The substitution cipher is a cipher that has been in use for many hundreds of years. It basically consists of substituting every plaintext character for a different ciphertext character. The cipher alphabet may be shifted or reversed or scrambled. In this project, we will combine two types of substitution cyphers: a simple substitution cipher followed by an affine cipher.
- string
- if statement
- for loop and while loop
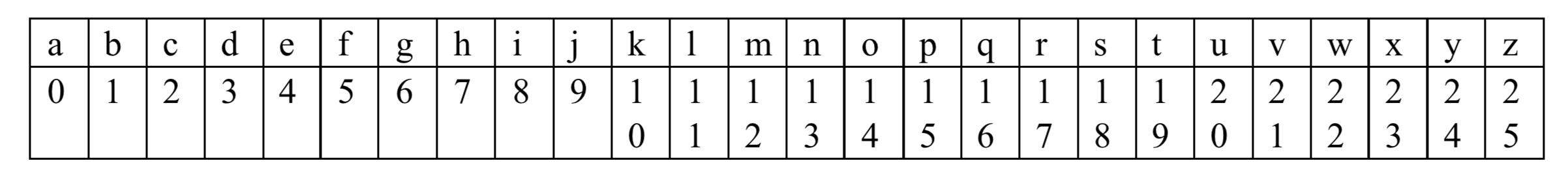
Simple substitution cipher: the cipher alphabet is created by first writing out a keyword, removing repeated letters in it, then writing all the remaining letters in the alphabet in the usual order. Consider the following example. Consider the alphabet being a single string consisting of the lower-case English letters as below (shown with each letter’s associated index, e.g. m’s index is 12):
Then, using this system, the keyword “michigan” gives us the following alphabet mapping:
Note how “michigan” starts the mapping, how the second “i” is skipped, and how the remaining letters continue in alphabetical order without the characters of “michigan”.
Using the example above, the word “green” is translated as follows:
- the ‘g’ is found at index 6 in the alphabet. The letter in the rotated alphabet is ‘n’.
- the ‘r’ is found at index 17, the rotated letter is ‘r’.
- the ‘e’ is found at index 4, the rotated letter is ‘g’.
- the ‘e’ is found at index 4, the rotated letter is ‘g’.
- the ‘n’ is found at index 13, the rotated letter is ‘l’.
Thus, the string ‘green’ becomes the string ‘nrggl’. You will use that cyphertext ‘nrggl’ as the starting point (“plaintext”) for the next stage, the affine cipher.
Affine cipher: The key for the Affine cipher consists of two numbers, a and b. It takes in a plain-text string, and translates it into a new string based on an encryption/decryption functions that rotate the alphabet of size m:
- The encryption function is y = (a * x + b) mod m
- The decryption function is the inverse operation
- Do the encryption backwards (mathematically decryption is x = a-1 * (y − b) mod m where a-1 satisfies the equation 1 = a * a-1 mod m, but in this case thinking mathematically will make programming much more difficult).
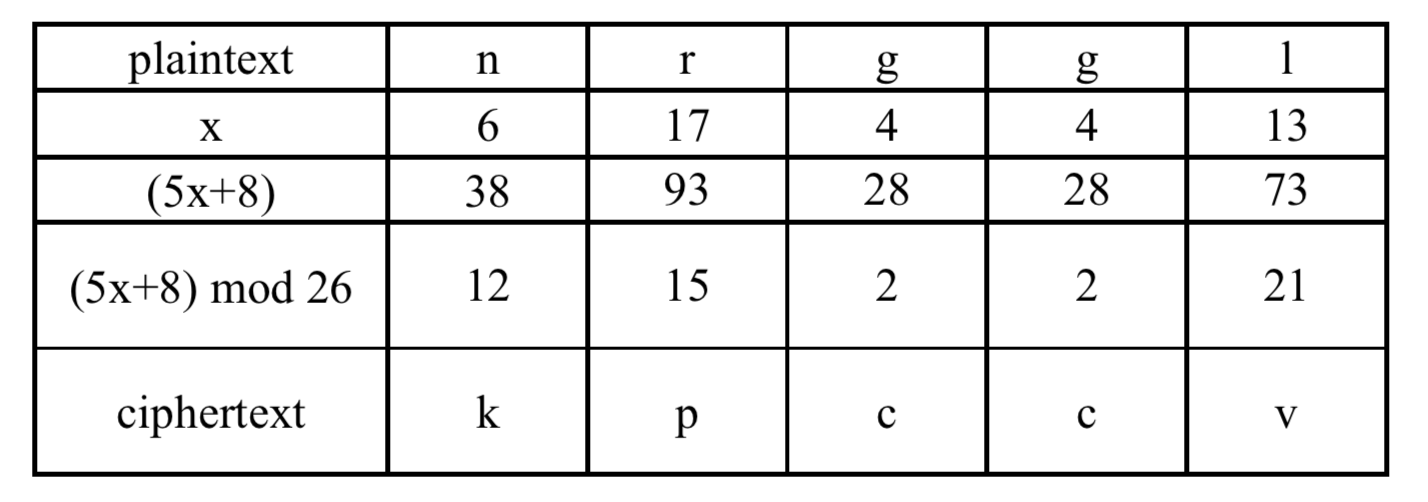
To encrypt consider our plaintext ‘green’ and its cyphertext ‘nrggl’ now using our affine key (a=5, b=8). After scrambling the alphabet using the keyword “michigan” and encrypting the plaintext "green” to “nrggl”, we will encrypt "nrggl" using the table mentioned above for the numeric values of each letter, from our key a is 5 and b is 8, and finally m is 26 since there are 26 characters in the alphabet being used. The first step is to write the numeric values of each letter using the scrambled alphabet. Then, take each value of x, and solve the first part of the equation, (5x + 8). After finding the value of (5x + 8) for each character, take the remainder when dividing the result of (5x + 8) by 26. The final step in encrypting the message is to look up each numeric value in the table for the corresponding letters. In this example, the encrypted text would be “kpccv”. The table below shows the completed table for encrypting a message in the Affine cipher.
Build the entire affine mapping and then use it to encrypt the plaintext.
To decrypt you want to reverse that process. That is, start with the ciphertext “k” and work backwards (using the affine mapping) to get “n” and repeat for the remaining characters.
The program should prompt the user for one of three commands:
- "e" to encode a string
- "d" to decode a string
- "q" to quit
Any other command should raise an error and reprompt. Accept either upper or lower case letters (Use the string method upper() or lower()). Use ‘q’ to control your while loop.
If the command is encode, then the program prompts for a string to encode and a keyword (which consist only of letters). The program then returns the encoded string (cipher text).
- To build the symmetric key, start with an empty string and as you loop through the keyword add characters to the key string (remember to check for duplicates before insertion. The string in operator is useful and remember that you can also use not as part of a Boolean expression, i.e. not in). Repeat to add the remaining characters in the alphabet.
- To encode you will find the string index() or find() methods useful for finding the index of a character in the alphabet.
- Important, the program should not encode any letter that is not in the lower-case alphabet. If upper case, then convert it to lower case. Punctuations, special characters and numbers should simply be passed through to the encoded string.
- The keyword should only contain lower case letters and its length should be between at least 1 and less or equal to 26. If not the case, then the program should display an error message and prompt the user to give another keyword.
- For the affine cipher always use a = 5, b = 8, and m = 26. (mod is Python’s % operator. Also, start with an empty cyphertext and add each encrypted character one at a time to the cyphertext as you encrypt each one.)
- The string isalpha() method may be helpful. Also, import string and string ascii_lowercase might also be useful.
If the command is decode, then the program should prompt for a string to decode and a keyword. The output should be the decoded string (plain text).
If the command is quit, then the program ends and prints a nice exit message.
if answer.upper() == 'E':
#When the input "e"
key = input("Please enter a keyword: ").lower()
#input keyword
while (key.isalpha() == False) or (len(key) > 26):
#When input character is greater than 26 or is not all characters.
print("There is an error in the keyword. \
It must be all letters and a maximum length of 26")
key = input("Please enter a keyword: ").lower()
else:
#Let's do the first loop
#Determine that all of the letters in the input key appear only once
#If there is a repeat
#delete
#Use slicing and splicing functions
#And I'm going to put them in order
for i in range(0,len(key)):
if key[i] not in new_key:
new_key = new_key + key[i]
#Let's do the second loop
#Pairing of strings
#If the same, then the letter ahead
#Use slicing and splicing functions
for j in range(0,len(new_key)):
same1 = old.find(new_key[j])
old = old[:same1] + old[same1+1:]
new_list = new_key + old
message = input("Enter your message: ").lower()
#Let's do the third cycle
#Enter a cipher
#The number of loops is the length of the ciphertext
#Look for the number of digits encrypted
#Then do the second encryption
#By affine code
#Output the letter of this number
for k in range(0,len(message)):
if message[k].isalpha() == False:
e = e + message[k]
else:
same2 = new.find(message[k])
num = (5*same2+8)%26
e = e + new_list[num]
print("your encoded message: ",e)- E-mail:liutia20@msu.edu
Thanks for reading this help document