In a nutshell:
-
One-click launch ec2 spot instances and attach EBS volumes to them
-
Instances and volumes will be properly tagged with your team and your name.
The only dependency is boto3, you probably already have it. If not you can install it using pip install boto3 . After that do:
python getbox install
That will install the binary to /usr/local/bin and will try to install bash completions as well.
It also assumes you have ssh key pair used to access EC2 instances in your ssh agent.
You'll need AWS creds. If you have used awscli on your machine before, you should be good. If not, install awscli and run aws configure.
Laziest way ever to get an instance in one command:
$ getbox get
<..a minute later..>
[ubuntu@ip-172-18-142-171 ~]$You get an ubuntu 17.04 linux box in us-west-2. It will have a 100GB EBS drive mounted at /mnt.
By default, EBS drive will be deleted when instance is terminated. You can change that behavior using getbox keep command or you can combine that getbox get r3.4xlarge keep. Remember that your spot instance can be terminated by Amazon at any time.
Since it will tag instances will your unix user name, don't run it as root or in a container.
Usage: getbox <cmd> [parameters]
get Get an ec2 instance and ssh into it. getbox get r3.8xlarge
...optionally, pass EBS volume id to attach. getbox get vol-321
...or both getbox get r3.8xlarge vol-321
...you can also name it getbox get r3.8xlarge --name mytestbox
...or specify EBS volume size getbox get r3.8xlarge 200GB
list List your instances and volumes getbox list
kill Kill an instance or (unattached) volume getbox kill 123
getbox kill vol-456
ssh Log into the instance (uses utility1 key) getbox ssh 123
keep Disable delete-on-termination on an attached EBS volume getbox keep vol-123
unkeep Enable delete-on-termination on an attached EBS volume getbox unkeep vol-123
install Install getbox to /usr/local/bin and add bash autocomplete getbox install
getbox ssh <instance-id> is a bit magic; if used from interactive console, it will just log you in. But if it detects that its output was redirected, it will return user@host string. That allows you to use custom ssh flags or rsync/scp like this: rsync -av . $(getbox ssh):
Also, when starting an instance with an existing EBS drive using getbox get vol-123141 if you don't specify instance type explicitly, getbox will automatically choose the instance type that was last used with that EBS volume.
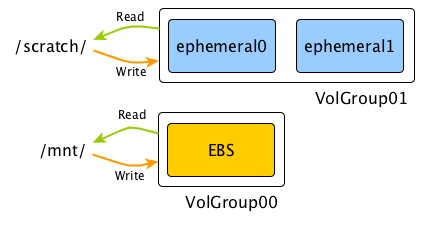
Ephemeral drives often provide much better performance in terms of iops and latency than EBS. With getbox, you have two options: either mount ephemeral drives as a separate "scratch" volume, or automatically mirror data both to EBS and ephemeral drives, so it survives instance termination.
EBS will be mounted at /mnt and ephemeral drives will be mounted as one RAID-0 lvm voume under /scratch. You will lose everything under /scratch when instance gets terminated.
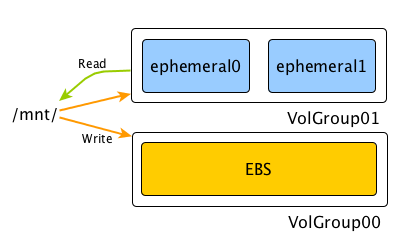
In this mode, toggled by --mirror flag, getbox creates a RAID volume so that all writes go both to ephemeral drives as well as EBS volume. It is set up so that reads only go to the ephemeral drive when possible, so you get random read performance closest to that of the ephemeral drive and write performance of the slowest of two, and you don't lose the data when instance terminates.
You get both the (read) performance and persistence!
There are a couple caveats:
- You cannot choose EBS volume size in this mode; it will be automatically choosen to match ephemeral storage, depending on your instance type.
- Currently you can only reuse mirrored EBS volume with the same instance type (since ephemeral drives size has to match EBS size).
getboxremembers what instance type was used, so you can just rungetbox get <volume-id>and it will start an instance of the same type and will reassemble RAID array. - When first launching the instance in this mode, it will require 10-50 minutes to resync the RAID array; you can use the instance during resync, but read performance will be that of EBS. You can check status of resync by using
mdadm --detail /dev/md0. - Remember that you still need to do
getbox keepto keep the EBS drive around when instance terminates.
You can customize some of getbox default parameters using JSON config file in your home dir named .getbox.
| Name | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
extra_tags |
Tags to assign to ec2 instance and EBS drive | |
owner_tag_name |
getbox also tags your instances with your username, this is the name of the tag |
"owner" |
ssh_user |
Linux username used to ssh into instances | "ubuntu" |
ssh_key_name |
Name of ssh keypair to use when creating an instance | "utility1" |
ssh_wait_timeout_seconds |
Timeout when trying to connect to a newly created instance | 600 |
ssh_flags |
Flags to use with ssh command for getbox ssh |
"-A" |
root_size_gb |
Default size of the root EBS drive (GiB) | 30 |
ami_id |
EC2 AMI id to use | "ami-790ec601" |
cuda_ami_id |
EC2 AMI id to use with GPU-enabled instances (can be null, then ami_id is used) |
"ami-a1e534d9" |
iam_role_arn |
EC2 IAM role arn to use for instance profile | |
security_groups |
A list of security group ids to use | |
subnets |
A list of subnets to use | |
spot_price |
Spot price | "3.00" |