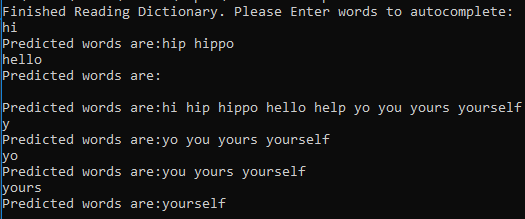
This is an implementation of a trie. A sample usage of a trie is autocompletion of words. Words sometimes have the same prefixes such as 'you', 'your', and 'yours' share the prefix 'yo'. A trie would allow one to complete words that start with 'yo' very quickly. A trie is very useful when things share common prefixes.
Simplest Example of Trie:
#include <vector>
#include "trie.hpp"
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// default constructor
Trie simpleEx = Trie();
simpleEx.insert("yo");
simpleEx.insert("you");
simpleEx.insert("your");
simpleEx.insert("yours");
simpleEx.insert("abc");
// the following lines should print "you your yours"
vector<string> rest = simpleEx.restOfString("yo");
for (auto i = rest.begin(); i != rest.end(); ++i){
cout << *i << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}Compile autoCompleteExample.cpp
From there you run the executable which takes in a file to a dictionary of words. smallDic.txt and google-10000-english.txt have been provided. Ex: sampleUsage smallDic.txt From there you can try words and see what is autocompleted.
- insert
- exists
- restOfWord
- remove
- removeAll
- size
- empty
- totalNodes
- showStatistics
The trie contains a Node root_, size_t size_, size_t wordsRemoved_. Size_ is the amount of words that are contained in the trie. WordsRemoved_ is the amount of words that have been removed since unused nodes were removed. Node root_ is the node that represents the root node of the trie.
A node contains an unordered map with char keys and the values are shared pointers to other nodes. The map is essentially the nodes childrens, where the keys are chars that the children contain, and the values are the nodes of that children map. Shared pointers were used because incomplete types are not allowed in unordered maps and allow for simple implementation. They also contain a bool value that tells the node if it is the last char in a word.
This trie implementation allows for O(l) search and insert time where l is the length of string being searched for. When inserting it travels from node to child node based on the chars from the input string adding nodes when necessary. Once it inserts that last char it will mark it as the end. When searching for a string each char is must inside the node and the last char must be marked as the end of the word. Using a map that stores the value of a node and its children nodes allows for O(1) search time between nodes resulting in O(l) insert and search time.
RestOfWord makes it to the end of the input string and searches child nodes for larger strings. This means that it takes O(l) time to find the end of the word and O(n) time searching children nodes. Best case is O(l) (it is not a substring of anything) worst case is O(n) (input an empty string). It will return a vector of with strings that contain the input as a prefix. Ex: inputing "yo" could return a vector with "you", "your", and "yours".
Remove makes it to the end of the input string and unmarks it as the end of a word. After a certain amount of words have been removed any used nodes will get removed. This allows for removing to be O(l) the majority of the time, where l is the length of the string being removed.
RemoveAll simply switches off the root node for an empty one. Size and empty are both O(1). TotalNodes, showStatistics, and print are O(n) where n is the amount of nodes in the trie.
Wikipedia Page for Trie (used to see what a Trie is)
Catch. (used for testing)
10000 most common english-Words (used for testing with a bunch of words)
[Dr Memory] (http://drmemory.org) (used to check for memery leaks and errors)