Moxy is a Homelab IoT "Platform" (for lack of a better term) that blurs the lines between hardware and software in the homelab. Here are the principal components of the platform:
- Centralized server power management using relays and current sensors
- Environmental sensors reporting real time metrics from the homelab
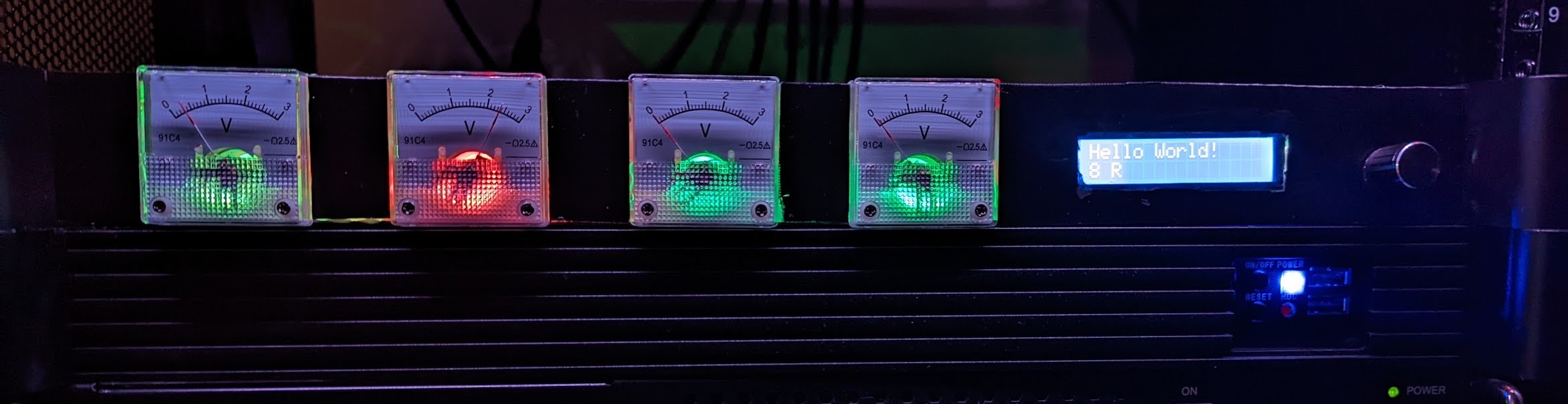
- Physical "dashboard" to display guages using old-fashioned panel meters, backlit by neopixels for extra color indication
Physical front panel interface: PWM-controlled panel meters, LCD screen, and rotary encoder

Home Assistant interface: communication coordinated via MQTT
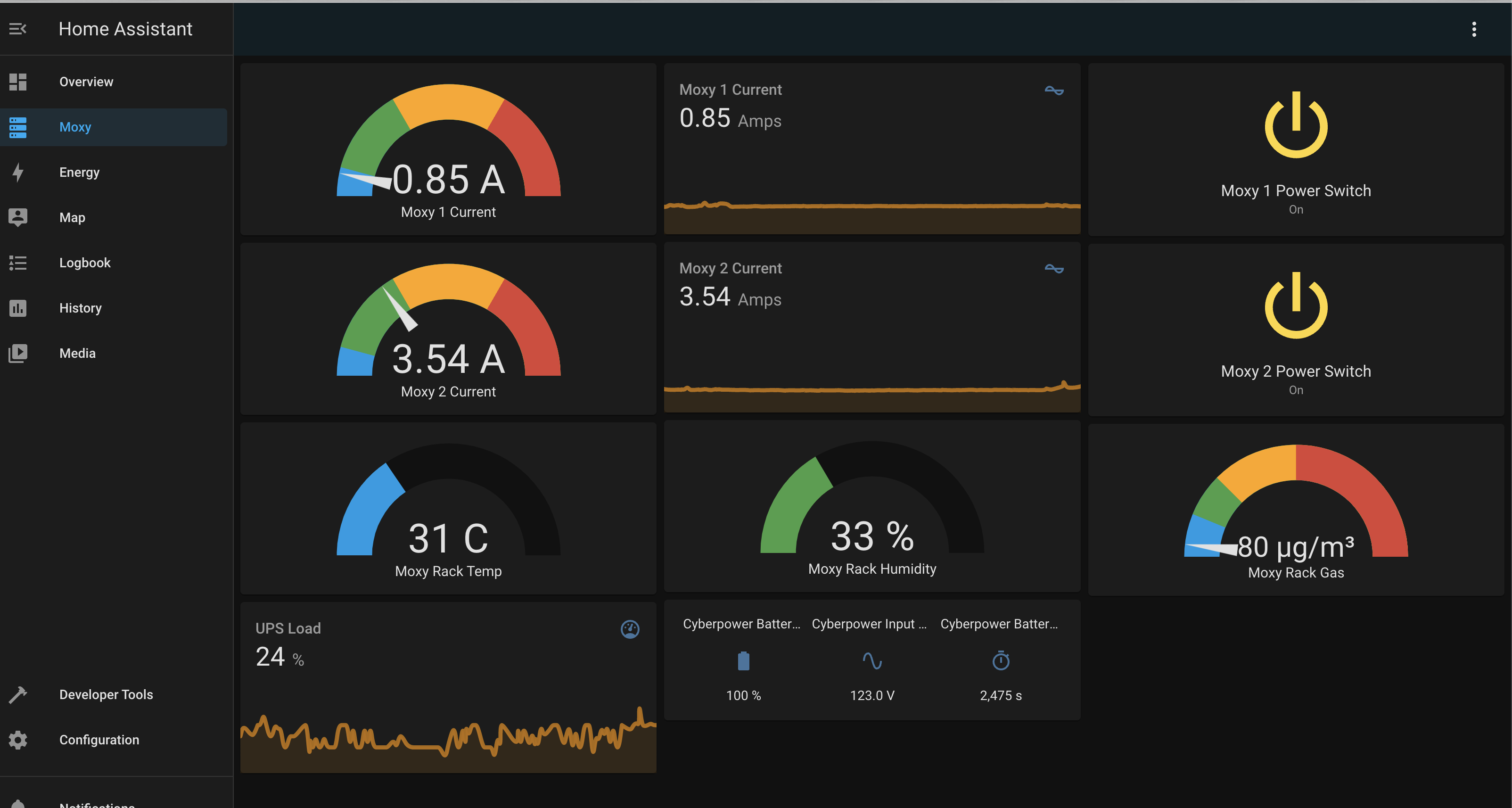
- MQTT
- Python 3
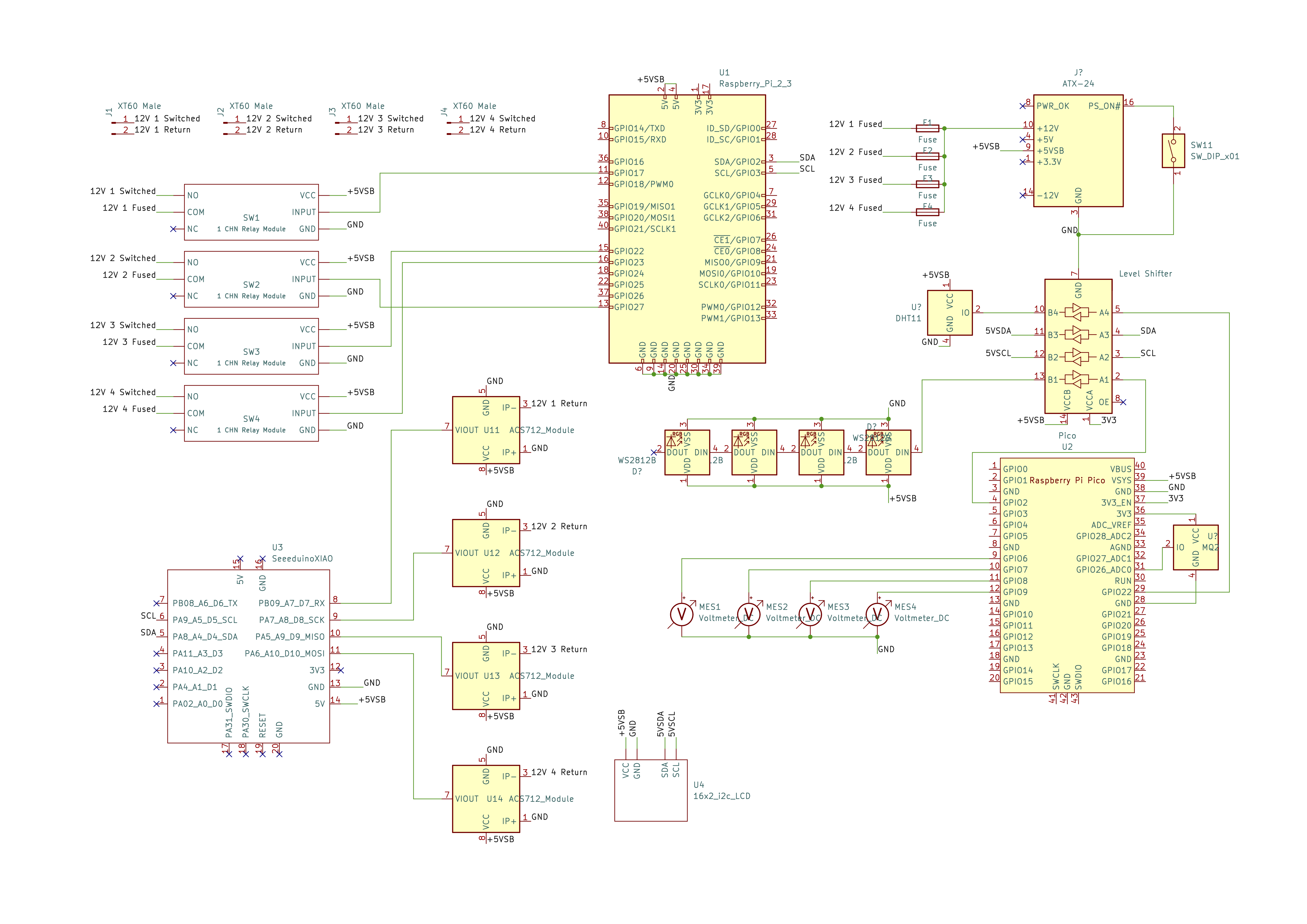
- I2C - to connect to microcontrollers and ADCs for sensors, analog meters (pwm), and LCD screen
- GPIO - for controlling relays and rotary encoder input
- Home Assistant
- 5 ADC pins
- 4 PWM pins
- 16x2 I2C LCD Screen
- 4x 30V 10A relays w/ optocouplers
- 4x ACS712 Hall-effect current sensors
- DHT11 temperature + humidity sensor
- MQ2 gas sensor
- Arduino-compatible microcontrollers
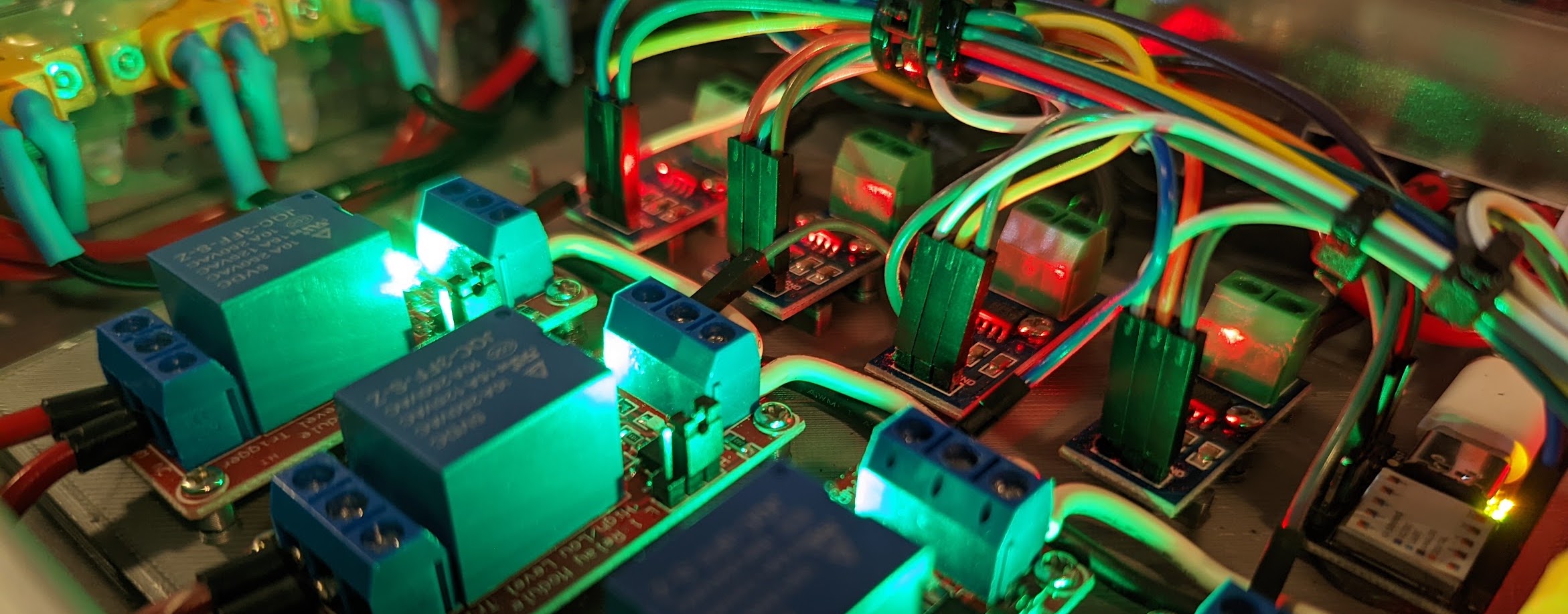
10A Relay Modules on (left), 20A hall-effect current sensor modules (right), XT60 output connectors (top right)
A bash script is included to assist in creating services for server-side components in systemd. See below for helpful commands on managing the services.
- Modify service definitions in
service_definitionsdirectory to reflect the location of the Python executables - Copy
config.ini.sampletoconfig.iniand replace values for your MQTT broker - Run
./install_systemd_services.sh- if successful, script will automatically start tailing journalctl logs to verify the services started successfully
journalctl --follow _SYSTEMD_UNIT=moxy.relays.service + _SYSTEMD_UNIT=moxy.sensors.service + _SYSTEMD_UNIT=moxy.panel.servicejournalctl -u moxy.{serviceName}.service -fsystemctl restart moxy.panel.service
systemctl restart moxy.sensors.service
systemctl restart moxy.relays.service