Difftastic is a structural diff tool that compares files based on their syntax.
For installation instructions, see Installation in the manual.
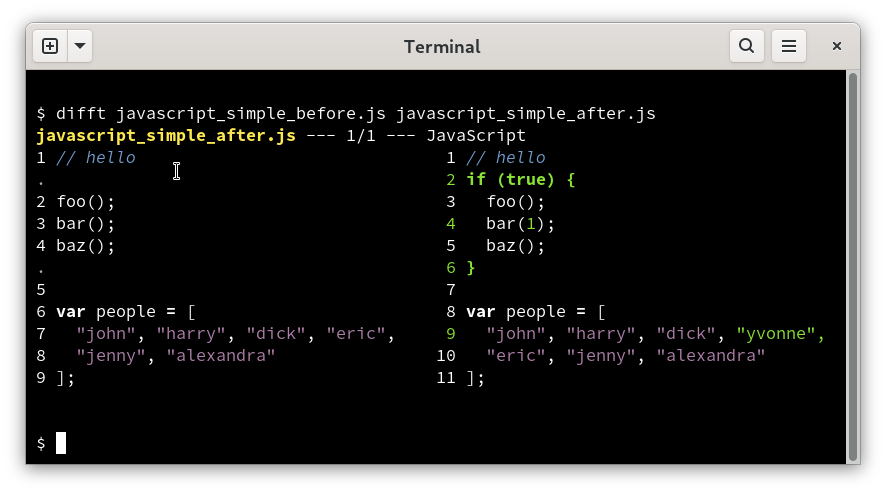
In this JavaScript example, we can see:
(1) Difftastic understands nesting. It highlights the matching { and
}, but understands that foo() hasn't changed despite the leading
whitespace.
(2) Difftastic understands which lines should be aligned. It's aligned
bar() on the left with bar(1) on the right, despite their changes.
(3) Difftastic understands that line-wrapping isn't
meaningful. "eric" is now on a new line, but it hasn't changed.
This one minute screencast demonstrates difftastic usage with both standalone files and git.
Difftastic supports over 20 programming languages, see the manual for the full list.
If a file has an unrecognised extension, difftastic uses a textual diff with word highlighting.
Performance. Difftastic scales relatively poorly on files with a large number of changes, and can use a lot of memory.
Display. Difftastic has a side-by-side display which usually works well, but can be confusing.
Robustness. Difftastic regularly has releases that fix crashes.
Patching. Difftastic output is intended for human consumption, and it
does not generate patches that you can apply later. Use diff if you
need a patch.
(Patch files are also line-oriented, which is too limited for difftastic. Difftastic might find additions and removals on the same line, and it tracks the relationship between line numbers in the old and new file.)
Merging. AST merging is a hard problem that difftastic does not address.
Word diffing can't do this.
Difftastic parses your code. It understands when whitespace matters,
such as inside string literals or languages like Python. It understands
that x-1 is three tokens in JS but one token in Lisp.
You can! The difftastic manual includes instructions for git usage. You can also use it with mercurial.
Probably not. Difftastic is young. Consider writing a plugin for your favourite tool, and I will link it in the README!
Difftastic is open source under the MIT license, see LICENSE for more details.
This repository also includes tree-sitter parsers by other authors in
the vendor/ directory. These are a mix of the MIT license and the
Apache license. See vendor/*/LICENSE for more details.
Files in sample_files/ are also under the MIT license unless stated
otherwise in their header.