An useful CP library on Vim editor.
I mainly use it for fast programming, and also for handling tricky codes like cycle detection or SCC.
I made it to use by myself. The readability would be poor. I am planning to fix it to be more readable to anyone.
I upload this library to convince that these codes are all written by myself before the contest.
- Codeforces or e.t.c.
Korean Explanation: My Blog Link
- OS: Ubuntu 18.04.4 LTS
- Compiler: g++ 7.4.0 with C++17
- Programming: Vim 8.0 on Ubuntu Bash Shell (CUI)
- Plugin 'VundleVim/Vundle.vim' is installed (But don't need to use on C++)
- Plugin 'The-NERD-tree' is useful.
- Plugin 'VundleVim/Vundle.vim' is installed (But don't need to use on C++)
- 'vimrc, cvimrc' inside
/vimis located in the home directory, as named '.vimrc, .cvimrc'
- Every C++ programmings are done inside the directory
~/c.- Type
mkdir ~/con your shell to create.
- Type
- Default input, output files are
~/c/input.txtand~/c/output.txt.- Type
touch ~/c/input.txtandtouch ~/c/output.txtto make them.
- Type
- Every .cpp library codes inside
/libraryon this repository will be located in~/c/library/.- Type
mkdir ~/c/libraryand copy & paste every .cpp code in this repository to the target folder.
- Type
In my case, I use the following file hierarchy.
home
├── .vimrc
├── .cvimrc
└── c
├── A.cpp
├── B.cpp
├── C.cpp
├── D.cpp
├── E.cpp
├── F.cpp
├── G.cpp // A to G: Codeforces Problems
├── input.txt // input file
├── output.txt // output file
├── X.cpp // main codes
└── library // library folder
├── aho_corasick.cpp
├── base.cpp
├── binary_indexed_tree.cpp
├── bipartite_matching.cpp
├── dinic.cpp
├── fast_fourier.cpp
├── fenwick_tree.cpp
├── gauss_elim.cpp
└── ...
-
I mainly use Ubuntu Bash Shell and CUI Vim on the Terminal.
-
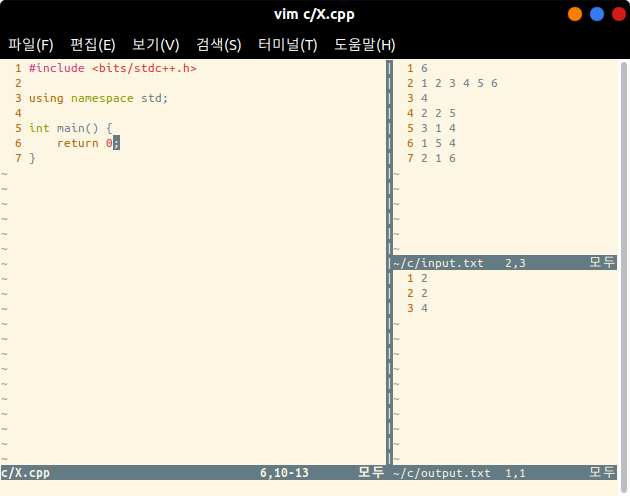
Access the programming file on the home directory. For example,
$ cd ~ $ vim c/X.cpp
-
Press [Ctrl + p] to show I/O files on the right side of the window.
-
Focus on the main programming file window and press [Ctrl + o] to close I/O files.
-
Type
:Baseto load~/c/library/base.cppfile.- You can edit the base file for your own preference.
-
Press [Ctrl + F5] [Enter] to compile the .cpp file.
-
Press [Ctrl + F6] [Enter] to run the compiled file reads input from
input.txtand outputsoutput.txt. -
Press [Ctrl + F7] [Enter] to run the compiled file on the Bash Shell.
-
Other key binding are easily implemented on the
cvimrcfile.
-
Make sure that your cursor is located in the global variable declaration area. (Not inside a function.)
-
Press [Leader + l] to see what we have inside the
~/c/libraryfolder.- The default Leader key is \ (backslash).
-
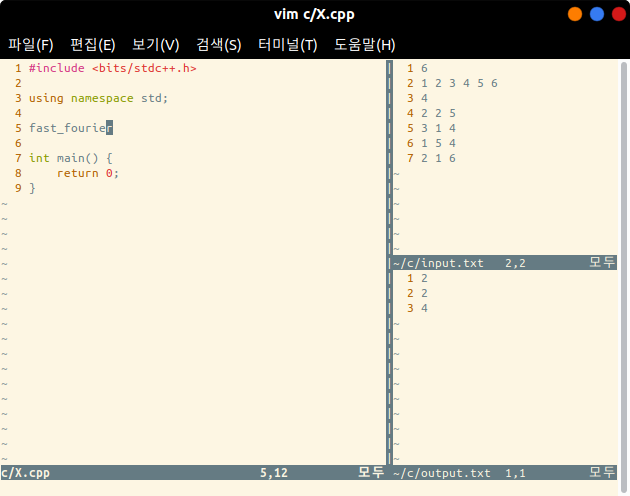
If you want to load
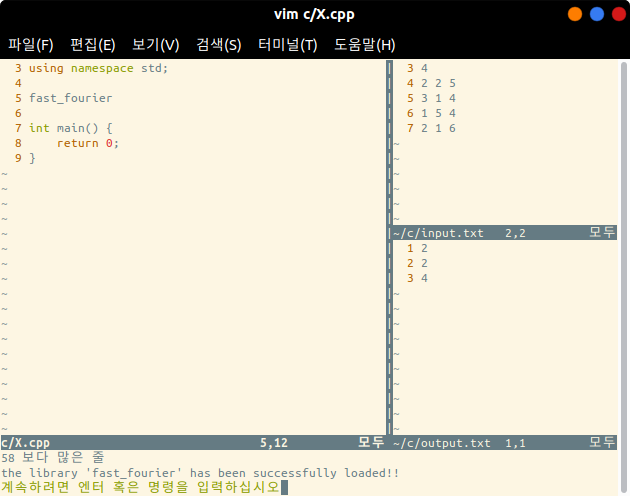
fast_fourier.cpp, then typefast_fouriercorrectly on Vim(chop.cpppart), and press to exit the Insert mode. And press [Leader + l].
- There are marks on every library code. For example, on
union_find.cpp,- You might see that the
class union_findis wrapped by the marks;//////// ---- Woosung Song's Source Code ---- ////////
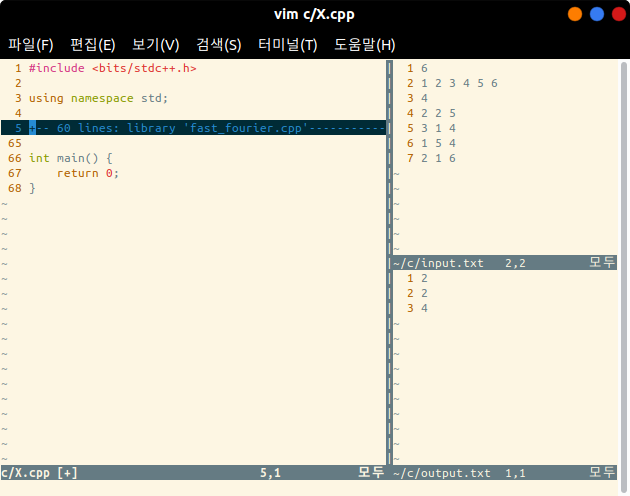
- When you press [Leader + l], the content between the two marks is loaded.
- You might see that the
- The mark can be edited on
.cvimrc. It is written with Vim-Python script. But I don't recommend to do that because you will have to do so many things to edit them all..
-
The common structure for every library code is that,
-
It begins with
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
-
Has the start mark with (You can insert it by pressing [Leader + m].)
//////// ---- Woosung Song's Source Code ---- //////// -
Library content wrapped by
#ifndef.#ifndef UNION_FIND_DEFINED class union_find { ... }; #endif #define UNION_FIND_DEFINED
- This is crucial to avoid the method overloading problem. (Which is not supported on C++.)
-
The end mark with (You can insert it by pressing [Leader + m].)
//////// ---- Woosung Song's Source Code ---- //////// -
(Optional) The test code.
int main() { union_find uf(10); // ... test code ... }
- The test code will not be added if you import your library. (Since it is not wrapped inside the marks.)
-
-
You can easily add your own library by just keeping the above basic structure.