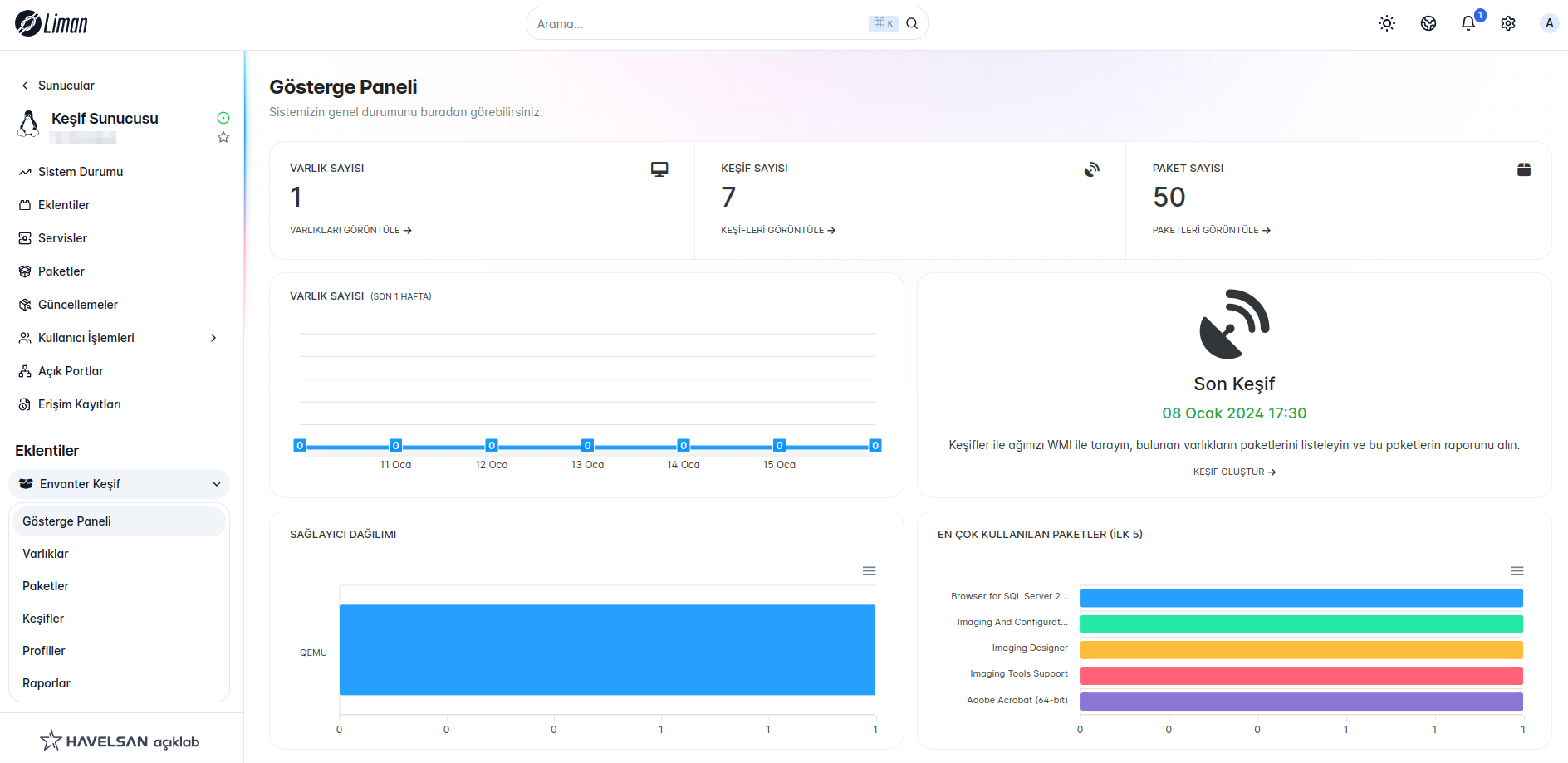
This service aims to scan the network with WMI, list the packages of the found machines, and get a report of these packages.
It currently supports postgresql, mysql and sqlite databases as storage.
Depending on your request, the relevant package is downloaded from the link here.
For Debian based systems:
sudo apt install ./inventory-server-{{release.number}}-x64.deb
For RHEL based systems:
sudo yum install ./inventory-server-{{release.number}}-x64.rpm
After installation, you should create a database and user on your database server.
Example for postgresql,
sudo -u postgres psql
postgres=# CREATE USER inventory WITH PASSWORD '****';
postgres=# CREATE DATABASE inventory WITH OWNER inventory;
postgres=# \q
The environment file is filled with appropriate data.
sudo nano /opt/inventory-server/.env
The content should look like the following :
DB_DRIVER=postgres/mysql/sqlite # Database type
DB_HOST=10.1.1.1 # Database ip address
DB_PORT=5432/3306 # Database port
DB_NAME=inventory # Database name
DB_USER=inventory # Database username
DB_PASS= # Database user's password
REPORT_ENGINE_URL=localhost:8001 # Report engine URL.
For Report Engine see here.
Finally, the service must be restarted.
sudo systemctl restart inventory-server@admin
To make sure it works correctly :
sudo systemctl status inventory-server@admin