Author: Leonardo Simões
Template Code for a Rest API in the Java language with Spring Framework and Gradle. The API has two resources: MainResource and AssociatedResource.
The project development steps were:
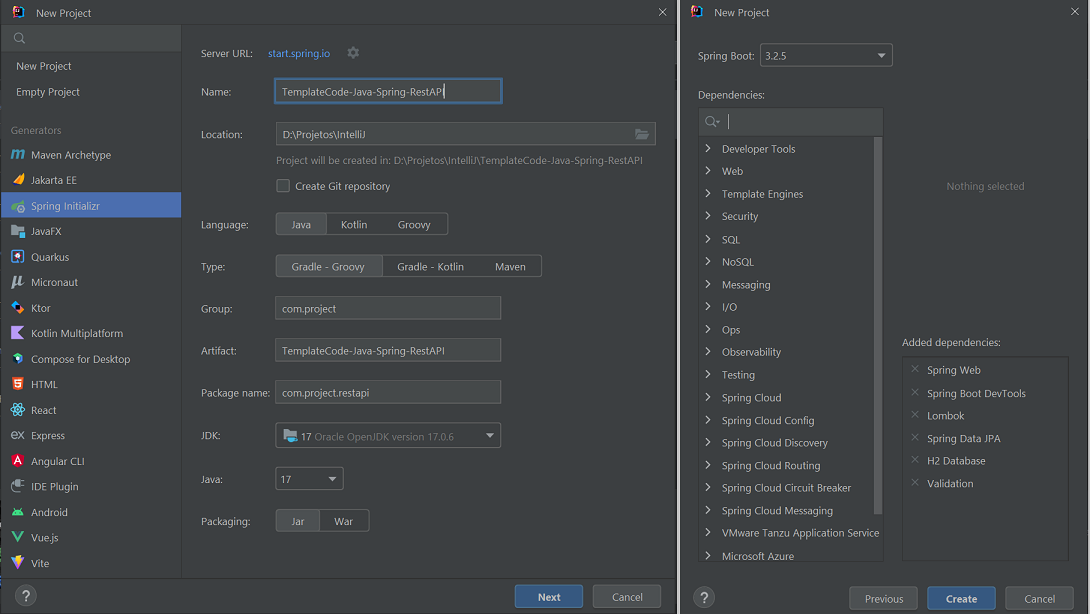
- Create project (in IntelliJ) with:
- Java language (17);
- Spring Framework (6.2.3);
- Dependencies: Web, DevTools, Lombok, JPA, H2 and Validation.
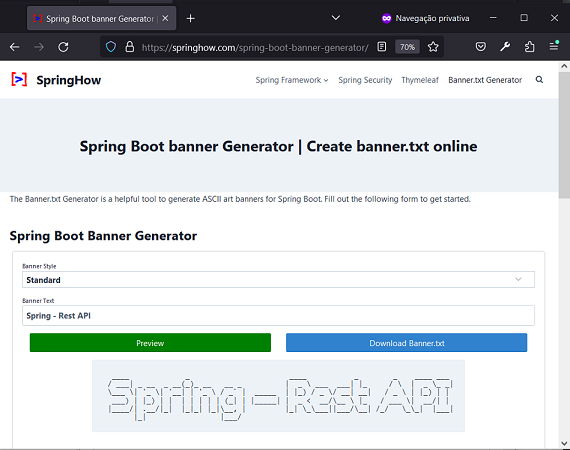
- Change the start of the Run screen with custom text (or image):
- format the desired text using
https://springhow.com/spring-boot-banner-generator/and downloadbanner.txt;
- place the
banner.txtfile insrc/main/resources(or another path); - (optional) add
${spring.application.name}andSpring Boot ${spring-boot.formatted-version}inbanner.txt; - (optional) configure the
banner.txtfile path inapplication.properties:spring.banner.location=classpath:/banner.txt.
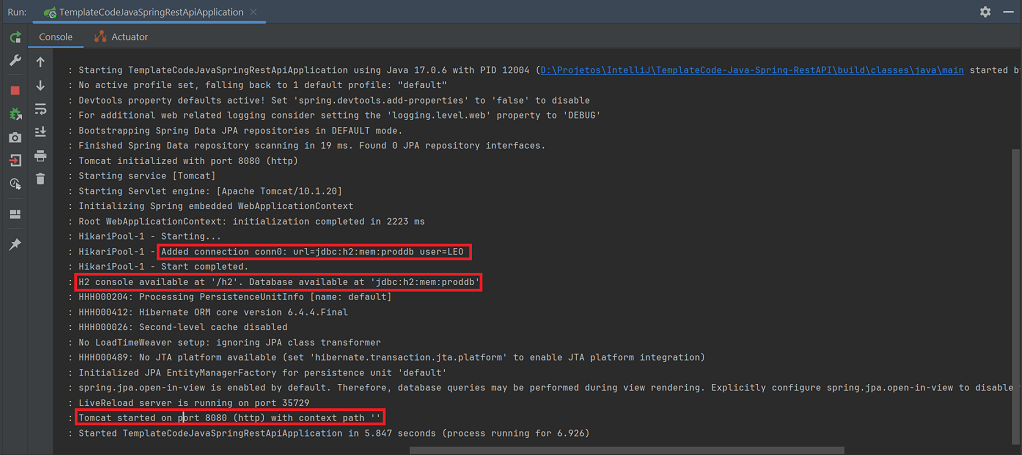
- Configure the H2 database:
- In
build.gradleconfigure according to the desired type of use:
implementation 'com.h2database:h2';runtimeOnly 'com.h2database:h2';testImplementation 'com.h2database:h2';
- In
application.properties:
# ======================================================
# APPLICATION
# ======================================================
spring.application.name=TemplateCode-Java-Spring-RestAPI
# spring.banner.location=classpath:/banner.txt
# ======================================================
# DATASOURCE - H2 DATABASE
# ======================================================
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:proddb
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username=leo
spring.datasource.password=senha
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
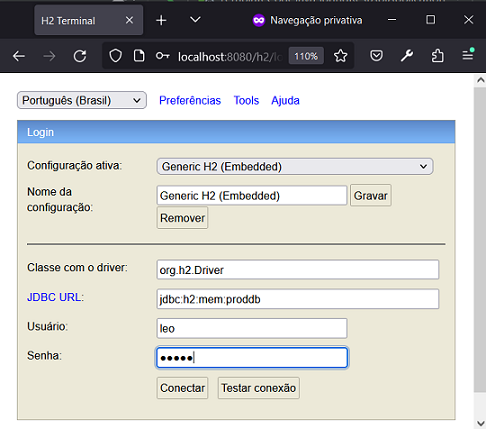
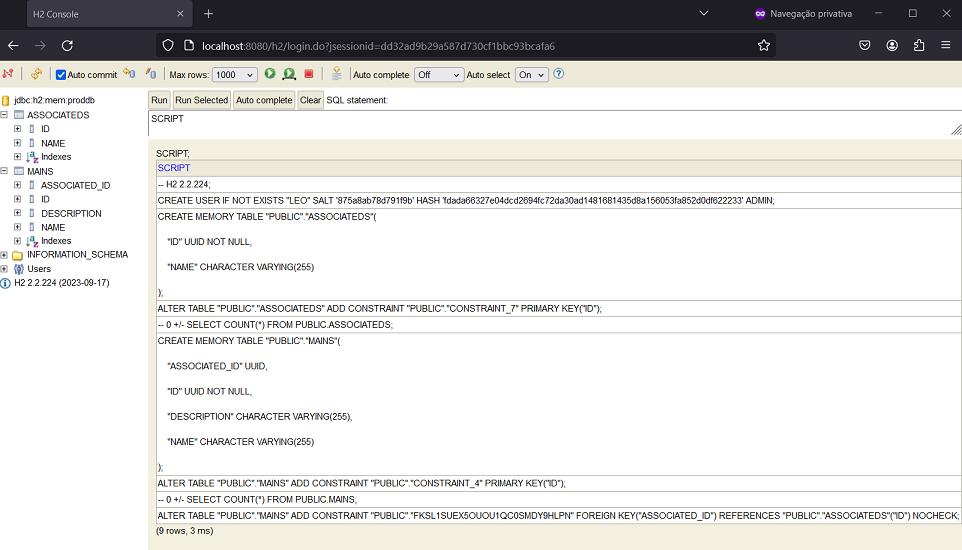
spring.h2.console.path=/h2- test access to the H2 console at
http://localhost:8080/h2/:
Note:
- By default, the usename would be "sa" and the password "", and the h2 console would be disabled.
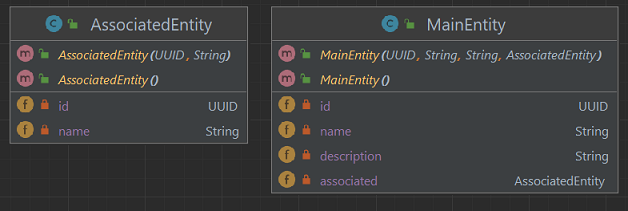
- Create AssociatedEntity class:
- in the
entitiespackage; - with attributes UUID id, String name;
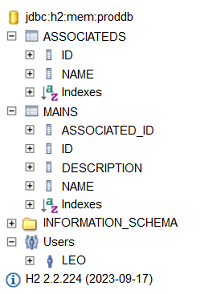
- corresponding to the table named
ASSOCIATEDS.
- Create MainEntity class:
- in the
entitiespackage; - with UUID id, String name, String description and AssociatedEntity associated attributes;
- corresponding to the table named
MAINS.
Note: When creating classes that represent database entities:
- annotate them with
@Entity,@Table(name="...")to map entity; - annotate them with
@Data,@Builder,@NoArgsConstructor,@AllArgsConstructorto use Lombok; - add attribute
UUID idannotated with@Idand@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.UUID); - configure relationships with
@ManyToOne,@OneToManyor@OneToOnein attributes that are objects; - configure the other columns with
@Columnand perhaps some validator like@NotBlankor@NotNull; - log into the H2 console and check if the tables were created correctly:
- Create tables from SQL script (not from Hibernate):
- run the application with
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create-dropinapplication.properties; - execute the command
SCRIPTor (SCRIPT TO 'D:/schema.sql') to obtain SQL code for creating tables; - place the content of the previous step in
src/main/resources/schema.sql; - run the application with
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=noneandspring.jpa.defer-datasource-initialization=trueinapplication.properties;
# spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create-drop
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=none
spring.jpa.defer-datasource-initialization=true
spring.sql.init.mode=always- (optional) configure the
schema.sqlfile path inapplication.properties:spring.sql.init.schema-locations=classpath:/schema.sql.
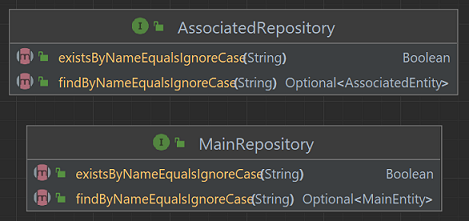
- Create
AssociatedRepositoryandMainRepositoryinterfaces:
- in the
repositoriespackage; - annotated with
@Repository; - extends
JPARepository; - have declaration of the methods
Boolean existsByNameEqualsIgnoreCase(String name)andOptional<MainEntity> findByNameEqualsIgnoreCase(String name);.
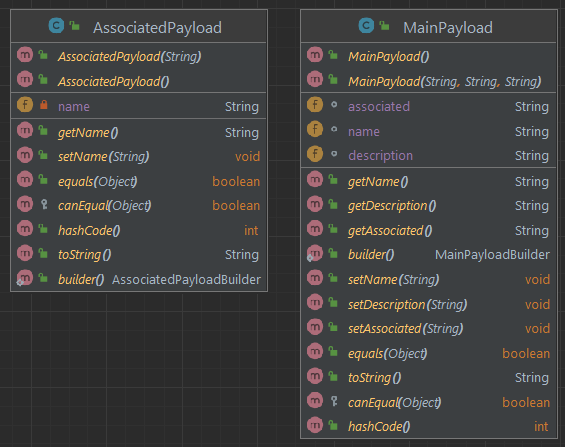
- Create dtos classes
AssociatedPayloadandMainPayload:
- in the
dtospackage; - annotated with
@Data,@Builder,@NoArgsConstructor,@AllArgsConstructorto use Lombok;
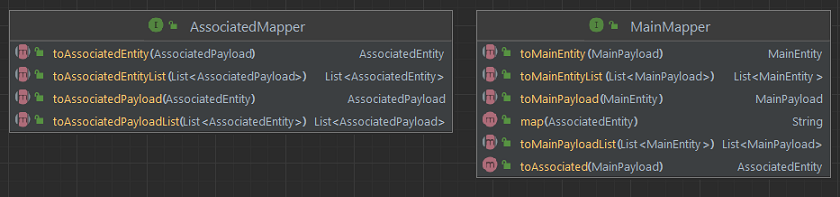
- Create mappers between dtos classes ("payloads") and entities classes ("entities"):
- add addons in
build.gradle:
// compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
implementation 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
implementation 'org.mapstruct:mapstruct:1.5.5.Final'
annotationProcessor 'org.mapstruct:mapstruct-processor:1.5.5.Final'
testAnnotationProcessor 'org.mapstruct:mapstruct-processor:1.5.5.Final'
implementation 'org.projectlombok:lombok-mapstruct-binding:0.2.0'- create the
AssociatedMapperandMainMapperinterfaces:- in the
mapperspackage; - annotated with
@Mapper; - with
INSTANCEattribute; - with 4 methods for conversions between entity and payload, and between list of entities and list of payloads;
MainMapperhas two helper methods:default AssociatedEntity toAssociated(MainPayload payload);default String map(AssociatedEntity associatedEntity);
- in the
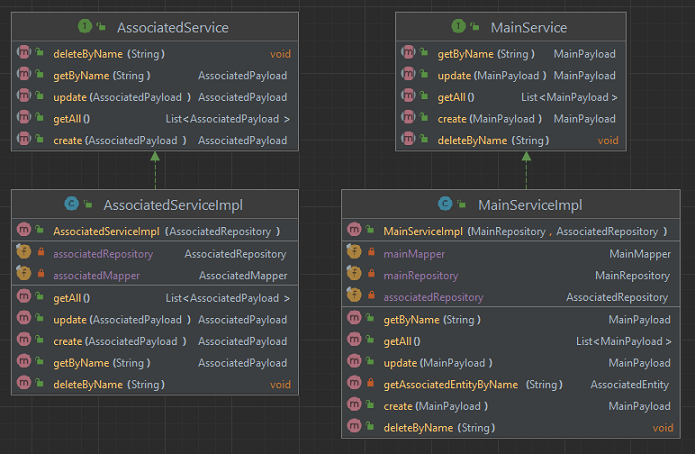
- Create Services layer:
- in the
servicespackage; - add
MainServiceandAssociatedServiceinterfaces; - add
MainServiceImplandAssociatedServiceImplclasses:- annotated with
@Service; - implement the interfaces;
- have the mapper and repository(ies) of the entity(ies);
- have a constructor with all attributes and annotated with
@Autowired;
- annotated with
- the methods must be
create,getByName,getAll,updateanddeleteByName;
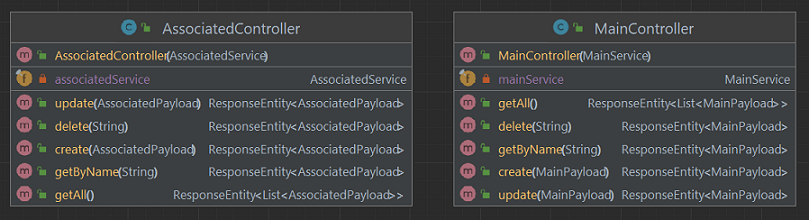
- Create Controllers layer:
- in the
controllerspackage; - add
MainControllerandAssociatedControllerclasses:- annotated with
@RestControllerand@RequestMapping("api/v1/..."); - have a constructor with an attribute and annotated with
@Autowired; - methods must be
create,getByName,getAll,updateanddeleteByName.
- annotated with
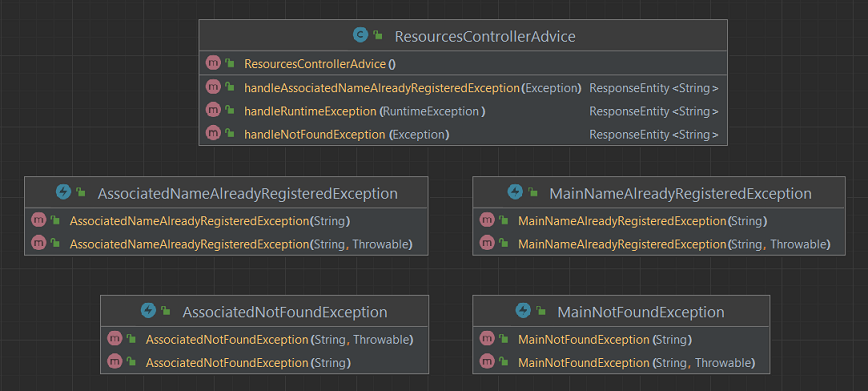
- Create Exceptions:
- in the
exceptionspackage; - with names
AssociatedNotFoundException,MainNotFoundExceptionandAssociatedNameAlreadyRegisteredExceptionMainNameAlreadyRegisteredException; - inherit from
RuntimeException; - have a constructor with argument
String messageand another withString message, Throwable causeas arguments; - use them instead of
RunTimeExceptionin Services implementations.
- Create
ResourcesControllerAdviceclass:
- in the
exceptionspackage; - annotated with
@RestControllerAdvice; - the methods:
- annotated with
@ExceptionHandler, and receives some exception; - has names starting with "handle";
- return
ResponseEntity<String>.
- annotated with
Spring - Guides - Tutorials - Building REST services with Spring: https://spring.io/guides/tutorials/rest
Baeldung - Rest with Spring Series: https://www.baeldung.com/rest-with-spring-series
Baeldung - Spring Boot With H2 Database: https://www.baeldung.com/spring-boot-h2-database
Baeldung - Quick Guide on Loading Initial Data with Spring Boot: https://www.baeldung.com/spring-boot-data-sql-and-schema-sql
DZone - That’s How You Can Use MapStruct With Lombok in Your Spring Boot Application: https://dzone.com/articles/thats-why-you-need-to-use-mapstruct-in-your-spring