🤗 HF Repo • 🤖 ModelScope • 🐦 Twitter • 👋 加入我们的 Discord 和 微信
📍在 智谱AI开放平台 体验和使用更大规模的 GLM 商业模型。
Read this in English
GLM-4-9B 是智谱 AI 推出的最新一代预训练模型 GLM-4 系列中的开源版本。 在语义、数学、推理、代码和知识等多方面的数据集测评中, GLM-4-9B 及其人类偏好对齐的版本 GLM-4-9B-Chat 均表现出超越 Llama-3-8B 的卓越性能。除了能进行多轮对话,GLM-4-9B-Chat 还具备网页浏览、代码执行、自定义工具调用(Function Call)和长文本推理(支持最大 128K 上下文)等高级功能。本代模型增加了多语言支持,支持包括日语,韩语,德语在内的 26 种语言。我们还推出了支持 1M 上下文长度(约 200 万中文字符)的 GLM-4-9B-Chat-1M 模型和基于 GLM-4-9B 的多模态模型 GLM-4V-9B。GLM-4V-9B 具备 1120 * 1120 高分辨率下的中英双语多轮对话能力,在中英文综合能力、感知推理、文字识别、图表理解等多方面多模态评测中,GLM-4V-9B 表现出超越 GPT-4-turbo-2024-04-09、Gemini 1.0 Pro、Qwen-VL-Max 和 Claude 3 Opus 的卓越性能。
| Model | Type | Seq Length | Download | Online Demo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLM-4-9B | Base | 8K | 🤗 Huggingface 🤖 ModelScope | / |
| GLM-4-9B-Chat | Chat | 128K | 🤗 Huggingface 🤖 ModelScope | 🤖 ModelScope CPU 🤖 ModelScope vLLM |
| GLM-4-9B-Chat-1M | Chat | 1M | 🤗 Huggingface 🤖 ModelScope | / |
| GLM-4V-9B | Chat | 8K | 🤗 Huggingface 🤖 ModelScope | / |
| Model | AlignBench | MT-Bench | IFEval | MMLU | C-Eval | GSM8K | MATH | HumanEval | NaturalCodeBench |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Llama-3-8B-Instruct | 6.40 | 8.00 | 68.6 | 68.4 | 51.3 | 79.6 | 30.0 | 62.2 | 24.7 |
| ChatGLM3-6B | 5.18 | 5.50 | 28.1 | 61.4 | 69.0 | 72.3 | 25.7 | 58.5 | 11.3 |
| GLM-4-9B-Chat | 7.01 | 8.35 | 69.0 | 72.4 | 75.6 | 79.6 | 50.6 | 71.8 | 32.2 |
| Model | MMLU | C-Eval | GPQA | GSM8K | MATH | HumanEval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Llama-3-8B | 66.6 | 51.2 | - | 45.8 | - | 33.5 |
| Llama-3-8B-Instruct | 68.4 | 51.3 | 34.2 | 79.6 | 30.0 | 62.2 |
| ChatGLM3-6B-Base | 61.4 | 69.0 | 26.8 | 72.3 | 25.7 | 58.5 |
| GLM-4-9B | 74.7 | 77.1 | 34.3 | 84.0 | 30.4 | 70.1 |
由于
GLM-4-9B在预训练过程中加入了部分数学、推理、代码相关的 instruction 数据,所以将 Llama-3-8B-Instruct 也列入比较范围。
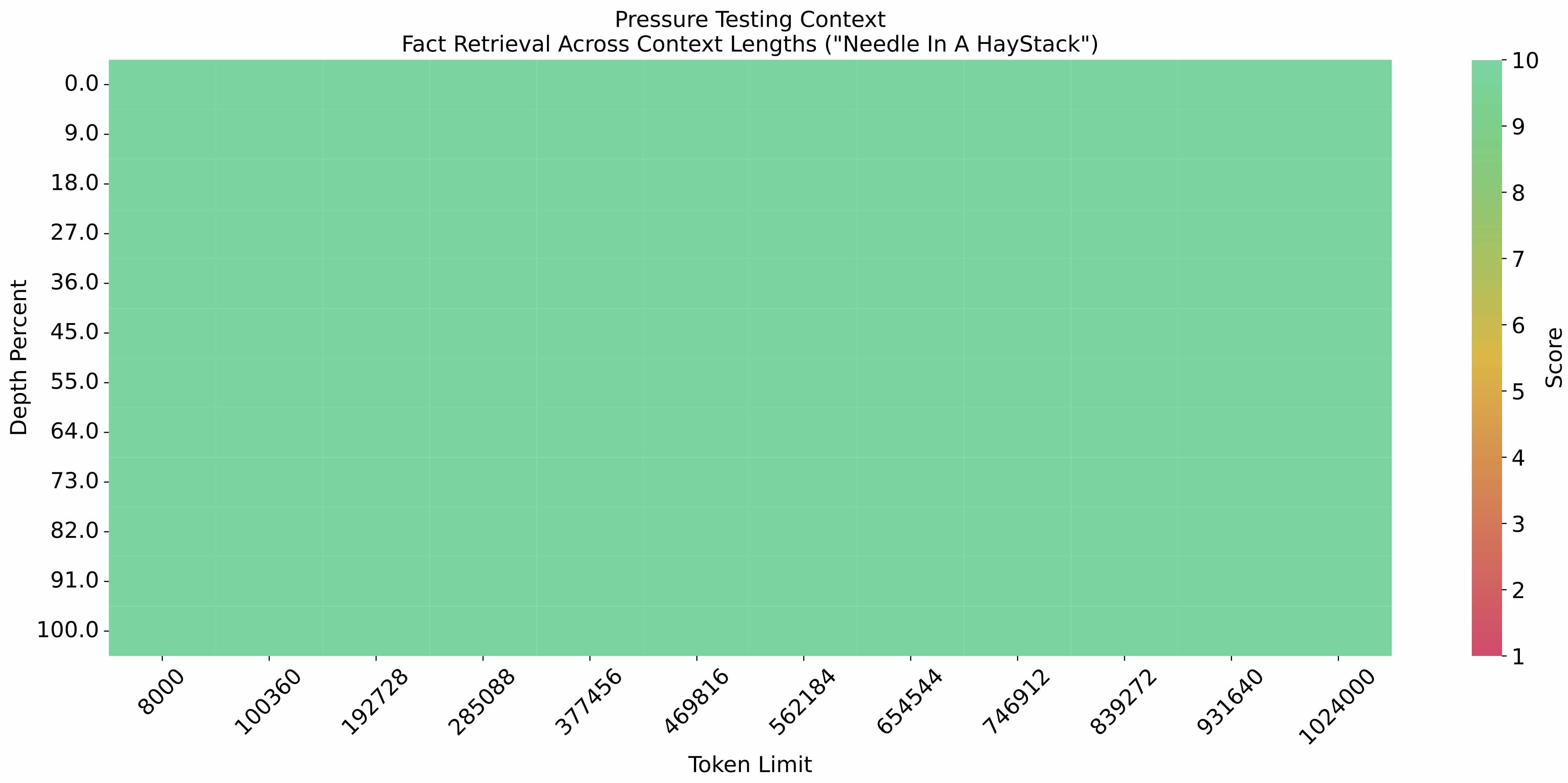
在 1M 的上下文长度下进行大海捞针实验,结果如下:
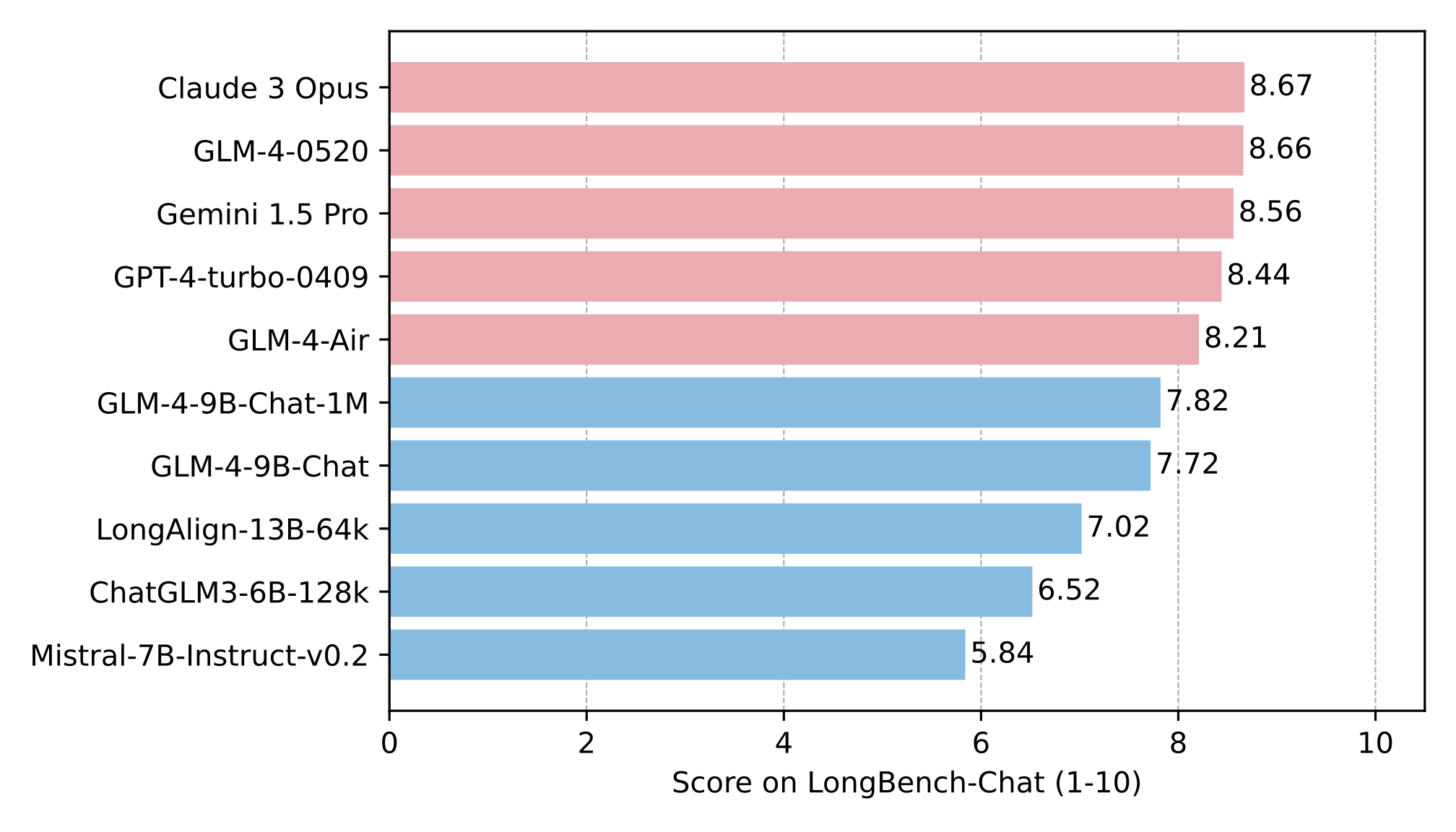
在 LongBench-Chat 上对长文本能力进行了进一步评测,结果如下:
在六个多语言数据集上对 GLM-4-9B-Chat 和 Llama-3-8B-Instruct 进行了测试,测试结果及数据集对应选取语言如下表
| Dataset | Llama-3-8B-Instruct | GLM-4-9B-Chat | Languages |
|---|---|---|---|
| M-MMLU | 49.6 | 56.6 | all |
| FLORES | 25.0 | 28.8 | ru, es, de, fr, it, pt, pl, ja, nl, ar, tr, cs, vi, fa, hu, el, ro, sv, uk, fi, ko, da, bg, no |
| MGSM | 54.0 | 65.3 | zh, en, bn, de, es, fr, ja, ru, sw, te, th |
| XWinograd | 61.7 | 73.1 | zh, en, fr, jp, ru, pt |
| XStoryCloze | 84.7 | 90.7 | zh, en, ar, es, eu, hi, id, my, ru, sw, te |
| XCOPA | 73.3 | 80.1 | zh, et, ht, id, it, qu, sw, ta, th, tr, vi |
我们在 Berkeley Function Calling Leaderboard 上进行了测试并得到了以下结果:
| Model | Overall Acc. | AST Summary | Exec Summary | Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Llama-3-8B-Instruct | 58.88 | 59.25 | 70.01 | 45.83 |
| gpt-4-turbo-2024-04-09 | 81.24 | 82.14 | 78.61 | 88.75 |
| ChatGLM3-6B | 57.88 | 62.18 | 69.78 | 5.42 |
| GLM-4-9B-Chat | 81.00 | 80.26 | 84.40 | 87.92 |
GLM-4V-9B 是一个多模态语言模型,具备视觉理解能力,其相关经典任务的评测结果如下:
| MMBench-EN-Test | MMBench-CN-Test | SEEDBench_IMG | MMStar | MMMU | MME | HallusionBench | AI2D | OCRBench | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gpt-4o-2024-05-13 | 83.4 | 82.1 | 77.1 | 63.9 | 69.2 | 2310.3 | 55.0 | 84.6 | 736 |
| gpt-4-turbo-2024-04-09 | 81.0 | 80.2 | 73.0 | 56.0 | 61.7 | 2070.2 | 43.9 | 78.6 | 656 |
| gpt-4-1106-preview | 77.0 | 74.4 | 72.3 | 49.7 | 53.8 | 1771.5 | 46.5 | 75.9 | 516 |
| InternVL-Chat-V1.5 | 82.3 | 80.7 | 75.2 | 57.1 | 46.8 | 2189.6 | 47.4 | 80.6 | 720 |
| LLaVA-Next-Yi-34B | 81.1 | 79.0 | 75.7 | 51.6 | 48.8 | 2050.2 | 34.8 | 78.9 | 574 |
| Step-1V | 80.7 | 79.9 | 70.3 | 50.0 | 49.9 | 2206.4 | 48.4 | 79.2 | 625 |
| MiniCPM-Llama3-V2.5 | 77.6 | 73.8 | 72.3 | 51.8 | 45.8 | 2024.6 | 42.4 | 78.4 | 725 |
| Qwen-VL-Max | 77.6 | 75.7 | 72.7 | 49.5 | 52.0 | 2281.7 | 41.2 | 75.7 | 684 |
| Gemini 1.0 Pro | 73.6 | 74.3 | 70.7 | 38.6 | 49.0 | 2148.9 | 45.7 | 72.9 | 680 |
| Claude 3 Opus | 63.3 | 59.2 | 64.0 | 45.7 | 54.9 | 1586.8 | 37.8 | 70.6 | 694 |
| GLM-4V-9B | 81.1 | 79.4 | 76.8 | 58.7 | 47.2 | 2163.8 | 46.6 | 81.1 | 786 |
硬件配置和系统要求,请查看这里。
使用 transformers 后端进行推理:
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
device = "cuda"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat", trust_remote_code=True)
query = "你好"
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template([{"role": "user", "content": query}],
add_generation_prompt=True,
tokenize=True,
return_tensors="pt",
return_dict=True
)
inputs = inputs.to(device)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
trust_remote_code=True
).to(device).eval()
gen_kwargs = {"max_length": 2500, "do_sample": True, "top_k": 1}
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, **gen_kwargs)
outputs = outputs[:, inputs['input_ids'].shape[1]:]
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True))使用 vLLM 后端进行推理:
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
# GLM-4-9B-Chat-1M
# max_model_len, tp_size = 1048576, 4
# 如果遇见 OOM 现象,建议减少max_model_len,或者增加tp_size
max_model_len, tp_size = 131072, 1
model_name = "THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat"
prompt = [{"role": "user", "content": "你好"}]
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name, trust_remote_code=True)
llm = LLM(
model=model_name,
tensor_parallel_size=tp_size,
max_model_len=max_model_len,
trust_remote_code=True,
enforce_eager=True,
# GLM-4-9B-Chat-1M 如果遇见 OOM 现象,建议开启下述参数
# enable_chunked_prefill=True,
# max_num_batched_tokens=8192
)
stop_token_ids = [151329, 151336, 151338]
sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.95, max_tokens=1024, stop_token_ids=stop_token_ids)
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(prompt, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
outputs = llm.generate(prompts=inputs, sampling_params=sampling_params)
print(outputs[0].outputs[0].text)使用 transformers 后端进行推理:
import torch
from PIL import Image
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
device = "cuda"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("THUDM/glm-4v-9b", trust_remote_code=True)
query = '描述这张图片'
image = Image.open("your image").convert('RGB')
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template([{"role": "user", "image": image, "content": query}],
add_generation_prompt=True, tokenize=True, return_tensors="pt",
return_dict=True) # chat mode
inputs = inputs.to(device)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"THUDM/glm-4v-9b",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
trust_remote_code=True
).to(device).eval()
gen_kwargs = {"max_length": 2500, "do_sample": True, "top_k": 1}
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, **gen_kwargs)
outputs = outputs[:, inputs['input_ids'].shape[1]:]
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))注意: GLM-4V-9B 暂不支持使用 vLLM 方式调用。
如果你想更进一步了解 GLM-4-9B 系列开源模型,本开源仓库通过以下内容为开发者提供基础的 GLM-4-9B的使用和开发代码
-
basic_demo: 在这里包含了
- 使用 transformers 和 vLLM 后端的交互代码
- OpenAI API 后端交互代码
- Batch 推理代码
-
composite_demo: 在这里包含了
- GLM-4-9B-Chat 以及 GLM-4V-9B 开源模型的完整功能演示代码,包含了 All Tools 能力、长文档解读和多模态能力的展示。
-
fintune_demo: 在这里包含了
- PEFT (LORA, P-Tuning) 微调代码
- SFT 微调代码
- LLaMA-Factory: 高效开源微调框架,已支持 GLM-4-9B-Chat 语言模型微调。
- SWIFT: 魔搭社区的大模型/多模态大模型训练框架,已支持 GLM4-9B-Chat/GLM4v-9B-Chat 模型微调。
- Xorbits Inference: 性能强大且功能全面的分布式推理框架,轻松一键部署你自己的模型或内置的前沿开源模型。
- self-llm: Datawhale 团队的提供的 GLM-4-9B 系列模型使用教程。
-
GLM-4 模型的权重的使用则需要遵循 模型协议。
-
本开源仓库的代码则遵循 Apache 2.0 协议。
请您严格遵循开源协议。
如果你觉得我们的工作有帮助的话,请考虑引用下列论文。
@inproceedings{zeng2022glm,
title={{GLM-130B:} An Open Bilingual Pre-trained Model},
author={Zeng, Aohan and Liu, Xiao and Du, Zhengxiao and Wang, Zihan and Lai, Hanyu and Ding, Ming and Yang, Zhuoyi and Xu, Yifan and Zheng, Wendi and Xia, Xiao and others},
booktitle={The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations,
{ICLR} 2023, Kigali, Rwanda, May 1-5, 2023},
year= {2023},
}
@inproceedings{du2022glm,
title={GLM: General Language Model Pretraining with Autoregressive Blank Infilling},
author={Du, Zhengxiao and Qian, Yujie and Liu, Xiao and Ding, Ming and Qiu, Jiezhong and Yang, Zhilin and Tang, Jie},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)},
pages={320--335},
year={2022}
}
@misc{wang2023cogvlm,
title={CogVLM: Visual Expert for Pretrained Language Models},
author={Weihan Wang and Qingsong Lv and Wenmeng Yu and Wenyi Hong and Ji Qi and Yan Wang and Junhui Ji and Zhuoyi Yang and Lei Zhao and Xixuan Song and Jiazheng Xu and Bin Xu and Juanzi Li and Yuxiao Dong and Ming Ding and Jie Tang},
year={2023},
eprint={2311.03079},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}