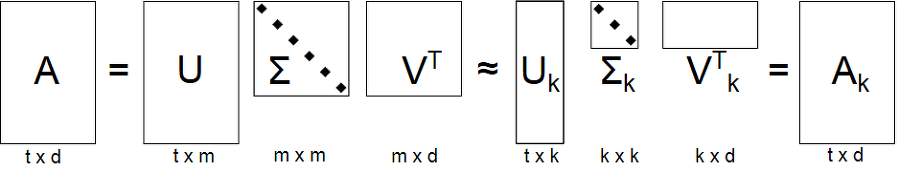In matrix factorization the goal is to estimate matrix
Collaborative Filtering is a method of making automatic predictions (filtering) about the interests of a user by collecting preferences or taste information from many users (collaborating). The underlying assumption of the collaborative filtering approach is that if a person A has the same opinion as a person B on an issue, A is more likely to have B's opinion on a different issue than that of a randomly chosen person.
Simply SVD is to decompose a matrix of
If you do this, we can get diagonal matrix(
Python is a simple language that is easy enough to understand directly. So it's not difficult to see and understand the code right away. But here are tips for Python beginners.
Default recommender class. You can choose which algorithm to use for the recommender system,
but only factorization (implement of Matrix Factorization Techniques for Recommender Systems) is currently implemented.
This class is basically written in both Python and Cython. This is because the matrix operation takes too long, so increase the calculation efficiency using Cython.
If Cython is not installed, run Python backend automatically.
Notice
By default, .py and .pyx code is supposed to do the same. This is a function for operate acceleration when Cython is supported, and if the library is not found, the same result is configured to run in just python. The details of the code may differ slightly due to computational efficiency or Cython constraints, but as a result, they perform the same.
This class accepts parameters factors, epochs, init_mean, init_derivation, learning_rate, regression_rate.
And, there are two methods. Simply, fit create feature matrix and predict return predicted value using created feature matrix.
-
fitTrain with train data. Create
biasandparamof each user, item.uniqueis indexer to compress given data. Calculatedotanderrorto updatebiasandparam.lrandregis rate of update values.Calculate current errors at line 65-66.
dot = sum(param_item[i, f] * param_user[u, f] for f in range(self.factors)) err = r - (mean + biase_user[u] + biase_item[i] + dot)Update
biasparts at line 69-70.biase_user[u] += self.lr * (err - self.reg * biase_user[u]) biase_item[i] += self.lr * (err - self.reg * biase_item[i])Update
paramparts at line 73-74.param_user[u] += self.lr * (err * param_item[i] - self.reg * param_user[u]) param_item[i] += self.lr * (err * param_user[u] - self.reg * param_item[i]) -
predictReturn prediction value which create using
biasandparammatrix.
- NumPy: is the fundamental package for scientific computing with Python.
- tqdm: is make loops show a smart progress meter.
Optional
- Cython: support compiled language, generates
Cythonextension modules, accelerate computing performance.
install packages using pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
Tested @ python3.7 in Ubuntu 18.04 LTS, macOS Catalina and Windows 10 (WSL2)
First of all, If you want to using Cython build it as follow:
python setup.py build_ext --inplace
And run main script using divided into train and test dataset.
Before that, split train and test dataset using scripts/split.py.
Below scripts generate dataset1_train/test.csv, dataset2_train/test.csv and tiny_train/test.csv in ./data/dataset directory.
Also you can split dataset different condition using --axis and --split parameters (See also file docstring and help message).
python scripts/split.py --dataset ./data/ml-20m/ratings.csv --result ./data/dataset
python main.py --train ./data/dataset/dataset1_train.csv --test ./data/dataset/dataset1_test.csv --result ./result.csv
Or using whole dataset directory with hard-coded condition (first, second, tiny).
First and second condition corresponds to given Dataset 1 and Dataset 2. Tiny is used for quick experimentation.
- first (train: 1104505203 <= timestamp <= 1230735592, test: 1230735600 <= timestamp <= 1262271552)
- second (train: timestamp <= 1388502016, test: 1388502017 <= timestamp)
- tiny (train: 1104505203 <= timestamp <= 1104555203, test: 1230735600 <= timestamp <= 1230755600)
python main.py --dataset [dataset_directory (./data/ml20m)] --mode [first, second, tiny]
Parameter search using ./scripts/parameter_search.py and ./data/search.json.
- best: 0.906 in Dataset 1 (
./B_results_DS1.csv). - best: 0.945 in Dataset 2 (
./B_results_DS2.csv).
To reproduce results, append below parameters when run main.py.
- Dataset 1:
--factor 50 --epoch 20 --mean .0 --dev .05 --lr .005 --reg .02 - Dataset 2:
--factor 100 --epoch 20 --mean .0 --dev .01 --lr .005 --reg .02
- train (timestamp condition between 1104505203 and 1230735592, 5187587 rows)
- test (timestamp condition between 1230735600 and 1262271552, 930093 rows)
| Error | Factor | Epoch | Mean | Dev | Lr | Reg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9062965664 | 50 | 20 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.005 | 0.02 |
| 0.9064882695 | 1000 | 20 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.02 |
| 0.9066755623 | 100 | 10 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| 0.9069686128 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.02 |
| 0.907114876 | 150 | 150 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.001 | 0.05 |
| 0.9074043211 | 150 | 100 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.001 | 0.05 |
| 0.9077045023 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.005 | 0.02 |
| 0.9077125512 | 25 | 100 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.001 | 0.01 |
| 0.9082157874 | 200 | 100 | 0 | 0.2 | 0.005 | 0.05 |
| 0.908252472 | 150 | 100 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.05 |
| 0.9090876701 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.005 | 0.1 |
| 0.909943722 | 25 | 20 | 0 | 0.2 | 0.005 | 0.01 |
| 0.9103295262 | 50 | 20 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.005 | 0.1 |
| 0.9110503496 | 150 | 10 | 0 | 0.2 | 0.005 | 0.05 |
| 0.9113505705 | 150 | 20 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.005 | 0.01 |
| 0.9131840053 | 150 | 200 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.0001 | 0.02 |
| 0.9131874063 | 200 | 10 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| 0.9141151526 | 150 | 150 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.0001 | 0.02 |
| 0.9143238066 | 1024 | 256 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 0.9150647162 | 25 | 100 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.0001 | 0.05 |
- train (timestamp condition under 1388502016, 19152913 rows)
- test (timestamp condition over 1388502017, 847350 rows)
| Error | Factor | Epoch | Mean | Dev | Lr | Reg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9447267353 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.02 |
| 0.9455785902 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.01 |
| 0.9458027524 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.005 | 0.02 |
| 0.9459471339 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.02 |
| 0.947802059 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.05 |
| 0.9538850398 | 2048 | 32 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.05 |
| 0.9548304784 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.001 |
| 0.9577116744 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 0.9584485671 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.05 |
| 0.9590505826 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.02 |
| 0.9593056715 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.01 |
| 0.9607800371 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.02 |
| 0.9615054369 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.01 |
| 0.9653931637 | 2048 | 32 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.0001 | 0.01 |
| 0.9653997554 | 256 | 32 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.0001 | 0.05 |
| 0.9665724879 | 2048 | 20 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.0001 | 0.05 |
| 0.966572501 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.005 | 0.0001 | 0.05 |
| 0.9672215359 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.0001 | 0.02 |
| 0.9674862554 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.0001 | 0.01 |
| 0.967486467 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.0001 | 0.01 |