-- Query season, country, and events for all summer events
SELECT
'summer' AS season,
country,
COUNT(DISTINCT event) AS events
FROM summer_games AS s
JOIN countries AS c
ON s.country_id = c.id
GROUP BY country
-- Combine the queries
UNION ALL
-- Query season, country, and events for all winter events
SELECT
'winter' AS season,
country,
COUNT(DISTINCT event) AS events
FROM winter_games AS w
JOIN countries AS c
ON w.country_id = c.id
GROUP BY country
-- Sort the results to show most events at the top
ORDER BY events DESC;-- Add outer layer to pull season, country and unique events
SELECT
season,
country,
COUNT(DISTINCT event) AS events
FROM
-- Pull season, country_id, and event for both seasons
(SELECT
'summer' AS season,
country_id,
event
FROM summer_games
UNION ALL
SELECT
'winter' AS season,
country_id,
event
FROM winter_games) AS subquery
JOIN countries AS c
ON subquery.country_id = c.id
-- Group by any unaggregated fields
GROUP BY season, country
-- Order to show most events at the top
ORDER BY events DESC;SELECT
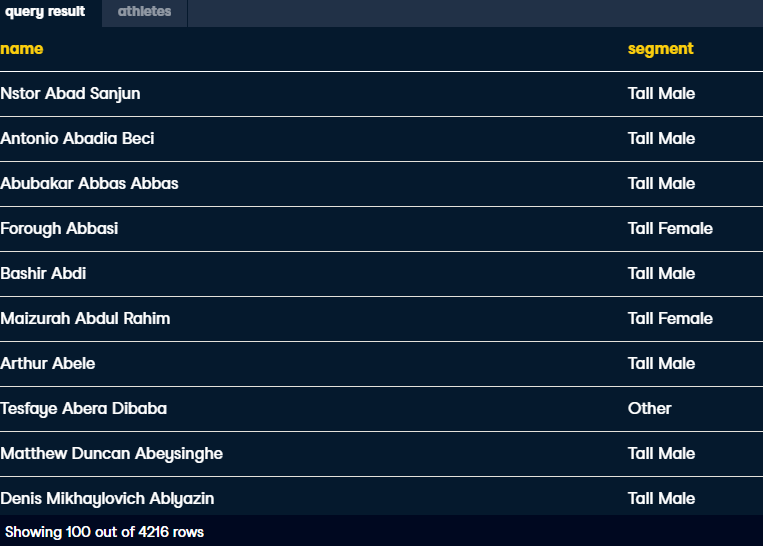
name,
-- Output 'Tall Female', 'Tall Male', or 'Other'
CASE when gender = 'F' and height >= 175 then 'Tall Female'
when gender = 'M' and height >= 190 then 'Tall Male'
else 'Other' END AS segment
FROM athletes;-- Pull in sport, bmi_bucket, and athletes
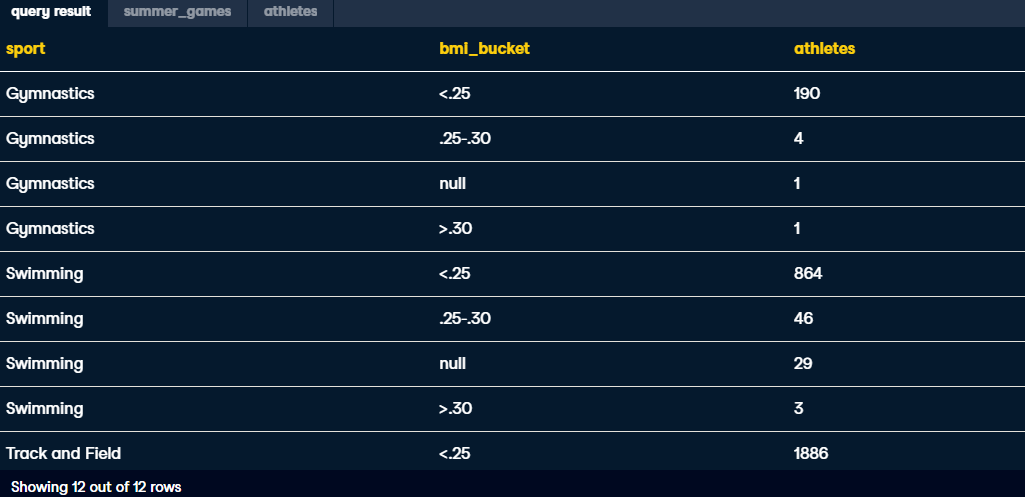
SELECT
sport,
-- Bucket BMI in three groups: <.25, .25-.30, and >.30
CASE WHEN 100*weight/height^2 <.25 THEN '<.25'
WHEN 100*weight/height^2 <=.30 THEN '.25-.30'
WHEN 100*weight/height^2 >.30 THEN '>.30' END AS bmi_bucket,
COUNT(DISTINCT athlete_id) AS athletes
FROM summer_games AS s
JOIN athletes AS a
ON s.athlete_id = a.id
-- GROUP BY non-aggregated fields
GROUP BY sport, bmi_bucket
-- Sort by sport and then by athletes in descending order
ORDER BY sport, athletes DESC;-- Pull summer bronze_medals, silver_medals, and gold_medals
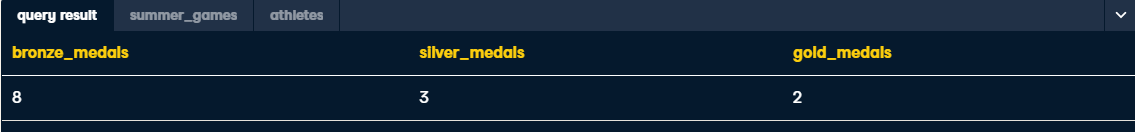
SELECT
sum(bronze) as bronze_medals,
sum(silver) as silver_medals,
sum(gold) as gold_medals
FROM summer_games
-- Add the WHERE statement below
WHERE athlete_id IN
-- Create subquery list for athlete_ids age 16 or below
(SELECT id
FROM athletes
WHERE age <= 16);-- Pull event and unique athletes from summer_games
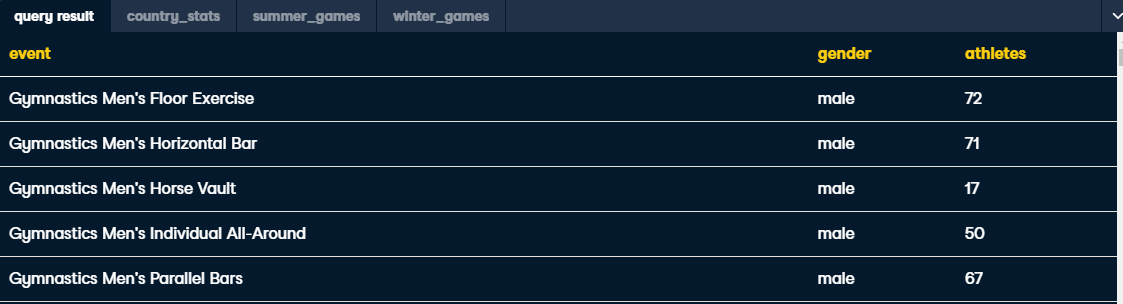
SELECT
event,
-- Add the gender field below
CASE when event LIKE '%Men%' then 'male'
ELSE 'female' END AS gender,
COUNT(DISTINCT athlete_id) AS athletes
FROM summer_games
GROUP BY event;ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP COLUMN column_name;ALTER TABLE table_name
RENAME COLUMN old_name TO new_name;INSERT INTO table VALUES ('valeur 1', 'valeur 2', ...)INSERT INTO players
SELECT DISTINCT firstname, lastname, name_club
FROM club_players;INSERT INTO table (nom_colonne_1, nom_colonne_2, ...
VALUES ('valeur 1', 'valeur 2', ...)INSERT INTO client (prenom, nom, ville, age)
VALUES
('Rébecca', 'Armand', 'Saint-Didier-des-Bois', 24),
('Aimée', 'Hebert', 'Marigny-le-Châtel', 36),
('Marielle', 'Ribeiro', 'Maillères', 27),
('Hilaire', 'Savary', 'Conie-Molitard', 58);CREATE TABLE sandbox.customers(
customer_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
customer_name varchar(255) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE sandbox.customer_country(
customer_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
customer_country varchar(255) NOT NULL
);DROP TABLE table_name where condition;UPDATE table
SET nom_colonne_1 = 'nouvelle valeur'
WHERE condition
SELECT A2.* FROM TableA A2
WHERE A2.my_id NOT IN
(Select tableA.my_id FROM
tableA
inner join
tableB
on tableA.my_id = tableB.my_id)SELECT order_id, customer_id, order_date, order_amount,
SUM(order_amount) OVER (
PARTITION BY customer_id
ORDER BY order_date
ROWS BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW
) AS running_total
FROM orders;WITH department_avg_salary AS (
SELECT department_id, AVG(salary) AS avg_salary
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id
)
SELECT employee_id, employee_name, salary, department_avg_salary.avg_salary
FROM employees
INNER JOIN department_avg_salary ON employees.department_id = department_avg_salary.department_id
WHERE salary > department_avg_salary.avg_salary;SELECT
product_id,
AVG(sale_amount) AS avg_sale_amount,
SUM(sale_amount) AS total_sale_amount,
region,
RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY region ORDER BY SUM(sale_amount) DESC) AS rank
FROM sales
GROUP BY product_id, region;SELECT
customer_id,
[1] AS Product1,
[2] AS Product2,
[3] AS Product3,
[4] AS Product4,
[5] AS Product5
FROM (
SELECT
customer_id,
product_id,
order_quantity
FROM orders
) p
PIVOT (
SUM(order_quantity)
FOR product_id IN ([1], [2], [3], [4], [5])
) AS pvt;SELECT
e.first_name,
e.last_name,
e.department_id,
s.salary
FROM
employees e
INNER JOIN salaries s ON e.employee_id = s.employee_id
INNER JOIN (
SELECT
department_id,
MAX(salary) AS max_salary
FROM
salaries
GROUP BY
department_id
) m ON s.department_id = m.department_id AND s.salary = m.max_salary;SELECT
c.customer_id,
c.customer_name,
c.city,
COUNT(o.order_id) AS order_count
FROM
customers c
CROSS JOIN (
SELECT DISTINCT
city
FROM
customers
) cities
LEFT JOIN orders o ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
WHERE
c.city = cities.city
GROUP BY
c.customer_id,
c.customer_name,
c.city;CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE monthly_sales_summary (
month DATE,
category VARCHAR(50),
total_sales DECIMAL(10,2)
);INSERT INTO monthly_sales_summary (month, category, total_sales)
SELECT
DATE_TRUNC('month', date) AS month,
category,
SUM(sales_amount) AS total_sales
FROM
sales
WHERE
date >= DATE_TRUNC('year', CURRENT_DATE) -- sales from the past year
GROUP BY
DATE_TRUNC('month', date),
category;SELECT
s.category,
mss.month,
mss.total_sales
FROM
sales s
JOIN monthly_sales_summary mss
ON s.category = mss.category
AND DATE_TRUNC('month', s.date) = mss.month
WHERE
s.date >= DATE_TRUNC('year', CURRENT_DATE) -- sales from the past year
ORDER BY
s.category,
mss.month;CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW monthly_sales_summary AS
SELECT
DATE_TRUNC('month', date) AS month,
category,
SUM(sales_amount) AS total_sales
FROM
sales
WHERE
date >= DATE_TRUNC('year', CURRENT_DATE) -- sales from the past year
GROUP BY
DATE_TRUNC('month', date),
category;SELECT
category,
month,
total_sales
FROM
monthly_sales_summary
ORDER BY
category,
month;https://learnsql.com/blog/coalesce-function-sql/
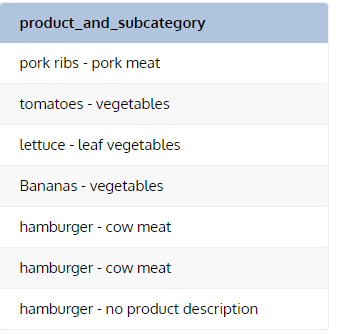
SELECT
product ||' - '||
COALESCE(subcategory, category, family, 'no product description ')
AS product_and_subcategory
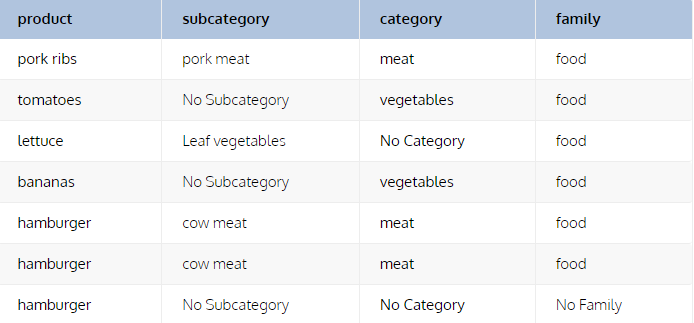
FROM stockSELECT product,
COALESCE(subcategory,'No Subcategory') AS subcategory,
COALESCE(category,'No Category') AS category,
COALESCE(family,'No Family') AS family
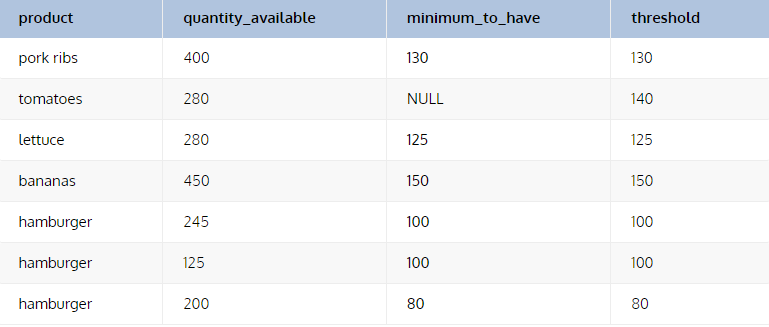
FROM stockSELECT product,
quantity_available,
minimum_to_have,
COALESCE(minimum_to_have, quantity_available * 0.5) AS threshold
FROM stockLa condition HAVING en SQL est presque similaire à WHERE à la seule différence que HAVING permet de filtrer en utilisant des fonctions telles que SUM(), COUNT(), AVG(), MIN() ou MAX().
SELECT colonne1, SUM(colonne2)
FROM nom_table
GROUP BY colonne1
HAVING fonction(colonne2) operateur valeur