The general structure of the database
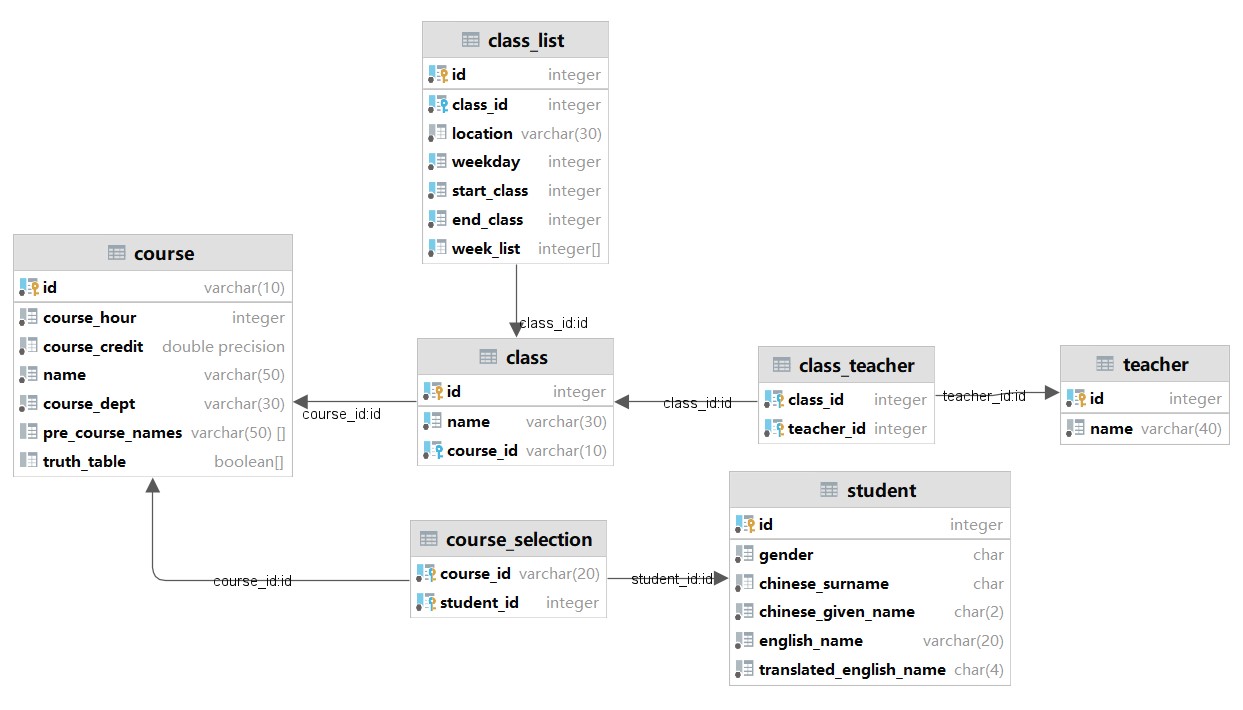
- course: stores the course information. Columns pre_course_names and truth_table stores the prerequisite course boolean function.
- class: each course contains many classes. In this table, we have course_id as a foreign key to express this relation.
- class_list: each class has many class lists, usually two. In this table, we have class_id as a foreign key to express this relation. This table also stores the information about the class lists.
- teacher: stores each teacher's id and names.
- class_teacher: The relation between classes and teachers. Because each class may have several teachers and each teacher may teach several classes
- student: stores information about student
- course_selection: The relation between courses and students. Clearly, each course has several students and each student selects several courses.
- Prepare the connect information in the
jdbc.propertiesfile, then load it in thegetConnection()method. - Prepare the
closeResources()method, which closes severalStatementsand oneConnection
Step 1: Extract the information for table course by constructing the Course class and using Gson.
An important method in Course class is standardize() , which standardizes the prerequisite string to preCourseNames and truthTable.
public void standardize(){
if(prerequisite!=null && prerequisite.length()>0){
//1.去除课程名中的空格,将中文括号改为英文括号
prerequisite=prerequisite.replace('(','(').replace(')',')')
.replace("SUSTech English ","SUSTech_English_")
.replace("大学物理 B","大学物理B")
.replace("化学原理 A","化学原理A")
.replace("化学原理 B","化学原理B")
.replace("学术英语 ","学术英语")
.replace("生理学与病理生理学 I","生理学与病理生理学I")
.replace("线性代数I A","线性代数I-A");
//2.生成prerequisiteCoursesNames
String[] temp=prerequisite.split(" ");
ArrayList<String> courses = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : temp) {
//去除“或者”、“并且”
if(!s.equals("或者") && !s.equals("并且") && !s.equals("")){
//去除单独括号&前后括号,并防止hasDoubleBracket的情况出现
while(true){
if(s.startsWith("(")){
s=s.substring(1);
continue;
}
if(!hasDoubleBracket(s)){
s=s.substring(0,s.length()-1);
continue;
}
break;
}
if(!courses.contains(s)){
courses.add(s);
}
//防止重复添加课程名
}
}
//将courses按名称长度降序排序,目的是避免3.1替换时出现:化学原理→化学原理实验→化学原理实验A(先替换前面的会有bug)的情况
courses.sort((o1, o2) -> o2.length() - o1.length());
preCoursesNames=courses.toArray(new String[0]);
//3.构建truthTable
//3.1将prerequisite公式化为formulatedPrerequisite
String formulatedPre =prerequisite;
for (int i = 0; i < preCoursesNames.length; i++) {
formulatedPre = formulatedPre.replace(preCoursesNames[i],String.valueOf((char)('A'+i)));
//最后替换A
}
formulatedPre = formulatedPre.replace(" 并且 ","&")
.replace(" 或者 ","|");
//3.2生成truthTable
//3.2.1用逆波兰算法生成后缀表达式
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
char[] chars = formulatedPre.toCharArray();
for (char c : chars) {
switch (c) {
case '(' -> stack.push('(');
case ')' -> {
char top;
while ((top = stack.pop()) != '(') {
sb.append(top);
}
}
case '&' -> {
if (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == '&') {
sb.append(stack.pop());
}
stack.push('&');
}
case '|' -> {
if (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == '&') {
sb.append(stack.pop());
}
if (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == '|') {
sb.append(stack.pop());
}
stack.push('|');
}
default ->//对应于字母A,B,C...
sb.append(c);
}
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
sb.append(stack.pop());
}
char[] postfix=sb.toString().toCharArray();
truthTable=new Boolean[(int)Math.pow(2, preCoursesNames.length)][1+ preCoursesNames.length];
for (int i = 0; i < Math.pow(2, preCoursesNames.length); i++) {
//3.2.2构建每行的真值表的变量取值
for (int j = 0; j < truthTable[0].length - 1; j++) {
truthTable[i][j]=(i&(1<<j))!=0;
//判断i的第j+1位是否为1
}
//3.2.3用栈计算后缀表达式
Stack<Boolean> stack2 = new Stack<>();
for (char c : postfix) {
switch (c) {
case '|' -> stack2.push(stack2.pop() | stack2.pop());
case '&' -> stack2.push(stack2.pop() & stack2.pop());
default -> stack2.push(truthTable[i][c - 'A']);
}
}
truthTable[i][truthTable[0].length - 1]=stack2.pop();
}
}
}After the standardization, store the courses in HashSet to filtrate the duplicate information of courses.
Step 2: Decouple the data of json file to different tables' information
This step extracts the data for table class, class_list, teacher, class_teacher
List<Clazz> classes=generateList("Clazz");//classes最终导入数据库
List<ClassList> classLists = new ArrayList<>();//classLists最终导入数据库
HashMap<String,Integer> teachers = new HashMap<>();//teachers最终导入数据库,String=老师名,int=id
ArrayList<ClassTeacher> classTeachers = new ArrayList<>();//classTeachers最终导入数据库
int classIdCount=0;
int teacherIdCount=32010000;//模拟真实情况
for (Clazz clazz : classes) {
//1.设定class自身id
clazz.setId(++classIdCount);
//2.生成teachers和classTeachers
clazz.splitTeacherNames();
if(clazz.getTeacher()!=null){
for (String teacherName : clazz.getTeacherNames()) {
//如果teachers中已经不包含该教师,则添加入teacher
if (!teachers.containsKey(teacherName)) {
teachers.put(teacherName, ++teacherIdCount);
}
//添加每一条class_teacher映射
classTeachers.add(new ClassTeacher(classIdCount, teachers.get(teacherName)));
}
}
//3.生成classLists
for (ClassList cl : clazz.getClassList()) {
cl.splitClassTime();
cl.setClassId(classIdCount);
classLists.add(cl);
}
}Step 3: After preparing all the data, we just need to load it to the database by constructing PreparedStatements and execute() them.
PS: Because the data size of json file is small, we don't compare the loading efficiency of different methods in this section.
Generally, we split the information in csv file to prepare for the tables course_selection, student by using the following script.
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(pathToCsvFile));
while((line=reader.readLine())!=null){
String[] info=line.split(",");
//导入表student中的数据
int studentId=Integer.parseint(info[3]);
char gender=info[1].charAt(0);
char chineseSurname=info[0].charAt(0);
String chineseGivenName=info[0].substring(1);
String englishName=info[2].substring(5,info[2].length()-1);
String translatedEnglishName=info[2].substring(0,4);
//导入表course_selection中的数据
for (int i = 4; i < info.length; i++) {
String courseId=info[i];
}
}This method only use Statement to load data.
Statement st=con.createStatement();
String sql="insert into student(id,gender,chinese_surname,chinese_given_name,english_name,translated_english_name)" +
"values("+studentId+",'"
+gender+"','"
+chineseSurname+"','"
+chineseGivenName+"','"
+englishName+"','"
+translatedEnglishName+"')";
st.execute(sql);This method costs 7534264 ms, so the efficiency is too slow.
This method use PreparedStatement, which is faster than Statement because PreparedStatement is recompiled.
while((line=reader.readLine())!=null){
String sql="insert into student(id,gender,chinese_surname,chinese_given_name,english_name,translated_english_name) values(?,?,?,?,?,?)";
PreparedStatement ps=con.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setObject(1,studentId);
ps.setObject(2,gender);
ps.setObject(3,chineseSurname);
ps.setObject(4,chineseGivenName);
ps.setObject(5,englishName);
ps.setObject(6,translatedEnglishName);
ps.execute();
}This method costs 6762351 ms. Compared with method 1, the efficiency is improved by 10.2%, which isn't obvious.
This method reuses only one PreparedStatement, which is generated out of the loop, so it saves the cost of generating PreparedStatement from SQL.
String sql="insert into student(id,gender,chinese_surname,chinese_given_name,english_name,translated_english_name) values(?,?,?,?,?,?)";
ps=con.prepareStatement(sql);
while((line=reader.readLine())!=null){
ps.setObject(1,studentId);
ps.setObject(2,gender);
ps.setObject(3,chineseSurname);
ps.setObject(4,chineseGivenName);
ps.setObject(5,englishName);
ps.setObject(6,translatedEnglishName);
ps.execute();
}This method costs 6436215 ms. Compared with method 2, the efficiency is improved by 4.8%, which isn't obvious.
This method uses batched execute to improve efficiency.
while((line=reader.readLine())!=null){
ps1.addBatch();
count1++;
if(count1%batchSize==0){
ps1.executeBatch();
ps1.clearBatch();
}
}This method costs 343098 ms. Compared with method 3, the efficiency is improved by 94.7%, the effect is very obvious.
This method closes AutoCommit to improve the efficiency.
con.setAutoCommit(false);
while((line=reader.readLine())!=null){
ps1.addBatch();
count1++;
if(count1%batchSize==0){
ps1.executeBatch();
ps1.clearBatch();
}
}
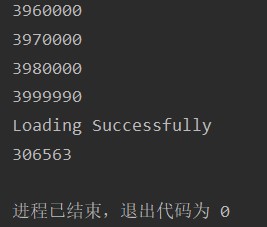
con.commit();This method costs 306563 ms. Compared with method 4, the efficiency is improved by 10.8%, which isn't obvious.
From the experiments above, we can see that the major enhancement of loading efficiency comes from the batch execute.
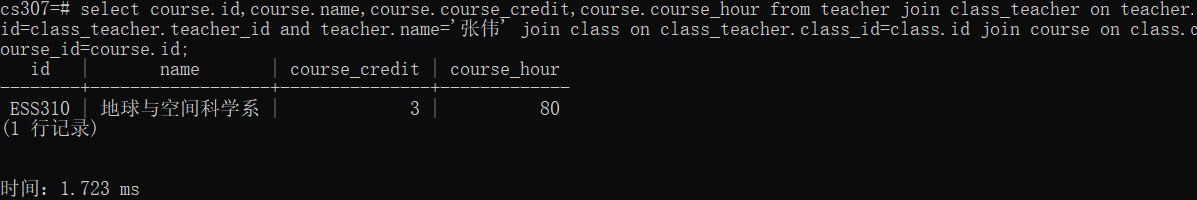
- select the course taught by "张伟"
select course.id,course.name,course.course_credit,course.course_hour
from teacher
join class_teacher on teacher.id = class_teacher.teacher_id
and teacher.name='张伟'
join class on class_teacher.class_id = class.id
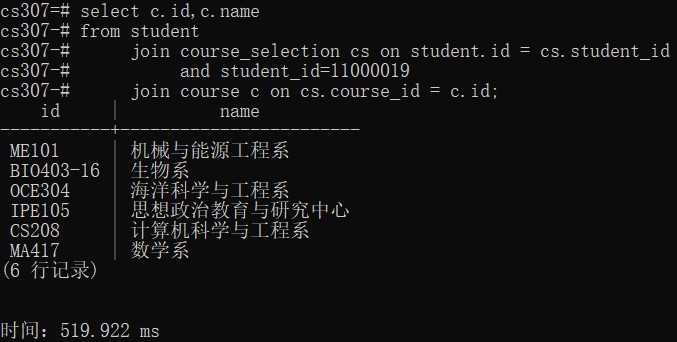
join course on class.course_id = course.id;- select the student's course selection whose id is 11000019
select c.id,c.name
from student
join course_selection cs on student.id = cs.student_id
and student_id=11000019
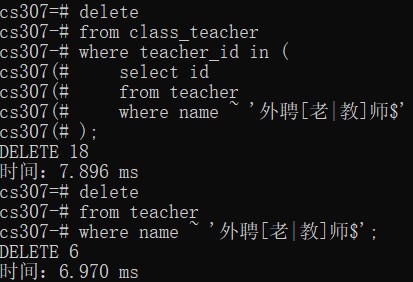
join course c on cs.course_id = c.id;- Use regex to delete the teachers with names ending with "外聘教师" or "外聘老师"
delete
from class_teacher
where teacher_id in (
select id
from teacher
where name ~ '外聘[老|教]师$'
);
delete
from teacher
where name ~ '外聘[老|教]师$';We can see that 18 lines are deleted from class_teacher table and 6 lines in teacher table.
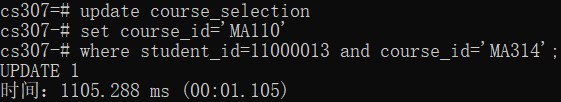
- The student with id 11000013 changes his/her course MA314 to MA110, we should update in the database.
update course_selection
set course_id='MA110'
where student_id=11000013 and course_id='MA314';- The student with id 11361551 adds a course CS203, we should update in the database.
insert into course_selection values ('CS203',11361551);In this section, we will query all the courses with id starting with "CS" in database. From this example, we can compare the advantages and disadvantages between database and file.
Design the following code
public static String[] findCourseNameById(String s){
Connection con=getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps=null;
ResultSet rs=null;
ArrayList<String> names=null;
String sql="select name from course where id like '"+s+"%'";
try {
ps=con.prepareStatement(sql);
rs=ps.executeQuery();
names = new ArrayList<>();
while(rs.next()){
names.add(rs.getString(1));
}
}
catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
closeResource(con,ps,rs);
}
assert names != null;
return names.toArray(new String[0]);
}Then we get the result of findCourseNamesById("CS")
 The time cost is 491 ms.
The time cost is 491 ms.
select name from course where id like 'CS%';Then we get the result
 The time cost is 0.682 ms, which is much faster than JDBC method.
The time cost is 0.682 ms, which is much faster than JDBC method.
From above we can compare the two method. JDBC: advantage:
- Code is easier to reuse and store
- Code is easier to expand and can provide more variety of functions
disadvantage:
- It's slow because it needs many other time costs
SQL: advantage:
- It's more faster because it does things directly
disadvantage:
- It's hard to expand because it's not a programming language.
When a database is created, it has a superuser by default, we firstly connect the database as the default user.
Then we can create a user, and set some privileges.
--创建用户test,并设置密码
create user test password '114514';
--将表course的owner设置为test
alter table course owner to test;
--赋予test查询权限
grant select on course to test;When we change the user to 'test' and execute the following SQL sentences.
update course
set course_credit=1.0
where id='MA212';We get Error: permission denied for table course, which means we don't have the privilege to update.
There are many other privileges such as login in, create user, create db... We can also manage a lot of users in a group, which is more convenient.
The loading time of the csv file using method 5 is 306563 ms
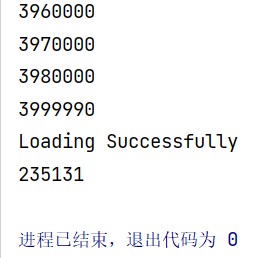
The loading time of the csv file using method 5 is 235131 ms, which is faster than Windows. This may be due to different process management between OS, and the type of CPU is also an important factor.