MDP implementation reference code
This implementation relies on the pymdptoolbox toolkit.
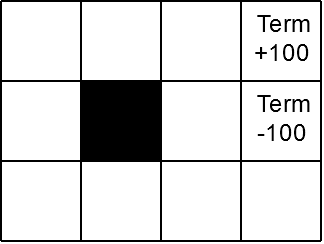
In this practical exercise, we will look at how MDP planning is implemented in a mathematical toolkit, and track the calculation of the rewards for each state via Value Iteration. The following code sets up an MDP environment (the basic case shown in class, shown in the Figure below) and computes the policy for the given MDP using the Value Iteration.
Then we provide a set of questions for you to implement and answer. This assignment is not graded.
-
Study the code of the MDP notebook and answer the following questions.
- What is the policy generated if we change the discount factor of the grid domain to 0.1?
- Use the following line
vi.verbose = Truebeforevi.run():
What is the variation for each of the first three iterations with the discount factor of 0.9 and how many iterations does the algorithm take to converge? - How does changes to the discount factor affect the variation of the state values over time?
-
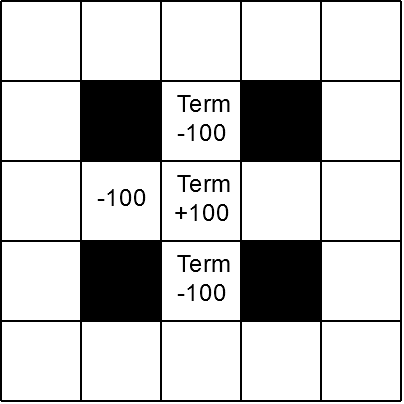
The scenario below has an interesting structure whereby the positive rewarding terminal state is partially surrounded by negatively-rewarding states. Program this scenario in pymdptoolbox and compute the optimal policy with a discount factor of 0.99.
- Define two new 5 by 5 scenarios with multiple obstacles and an interesting geometry following the guidelines below. Calculate the policy with discount factor 0.99, and then try to explain intuitively the reason for the resulting policies, given the initial parameters. These two scenarios must have the following characteristics:
- A scenario with one (or more) terminal states with positive rewards and at least one other state with the same amount of, but negative reward and no terminal states with negative rewards.
- A scenario with one terminal state with a negative reward and at least one non-terminal state with a positive reward.
In LAPRO you can just run (for Linux):
jupyter notebookand for Windows you should execute Jupyter Notebook from the start menu. Open the given URL in a browser, and navigate to the folder of the cloned repository of this assignment.
Conda is required to run this assignment, and will install Jupyter for you. The following sequence of steps creates a virtual environment and installs the required dependencies for Python 3.6:
conda create -n py36_heu python=3.6
source activate py36_heu #For windows: conda activate py36_heu
pip install ipykernel
python -m ipykernel install --name py36_heu