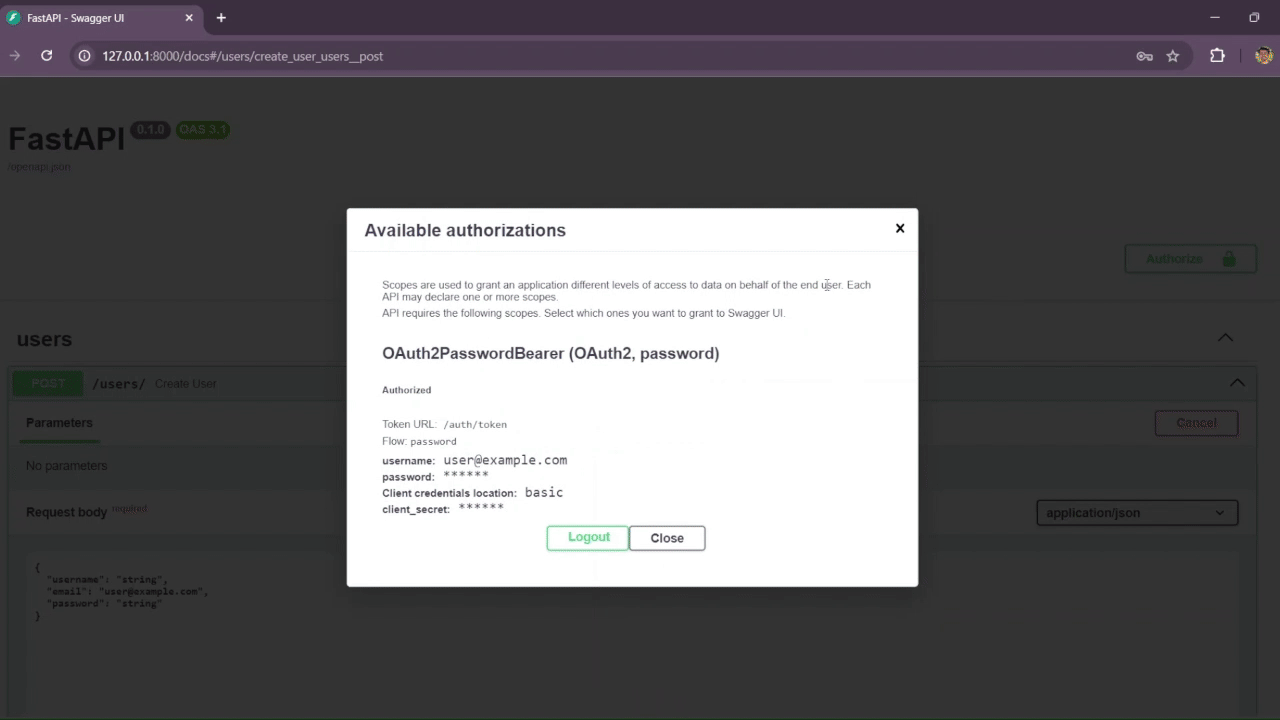
The /book route is responsible for the CRUD operations related to books. To register a book, it requires the title, the year, and the author_id, as it is only possible to register a book with an existing author. For every input, Pydantic coerces the title string by removing trailing spaces, converting all characters to lowercase, and removing duplicate spaces between words to sanitize the inputs in the database. Creating, updating, and deleting books is only possible with authentication.
The /author route is responsible for the CRUD operations related to authors. To register an author, it requires just the name, and, as in the book route, Pydantic automatically coerces it by removing trailing spaces, converting all characters to lowercase, and removing duplicate spaces between words to sanitize the inputs in the database. Creating, updating, and deleting authors is only possible with authentication.
.
├── Dockerfile
├── README.md
├── alembic.ini
├── docker-compose.yaml
├── entrypoint.sh
├── migrations
│ ├── README
│ ├── env.py
│ ├── script.py.mako
│ └── versions
│ ├── 5f80c5793a3a_create_users_table.py
│ ├── 7e20a64d10d4_create_authors_and_book_tables.py
├── poetry.lock
├── pyproject.toml
├── src
│ ├── app.py
│ ├── database.py
│ ├── models.py
│ ├── routers
│ │ ├── auth.py
│ │ ├── author.py
│ │ ├── books.py
│ │ └── users.py
│ ├── schemas
│ │ ├── authors.py
│ │ ├── base.py
│ │ ├── books.py
│ │ ├── token.py
│ │ └── users.py
│ ├── security.py
│ └── settings.py
└── tests
├── conftest.py
├── test_app.py
├── test_auth.py
├── test_author.py
├── test_book.py
├── test_security.py
└── test_users.py
All the steps here were intended to a bash terminal.
This section shows how to run the project both with Docker or locally. Regardless of the method, start with the following steps:
1 - Clone the repo locally:
git clone https://github.com/lealre/madr-fastapi.git2 - Access the project directory:
cd madr-fastapiTo run this project using Docker, it's first necessary to set the environment variables in the .env file. An example of what this project uses can be found in the .env-example file:
DATABASE_URL="postgresql+psycopg://app_user:app_password@madr_database:5432/app_db"
SECRET_KEY= 'your-secret-key'
ALGORITHM= 'HS256'
ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRE_MINUTES= 60
Copy these variables as they are and place them in your .env file and this will be enough to configure the project.
Once the variables in the .env file are defined, the following command will build and start the Docker containers with both PostgreSQL and the API running on localhost:
docker compose up --build -d--build tells Docker Compose to build the images for the services defined in the docker-compose.yml file before starting the containers. If the images already exist and have not changed, Docker Compose will use the existing images. However, if there are changes in the Dockerfiles or in the context of the build (e.g., updated application code), this flag ensures that the images are rebuilt.
-d flag stands for "detached" mode, which means that Docker Compose will run the containers in the background. This allows you to continue using your terminal for other tasks while the containers run in the background.
You can access the Swagger documentation by navigating to the /docs endpoint in your browser:
http://localhost:8000/docsThis will open the interactive API documentation provided by Swagger.
To run the project locally, the .env file is not strictly necessary, as it uses SQLite3 by default. All environment variables are configured to use standard values if the .env file is not set.
# src/settings.py
class Settings(BaseSettings):
model_config = SettingsConfigDict(
env_file='.env', env_file_encoding='utf-8'
)
DATABASE_URL: str = 'sqlite:///database.db'
SECRET_KEY: str = 'your-secret-key'
ALGORITHM: str = 'HS256'
ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRE_MINUTES: int = 60The project setup uses pyenv and poetry.
After completing steps 1 and 2:
3 - Set the Python version with pyenv:
pyenv local 3.12.24 - Create the virtual environment:
poetry env use 3.12.25 - Activate the virtual environment:
poetry shell6 - Install dependencies:
poetry install7 - Create the SQLite3 database locally:
alembic upgrade head8 - Run the server:
task runAfter these steps, you can access the Swagger documentation by navigating to the /docs endpoint in your browser:
http://localhost:8000/docsThis will open the interactive API documentation provided by Swagger.
NOTES
To run the tests, it is necessary to have Docker installed, as testcontainers builds a PostgreSQL instance for use.
task testBefore starting the tests, Ruff will detect format errors based on the points below:
- Import-related checks
- Flake8 style checks
- Error-related checks
- Warning-related checks
- Pylint-related checks
- Type-related checks, similar to Pylint
To automatically format the project based on these criteria, use:
task formatAfter running the tests, the coverage report is generated as an HTML file in htmlcov/index.html.
- Change the API to operate asynchronously.
- Create a simple front-end for user interaction.