This repository contains the code for an API Gateway that acts as an entry point to interact with microservices managing orders and products. The API Gateway handles authentication, routing, and forwards requests to the appropriate microservices. This README file provides instructions on how to execute and use the API Gateway.
Docker installed on your machine. Docker Compose installed on your machine. Understanding of RESTful APIs and gRPC communication. Execution:
- Clone the Repository: Clone this repository to your local machine using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/leganux/rumor-typeORM- Rename env_example on the api gateway, order and product services folders to .env (and modify them if needed)
mv env_example .env- Start Docker Compose: Run the following command to start Docker Compose, which will set up the API Gateway along with the required microservices:
docker-compose up- Access the API: Once Docker Compose has successfully started, you can access the API using the base URL http://localhost:8080.
-rumor
-api-gateway
-grpc-protocols
-event-service
-user-service
-invite-request-service
-guest-service
RADME.md
docker-compose.yml
Description Folders
-
api-gateway: Includes files from GO project, gateway api client is connected to product and order services.
-
grpc-protocols: Includes generated files from protoc for both projects client service and servers in nestjs, includes proto files too.
-
event-service: Includes order micro-service nestjs files to control events.
-
user-service: Includes product micro-service nestjs files to control users.
-
invite-request-service: Includes product micro-service nestjs files to control invite-request.
-
guest-service: Includes product micro-service nestjs files to control guests.
-
docker-compose.yml: The compose file to run all infrastructure of this project
-
README.md: This file documentation
-
rumor_typeorm.postman_collection.json: Its file of postman documentation
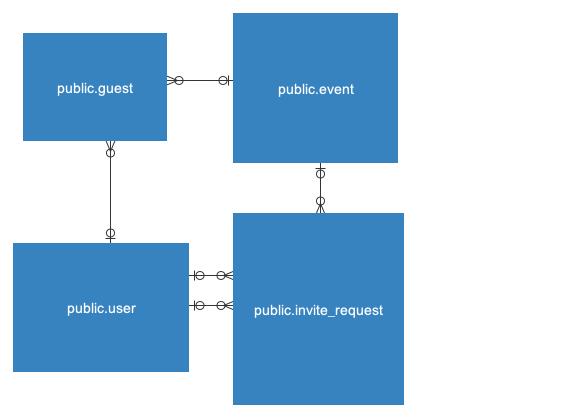
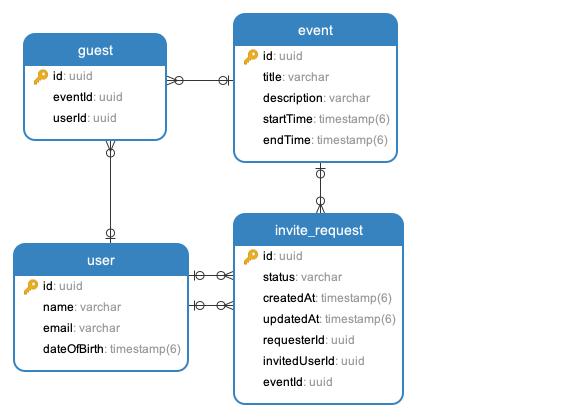
In the next diagram you can see the database structure and relationship model, There are 4 tables
Description
Users Table: This table serves as a repository for user information. It includes fields such as user ID, name, email, and any other pertinent details. The user ID acts as the primary key for this table.
Events Table: This table stores information regarding various events. It comprises fields like event ID, title, description, event start time, and event end time. The event ID serves as the primary key for this table.
Guests Table: The guests table maintains data about attendees for each event. It contains fields such as guest ID, event ID (which is a foreign key referencing the Events table), user ID (a foreign key referencing the Users table to denote which user is attending the event), and any other relevant information. The combination of guest ID and event ID serves as the primary key for this table.
Invite Requests Table: This table manages invite requests initiated by users to other guests for specific events. It consists of fields like invite request ID, requester user ID (a foreign key referencing the Users table), invitee user ID (another foreign key referencing the Users table), event ID (a foreign key referencing the Events table), status ( indicating the status of the request, e.g., pending, accepted, declined), as well as timestamp fields for when the request was made and last updated. The invite request ID is designated as the primary key for this table.
Relationships
- Users Table to Events Table: One-to-many relationship. One user can be associated with multiple events, but each event is linked to only one user (e.g., event organizer).
- Events Table to Guests Table: One-to-many relationship. An event can have multiple guests, but each guest belongs to only one event.
- Users Table to Guests Table: One-to-many relationship. One user can attend multiple events as a guest, and each event guest is associated with only one user.
- Users Table to Invite Requests Table (twice): One-to-many relationship. One user can make multiple invite requests and receive multiple invite requests for different events.
Why I decided Use UUID?
Implementing UUIDs in your database provides several benefits over using numeric IDs. UUIDs ensure global uniqueness without the need for centralized ID management systems, enhancing scalability and decentralization. They improve security by being unpredictable, preventing enumeration attacks, and offer greater data privacy by avoiding the leakage of information about entity creation order or total entity count. UUIDs are compatible across different systems and platforms, facilitating interoperability and simplifying integration efforts. Their flexibility in variant selection allows developers to tailor UUID generation to specific requirements, making them a robust choice for uniquely identifying entities in distributed and scalable database environments.
Example:
{
"id": "936a4103-2352-4480-86fb-d51386bb002b",
"name": "Erick",
"email": "erick@mail.com",
"date_of_birth": "Sun Apr 11 1993 00:00:00 GMT+0000 (Coordinated Universal Time)"
}- POST /login: Endpoint to authenticate and receive a JWT token. Requires a JSON body with username and password fields.
const myHeaders = new Headers();
myHeaders.append("Content-Type", "application/json");
const raw = JSON.stringify({
"Username": "admin",
"Password": "Kt3RickS0n"
});
const requestOptions = {
method: "POST",
headers: myHeaders,
body: raw,
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/login", requestOptions)
.then((response) => response.text())
.then((result) => console.log(result))
.catch((error) => console.error(error));- POST /api/users/create: Endpoint to create a new user to database
const myHeaders = new Headers();
myHeaders.append("Authorization", "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJleHAiOjE3MTMxMTk3NzksInVzZXJuYW1lIjoiYWRtaW4ifQ.ImKCetVv2UH464tyxI7AVkPkluSxvKhaPglzAnzCSDg");
myHeaders.append("Content-Type", "application/json");
const raw = JSON.stringify({
"name": "Erick",
"email": "erick@mail.com",
"date_of_birth": "1993-04-11"
});
const requestOptions = {
method: "POST",
headers: myHeaders,
body: raw,
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/users/create", requestOptions)
.then((response) => response.text())
.then((result) => console.log(result))
.catch((error) => console.error(error));- GET /api/users: Endpoint to get all users on database
const myHeaders = new Headers();
myHeaders.append("Authorization", "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJleHAiOjE3MTMxMjAwODIsInVzZXJuYW1lIjoiYWRtaW4ifQ.dau9chLloE8Yaff0BCpA6atEPz7QKM8pramD81GxJig");
myHeaders.append("Content-Type", "application/json");
const requestOptions = {
method: "GET",
headers: myHeaders,
body: raw,
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/users", requestOptions)
.then((response) => response.text())
.then((result) => console.log(result))
.catch((error) => console.error(error));- GET /api/users/get?id=<id_user>: Endpoint to get a user from database
const myHeaders = new Headers();
myHeaders.append("Authorization", "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJleHAiOjE3MTMxMjAwODIsInVzZXJuYW1lIjoiYWRtaW4ifQ.dau9chLloE8Yaff0BCpA6atEPz7QKM8pramD81GxJig");
myHeaders.append("Content-Type", "application/json");
const requestOptions = {
method: "GET",
headers: myHeaders,
body: raw,
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/users/get?id=936a4103-2352-4480-86fb-d51386bb002b", requestOptions)
.then((response) => response.text())
.then((result) => console.log(result))
.catch((error) => console.error(error));- GET /api/users/update: Endpoint to update an user from database
const myHeaders = new Headers();
myHeaders.append("Authorization", "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJleHAiOjE3MTMxMjAwODIsInVzZXJuYW1lIjoiYWRtaW4ifQ.dau9chLloE8Yaff0BCpA6atEPz7QKM8pramD81GxJig");
myHeaders.append("Content-Type", "application/json");
const raw = JSON.stringify({
"name": "Erick2",
"email": "eric2k@mail.com",
"date_of_birth": "1993-04-11",
"id": "936a4103-2352-4480-86fb-d51386bb002b"
});
const requestOptions = {
method: "PUT",
headers: myHeaders,
body: raw,
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/users/update", requestOptions)
.then((response) => response.text())
.then((result) => console.log(result))
.catch((error) => console.error(error));- POST /api/events/create: Endpoint to create a new event to database
const myHeaders = new Headers();
myHeaders.append("Authorization", "your_token");
myHeaders.append("Content-Type", "application/json");
const raw = JSON.stringify({
"title": "Título del evento",
"description": "Descripción del evento",
"start_time": "2024-04-13T08:00:00",
"end_time": "2024-04-13T10:00:00"
});
const requestOptions = {
method: "POST",
headers: myHeaders,
body: raw,
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/events/create", requestOptions)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));- GET /api/events: Endpoint to get all event on database
const requestOptions = {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Authorization": "your_token",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/events", requestOptions)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));- GET /api/events/get?id=<id_user>: Endpoint to get a event from database
const requestOptions = {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Authorization": "your_token",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/events/get?id=ID_DEL_EVENTO", requestOptions)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));- PUT /api/events/update: Endpoint to update an event from database
const myHeaders = new Headers();
myHeaders.append("Authorization", "your_token");
myHeaders.append("Content-Type", "application/json");
const raw = JSON.stringify({
"id": "ID_DEL_EVENTO",
"title": "Nuevo título del evento",
"description": "Nueva descripción del evento",
"start_time": "2024-04-13T09:00:00",
"end_time": "2024-04-13T11:00:00",
});
const requestOptions = {
method: "PUT",
headers: myHeaders,
body: raw,
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/events/update", requestOptions)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));- DELETE /api/events/delete: Endpoint to update an event from database
const myHeaders = new Headers();
myHeaders.append("Authorization", "your_token");
const requestOptions = {
method: "DELETE",
headers: myHeaders,
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/events/delete?id=ID_DEL_EVENTO", requestOptions)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));- POST /api/guests/create: Endpoint to create a new guest to database
const myHeaders = new Headers();
myHeaders.append("Authorization", "tu_token_de_autorización");
myHeaders.append("Content-Type", "application/json");
const raw = JSON.stringify({
"event": {
"id": "Event_ID"
},
"user": {
"id": "User_id"
}
});
const requestOptions = {
method: "POST",
headers: myHeaders,
body: raw,
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/guests/create", requestOptions)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));- GET /api/guests: Endpoint to get all guest on database
const requestOptions = {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Authorization": "tu_token_de_autorización",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/guests", requestOptions)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));- GET /api/guests/get?id=<id_user>: Endpoint to get a guest from database
const requestOptions = {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Authorization": "tu_token_de_autorización",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/guests/get?id=ID_DEL_INVITADO", requestOptions)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));- GET /api/guests/update: Endpoint to update an guest from database
const myHeaders = new Headers();
myHeaders.append("Authorization", "tu_token_de_autorización");
myHeaders.append("Content-Type", "application/json");
const raw = JSON.stringify({
"id": "ID_DEL_INVITADO",
"event": {
"id": "ID_DEL_EVENTO"
},
"user": {
"id": "ID_DEL_USUARIO"
}
});
const requestOptions = {
method: "PUT",
headers: myHeaders,
body: raw,
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/guests/update", requestOptions)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));- DELETE /api/guests/delete: Endpoint to update an guest from database
const myHeaders = new Headers();
myHeaders.append("Authorization", "tu_token_de_autorización");
const requestOptions = {
method: "DELETE",
headers: myHeaders,
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/guests/delete?id=ID_DEL_INVITADO", requestOptions)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));- POST /api/invite-requests/create: Endpoint to create a new invite-requests to database
const myHeaders = new Headers();
myHeaders.append("Authorization", "tu_token_de_autorización");
myHeaders.append("Content-Type", "application/json");
const raw = JSON.stringify({
"requester": {
"id": "ID_DEL_USUARIO_QUE_ENVÍA_LA_SOLICITUD"
},
"invited_user": {
"id": "ID_DEL_USUARIO_INVITADO"
},
"event": {
"id": "ID_DEL_EVENTO"
},
"status": "Pendiente",
"created_at": "Fecha_y_hora_de_creación"
});
const requestOptions = {
method: "POST",
headers: myHeaders,
body: raw,
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/invite-requests/create", requestOptions)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));- GET /api/invite-requests: Endpoint to get all invite-requests on database
const requestOptions = {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Authorization": "tu_token_de_autorización",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/invite-requests", requestOptions)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));- GET /api/invite-requests/get?id=<id_user>: Endpoint to get a invite-requests from database
const requestOptions = {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Authorization": "tu_token_de_autorización",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/invite-requests/get?id=ID_DE_LA_SOLICITUD", requestOptions)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));- GET /api/invite-requests/update: Endpoint to update an invite-requests from database
const myHeaders = new Headers();
myHeaders.append("Authorization", "tu_token_de_autorización");
myHeaders.append("Content-Type", "application/json");
const raw = JSON.stringify({
"id": "ID_DE_LA_SOLICITUD",
"requester": {
"id": "ID_DEL_USUARIO_QUE_ENVÍA_LA_SOLICITUD"
},
"invited_user": {
"id": "ID_DEL_USUARIO_INVITADO"
},
"event": {
"id": "ID_DEL_EVENTO"
},
"status": "Aceptada",
"updated_at": "Fecha_y_hora_de_actualización"
});
const requestOptions = {
method: "PUT",
headers: myHeaders,
body: raw,
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/invite-requests/update", requestOptions)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));- DELETE /api/invite-requests/delete: Endpoint to update an invite-requests from database
const myHeaders = new Headers();
myHeaders.append("Authorization", "tu_token_de_autorización");
const requestOptions = {
method: "DELETE",
headers: myHeaders,
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/invite-requests/delete?id=ID_DE_LA_SOLICITUD", requestOptions)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));const myHeaders = new Headers();
myHeaders.append("Authorization", "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJleHAiOjE3MTMxMjAwODIsInVzZXJuYW1lIjoiYWRtaW4ifQ.dau9chLloE8Yaff0BCpA6atEPz7QKM8pramD81GxJig");
const raw = "";
const requestOptions = {
method: "DELETE",
headers: myHeaders,
body: raw,
redirect: "follow"
};
fetch("http://localhost:8080/api/users/delete?id=936a4103-2352-4480-86fb-d51386bb002b", requestOptions)
.then((response) => response.text())
.then((result) => console.log(result))
.catch((error) => console.error(error));- status: The code status
- data: The information tha user request for
- error: The internal error message
- success: If request was correct or not
- Message: A message to show to user
OK Response Example
{
"status": 200,
"data": {
"products": [
{
"id": "1",
"name": "Coke 100 Ml2",
"description": "Soda 100 ML cola flavor2",
"price": 34.2,
"quantity": 5
}
]
},
"error": "",
"success": true,
"message": "OK"
}Error Response Example
{
"status": 500,
"data": null,
"error": "Internal Server Error: rpc error: code = Unknown desc = Internal server error",
"success": false,
"message": "Error retrieving product"
}To execute testing
go test*note: Testing evaluates only mock structure of response, cause go cannot instantiate GRPC communication
To access any endpoint other than /login, you need to include the JWT token received from the /login endpoint in the request headers under the key Authorization.
The API Gateway provides a centralized entry point to interact with microservices managing events, users, guests, and request-invitation. By following the provided instructions, you can easily set up and utilize the API Gateway to perform various operations.

This project is a test for rumor made by https://www.kingtide.com and Angel Erick Cruz O. © 2024 rights reserved.
This project is distributed under the MIT license.
The project was made with
This project was built with docker, nestjs, go, nodejs, grpc and other tools. Their logos and base software for their implementation reserve their rights to their own creators.