Release Version: 1.2
TinyAFL is built on top of AFL and TinyInst.
It can be fuzz on windows user-mode application without source (supports both x32 and x64) but it is not so reliable and dirty. It still has some instrument bugs, I will fix it when I fully understand TinyInst :P
TinyAFL works similarly to WinAFL. However I use TinyInst (commit cfb9b15a53e5e6489f2f72c77e804fb0a7af94b5) for coverage. More about TinyInst can be found here.
TinyAFL supports AFLfast's power schedules by Marcel Böhme and MOpt mutator of MOpt-AFL. I add these features based on afl++
I have reported some MediaFoundations bugs using this tool.
- [Microsoft] CVE-2020-1319, CVE-2020-17105, CVE-2020-17109, CVE-2020-17022, CVE-2021-1643, CVE-2021-1644 ...
- [Microsoft] CVE-2021-24080 - found by Symeon Paraschoudis
Although TinyAFL x64 can run both for 32bit and 64bit targets, I still recommend TinyAFL 32bit for 32bit targets and TinyAFL 64bit for 64bit targets.
- Open a terminal and set up your build environment (e.g. On Windows, run vcvars64.bat / vcvars32.bat)
- Navigate to the directory containing the source
- Run the following commands (change the generator according to the version of IDE and platform you want to build for):
mkdir build64
cd build64
cmake -G "Visual Studio 16 2019" -A x64 ..
cmake --build . --config Release
The command line for TinyAFL:
AFL.exe [ afl options ] -- target_cmd_line
The following TinyAFL options are supported:
Required parameters:
-i dir - input directory with test cases
-o dir - output directory for fuzzer findings
Execution control settings:
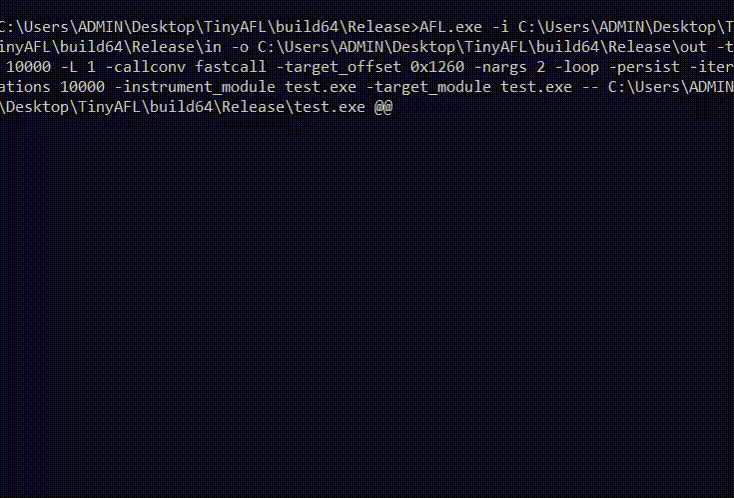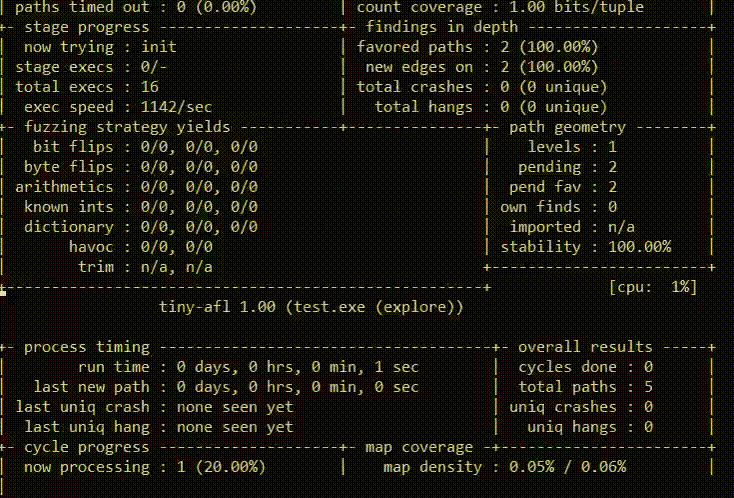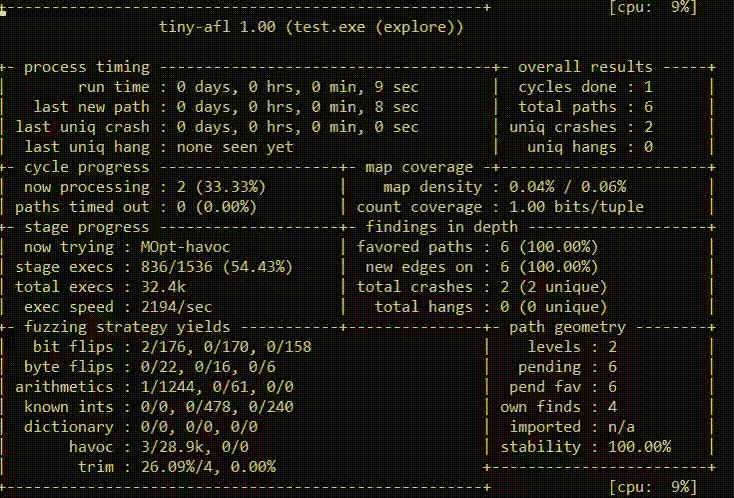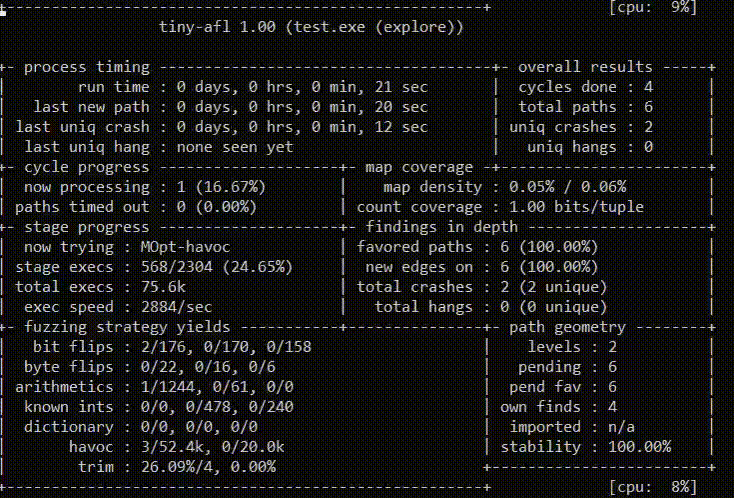
-p schedule - power schedules recompute a seed's performance score.
<explore(default), fast, coe, lin, quad, exploit, mmopt, rare>
-f file - location read by the fuzzed program (stdin)
-s - use share memory
-t msec - timeout for each run
-Q - use binary-only instrumentation (QEMU mode)
Mutator settings:
-L minutes - use MOpt(imize) mode and set the time limit for entering the
pacemaker mode (minutes of no new paths). 0 = immediately,
-1 = immediately and together with normal mutation).
Fuzzing behavior settings:
-x dir - optional fuzzer dictionary (see README)
Other stuff:
-M / -S id - distributed mode (see parallel_fuzzing.txt)
-C - crash exploration mode (the peruvian rabbit thing)
-e ext - file extension for the fuzz test input file (if needed)
-header_only - mutate only header of testcase (if needed)
-size_of_header - size of header will mutate when use option -header_only (default: 0x200)
tiny-afl settings:
-instrument_module path - path to instrumented PE
I add the feature to only mutate the test case header when fuzz (depending on the file format). I believe that some file format exceptions only happen when fields in the header change. To see the supported instrument flags, please refer to the mode-specific documentation at TinyInst.
WinAFL supports shared memory mode. This can be enabled by giving -s option to AFL.exe. If you are using shared memory mode then you need to make sure that in your harness you specifically read data from shared memory/stream instead of file. check a simple harness here:
https://github.com/googleprojectzero/Jackalope/blob/6d92931b2cf614699e2a023254d5ee7e20f6e34b/test.cpp#L111
https://github.com/googleprojectzero/Jackalope/blob/6d92931b2cf614699e2a023254d5ee7e20f6e34b/test.cpp#L41
AFL.exe -i in -o out -p fast -t 10000 -callconv fastcall -target_offset 0x1260 -nargs 2 -loop -persist -iterations 10000 -instrument_module demo.dll -target_module test.exe -- test.exe -f @@
python winafl-cmin.py -h
[...]
Examples of use:
* Typical use
afl-cmin.py -t 5000 -i in -o min -p demo.dll -- test.exe
* Dry-run, keep crashes only with 4 workers with a working directory:
afl-cmin.py -C --dry-run -w 4 --working-dir D:\dir -i in -i C:\fuzz\in -o min -p demo.dll -- test.exe -f @@
* Read specific file on specific location
afl-cmin.py -t 5000 -i in -o min -f foo.ext -p m.dll -- test.exe -f @@
* Read from specific file with pattern
afl-cmin.py -t 5000 -i in -o min -f prefix-@@-foo.ext -p demo.dll -- test.exe -f @@
afl-tmin.exe -h
[...]
afl-tmin.exe [ options ] -- /path/to/target_app [ ... ]
Required parameters:
-i file - input test case to be shrunk by the tool
-o file - final output location for the minimized data
-instrument_module module - target module to test
Execution control settings:
-t msec - timeout for each run (10000 ms)
Special thanks to Ivan Fratric "ifsecure" security researcher of Google Project Zero has published a great tool for coverage-guided