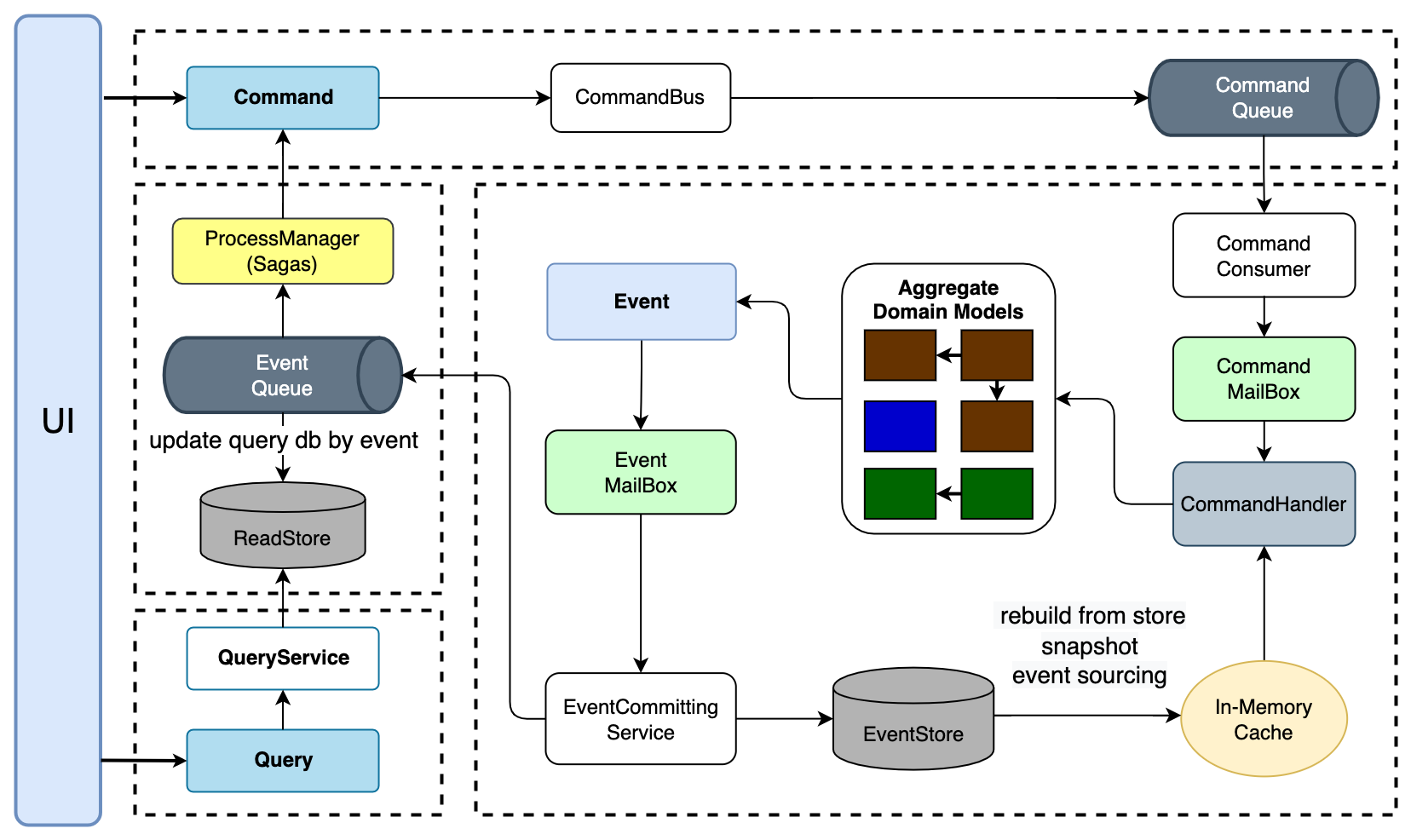
enode是基于JVM平台,采用Domain Driven Design**落地的一个Open Source应用框架,主要服务于云原生和微服务场景。
基于【DDD】【CQRS】【ES】【EDA】【In-Memory】架构风格,实现了CQRS架构面临的大部分技术问题,让开发者可以专注于业务逻辑和业务流程的开发,而无需关心纯技术问题。
- 一个命令一次只能修改一个聚合根
- 聚合间只能通过领域消息交互
- 聚合内强一致性
- 聚合间最终一致性
- 编排(
Choreography) 参与者(子事务)之间的调用、分配、决策和排序,通过交换事件进行进行。是一种去中心化的模式,参与者之间通过消息机制进行沟通,通过监听器的方式监听其他参与者发出的消息,从而执行后续的逻辑处理。
enode中使用的就是这种模式
- 控制(
Orchestration) 提供一个控制类,方便参与者之间的协调工作。事务执行的命令从控制类发起,按照逻辑顺序请求Saga的参与者,从参与者那里接受到反馈以后,控制类在发起向其他参与者的调用。所有Saga的参与者都围绕这个控制类进行沟通和协调工作。
Apache ServiceComb使用的是这种模式
- 实现
CQRS架构,解决CQRS架构的C端的高并发写的问题,以及CQ两端数据同步的顺序性保证和幂等性,支持C端完成后立即返回Command的结果,也支持CQ两端都完成后才返回Command的结果 - 聚合根常驻内存(
In-Memory Domain Model),设计上尽可能的避免了聚合根重建,可以完全以OO的方式来设计实现聚合根,不必为ORM的阻抗失衡而烦恼 - 基于聚合根
ID+ 事件版本号的唯一索引,实现聚合根的乐观并发控制 - 通过聚合根
ID对命令或事件进行路由,聚合根的处理基于Actor**,做到最小的并发冲突、最大的并行处理,Group Commit Domain event - 架构层面严格规范了开发人员该如何写代码,和
DDD开发紧密结合,严格遵守聚合内强一致性、聚合之间最终一致性的原则 - 先进的
Saga机制,以事件驱动的流程管理器(Process Manager)的方式支持一个用户操作跨多个聚合根的业务场景,如订单处理,从而避免分布式事务的使用 - 基于
ES(Event Sourcing)的**持久化C端的聚合根的状态,让C端的数据持久化变得通用化,具有一切ES的优点 - 在设计上完全与IoC容器解耦,同时保留了扩展性,目前适配了SpringBoot
- 通过基于分布式消息队列横向扩展的方式实现系统的可伸缩性(基于队列的动态扩容/缩容),接口抽象极简,只要求最基础的队列能力,目前适配了
Kafka、RocketMQ(ONS)、Pulsar - EventStore内置适配了
JDBC、MySQL、PostgreSQL、MongoDB存储,可针对性实现对应扩展 - 框架完全采用响应式编程理念,在
db层面使用了异步驱动,同时集成了kotlin coroutine
- 可参考samples模块中的例子
目前基于enode开发的项目 conference
不管是DDD也好,CQRS架构也好,虽然都做到了让领域对象不仅有状态,而且有行为,但还不够彻底。因为对象的行为总是“被调用”的。因为贫血模型的情况下,对象是提供了数据让别人去操作或者说被别人使用;而充血模型的情况下,对象则是提供了数据和行为,但还是让别人去操作或者说被别人使用。
真正的面向对象编程中的对象应该是一个”活“的具有主观能动性的存在于内存中的客观存在,它们不仅有状态而且还有自主行为。
- 对象的状态可以表现出来被别人看到,但是必须是只读的,没有人可以直接去修改一个对象的状态,它的状态必须是由它自己的行为导致自己的状态的改变。
- 对象的行为就是对象所具有的某种功能。对象的行为本质上应该是对某个消息的主动响应,这里强调的是主动,就是说对象的行为不可以被别人使用,而只能自己主动的去表现出该行为。
enode在使用便利性了做了很多尝试和努力,而且针对消息队列和EventStore的实现对开发者都是开放的,同时和Spring高度集成,开箱即用。
新增@EnableEnode注解,可自动配置Bean,简化了接入方式。
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEnode(value = "org.enodeframework.tests")
@ComponentScan(value = "org.enodeframework.tests")
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}如果需要使用RokcetMQ和ONS的tag功能,相应的配置spring.enode.mq.tag.*属性即可:
# enode eventstore (memory, mysql, tidb, pg, mongo)
spring.enode.eventstore=mongo
# enode messagequeue (kafka, pulsar, rocketmq, ons)
spring.enode.mq=kafka
spring.enode.mq.topic.command=EnodeBankCommandTopic
spring.enode.mq.topic.event=EnodeBankEventTopic如果把生成者和消费者配置在一个config文件中,这里会产生存在一个循环依赖,为了避免这种情况,建议分开两个文件配置
@Bean
public ProducerFactory<String, String> producerFactory() {
Map<String, Object> props = new HashMap<>();
props.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, Constants.KAFKA_SERVER);
props.put(ProducerConfig.RETRIES_CONFIG, 1);
props.put(ProducerConfig.BATCH_SIZE_CONFIG, 16384);
props.put(ProducerConfig.LINGER_MS_CONFIG, 1);
props.put(ProducerConfig.BUFFER_MEMORY_CONFIG, 1024000);
props.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class);
props.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class);
return new DefaultKafkaProducerFactory<>(props);
}
@Bean
public KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate(ProducerFactory<String, String> producerFactory) {
return new KafkaTemplate<>(producerFactory);
}@Value("${spring.enode.mq.topic.command}")
private String commandTopic;
@Value("${spring.enode.mq.topic.event}")
private String eventTopic;
@Bean
public ConsumerFactory<String, String> consumerFactory() {
Map<String, Object> props = new HashMap<>();
props.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, Constants.KAFKA_SERVER);
props.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, Constants.DEFAULT_PRODUCER_GROUP);
props.put(ConsumerConfig.ENABLE_AUTO_COMMIT_CONFIG, false);
props.put(ConsumerConfig.AUTO_COMMIT_INTERVAL_MS_CONFIG, "100");
props.put(ConsumerConfig.SESSION_TIMEOUT_MS_CONFIG, "15000");
props.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class);
props.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class);
return new DefaultKafkaConsumerFactory<>(props);
}
@Bean
public KafkaMessageListenerContainer<String, String> commandListenerContainer(KafkaMessageListener commandListener, ConsumerFactory<String, String> consumerFactory) {
ContainerProperties properties = new ContainerProperties(commandTopic);
properties.setGroupId(Constants.DEFAULT_CONSUMER_GROUP);
properties.setMessageListener(commandListener);
properties.setMissingTopicsFatal(false);
return new KafkaMessageListenerContainer<>(consumerFactory, properties);
}
@Bean
public KafkaMessageListenerContainer<String, String> domainEventListenerContainer(KafkaMessageListener domainEventListener, ConsumerFactory<String, String> consumerFactory) {
ContainerProperties properties = new ContainerProperties(eventTopic);
properties.setGroupId(Constants.DEFAULT_PRODUCER_GROUP);
properties.setMessageListener(domainEventListener);
properties.setMissingTopicsFatal(false);
properties.setAckMode(ContainerProperties.AckMode.MANUAL);
return new KafkaMessageListenerContainer<>(consumerFactory, properties);
}public class DbConfig {
@Bean("enodeMongoClient")
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.enode", name = "eventstore", havingValue = "mongo")
public MongoClient mongoClient(Vertx vertx) {
return MongoClient.create(vertx, new JsonObject().put("db_name", "test"));
}
@Bean("enodeMySQLPool")
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.enode", name = "eventstore", havingValue = "mysql")
public MySQLPool enodeMySQLPool() {
MySQLConnectOptions connectOptions = MySQLConnectOptions.fromUri(jdbcUrl.replaceAll("jdbc:", ""))
.setUser(username)
.setPassword(password);
PoolOptions poolOptions = new PoolOptions()
.setMaxSize(5);
return MySQLPool.pool(connectOptions, poolOptions);
}
@Bean("enodePgPool")
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.enode", name = "eventstore", havingValue = "pg")
public PgPool pgPool() {
PgConnectOptions connectOptions = PgConnectOptions.fromUri(pgJdbcUrl.replaceAll("jdbc:", ""))
.setUser(pgUsername)
.setPassword(pgPassword);
PoolOptions poolOptions = new PoolOptions()
.setMaxSize(5);
return PgPool.pool(connectOptions, poolOptions);
}
@Bean("enodeMySQLDataSource")
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.enode", name = "eventstore", havingValue = "jdbc-mysql")
public DataSource enodeMySQLDataSource() {
HikariDataSource dataSource = new HikariDataSource();
dataSource.setJdbcUrl(jdbcUrl);
dataSource.setUsername(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
dataSource.setDriverClassName(com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver.class.getName());
return dataSource;
}
@Bean("enodePgDataSource")
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.enode", name = "eventstore", havingValue = "jdbc-pg")
public DataSource enodePgDataSource() {
HikariDataSource dataSource = new HikariDataSource();
dataSource.setJdbcUrl(pgJdbcUrl);
dataSource.setUsername(pgUsername);
dataSource.setPassword(pgPassword);
dataSource.setDriverClassName(org.postgresql.Driver.class.getName());
return dataSource;
}
}event_stream 表中存储的是每个聚合根和对应版本的领域事件历史记录
published_version 表中存储的每个聚合根当前的消费进度(版本)
注意有两个唯一索引,这个是实现幂等的常用思路,因为我们认为大部分情况下不会出现重复写问题
CREATE TABLE event_stream (
id BIGINT AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL,
aggregate_root_type_name VARCHAR(256) NOT NULL,
aggregate_root_id VARCHAR(36) NOT NULL,
version INT NOT NULL,
command_id VARCHAR(36) NOT NULL,
gmt_create DATETIME NOT NULL,
events MEDIUMTEXT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id),
UNIQUE KEY uk_aggregate_root_id_version (aggregate_root_id, version),
UNIQUE KEY uk_aggregate_root_id_command_id (aggregate_root_id, command_id)
) ENGINE = InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8mb4;
CREATE TABLE published_version (
id BIGINT AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL,
processor_name VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL,
aggregate_root_type_name VARCHAR(256) NOT NULL,
aggregate_root_id VARCHAR(36) NOT NULL,
version INT NOT NULL,
gmt_create DATETIME NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id),
UNIQUE KEY uk_processor_name_aggregate_root_id (processor_name, aggregate_root_id)
) ENGINE = InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8mb4;CREATE TABLE event_stream (
id bigserial,
aggregate_root_type_name varchar(256),
aggregate_root_id varchar(36),
version integer,
command_id varchar(36),
gmt_create date,
events text,
PRIMARY KEY (id),
CONSTRAINT uk_aggregate_root_id_version UNIQUE (aggregate_root_id, version),
CONSTRAINT uk_aggregate_root_id_command_id UNIQUE (aggregate_root_id, command_id)
);
CREATE TABLE published_version (
id bigserial,
processor_name varchar(128),
aggregate_root_type_name varchar(256),
aggregate_root_id varchar(36),
version integer,
gmt_create date,
PRIMARY KEY (id),
CONSTRAINT uk_processor_name_aggregate_root_id UNIQUE (processor_name, aggregate_root_id)
);db.event_stream.createIndex({aggregateRootId:1,commandId:1},{unique:true})
db.event_stream.createIndex({aggregateRootId:1,version:1},{unique:true})
db.published_version.createIndex({processorName:1,aggregateRootId:1},{unique:true})新增了三个注解,系统限定了只扫描@Command和@Event标识的类,执行的方法上需要添加@Subscribe注解:
@Command@Event@Subscribe
启动时会扫描包路径下的注解,注册成Spring Bean,和@Component作用相同。
命令可以被拒绝。
事件已经发生。
这可能是最重要的原因。在事件驱动的体系结构中,毫无疑问,引发的事件代表了已发生的事情。
现在,因为命令是我们想要发生的事情,并且事件已经发生了,所以当我们命名这些事情时,我们应该使用不同的词,命令一般是名词,事件一般是过去分词
举个例子,拿订单系统来说,我们有个外部支付系统的依赖。
当用户在支付系统完成支付后,支付系统会向订单系统发送一个Command,MarkOrderAsPayed(标记订单已支付),订单在处理这个Command时,获取当前订单,调用订单的标记已支付(行为),产生了OrderPayed(订单已支付)事件。
我们可以看到,命令通常由系统外调用,事件是由处理程序和系统中的其他代码提供的。
这是他们分开表示的另一个原因。概念清晰度。
命令和事件都是消息。但它们实际上是独立的概念,应该明确地对概念进行建模。
这两者我理解都是符合人类思维的,首先是基于大脑接收到感知到的消息(Event)产生一个想法【意图】(Command),然后如何实现这个想法,思考的维度是过程式的,在实现的过程中,会产生一些事件消息,这个消息又会影响到大脑。如此循环往复
-
目前enode函数调用的实现是放在
kotlin coroutine中来执行的,这里涉及到实际执行的任务类型,针对计算密集型和IO密集型的任务,目前没有做可定制化的配置,后续的版本会考虑加上, 使用也很简单,@Subscribe方法体加上suspend标记即可。 -
针对
Java异步编程做了深度优化,支持CommandHandler和EventHandler中定义CompletableFuture返回值,阻塞调用封装在协程中,避免使用#join() #get()等阻塞代码,同时也支持kotlin suspend
@Command
class ChangeNoteTitleCommandHandler {
@Subscribe
suspend fun handleAsync(context: CommandContext, command: ChangeNoteTitleCommand) {
val note = context.get(command.getAggregateRootId(), true, Note::class.java)
note.changeTitle(command.title)
}
}@Subscribe
public CompletableFuture<BankAccount> handleAsync(CommandContext context, AddTransactionPreparationCommand command) {
CompletableFuture<BankAccount> future = context.getAsync(command.getAggregateRootId(), BankAccount.class);
future.thenAccept(bankAccount -> {
bankAccount.addTransactionPreparation(command.transactionId, command.transactionType, command.preparationType, command.amount);
});
return future;
}发送命令消息:
CompletableFuture<CommandResult> future = commandService.executeAsync(createNoteCommand, CommandReturnType.EventHandled);命令处理:
/**
* 银行账户相关命令处理
* CommandHandler<CreateAccountCommand>, //开户
* CommandAsyncHandler<ValidateAccountCommand>, //验证账户是否合法
* CommandHandler<AddTransactionPreparationCommand>, //添加预操作
* CommandHandler<CommitTransactionPreparationCommand> //提交预操作
*/
@Command
public class BankAccountCommandHandler {
/**
* 开户
*/
@Subscribe
public void handleAsync(CommandContext context, CreateAccountCommand command) {
context.addAsync(new BankAccount(command.getAggregateRootId(), command.owner));
}
/**
* 添加预操作
*/
@Subscribe
public CompletableFuture<BankAccount> handleAsync(CommandContext context, AddTransactionPreparationCommand command) {
CompletableFuture<BankAccount> future = context.getAsync(command.getAggregateRootId(), BankAccount.class);
future.thenAccept(bankAccount -> {
bankAccount.addTransactionPreparation(command.transactionId, command.transactionType, command.preparationType, command.amount);
});
return future;
}
/**
* 验证账户是否合法
*/
@Subscribe
public void handleAsync(CommandContext context, ValidateAccountCommand command) {
ApplicationMessage applicationMessage = new AccountValidatePassedMessage(command.getAggregateRootId(), command.transactionId);
//此处应该会调用外部接口验证账号是否合法,这里仅仅简单通过账号是否以INVALID字符串开头来判断是否合法;根据账号的合法性,返回不同的应用层消息
if (command.getAggregateRootId().startsWith("INVALID")) {
applicationMessage = new AccountValidateFailedMessage(command.getAggregateRootId(), command.transactionId, "账户不合法.");
}
context.setApplicationMessage(applicationMessage);
}
/**
* 提交预操作
*/
@Subscribe
public CompletableFuture<BankAccount> handleAsync(CommandContext context, CommitTransactionPreparationCommand command) {
CompletableFuture<BankAccount> future = context.getAsync(command.getAggregateRootId(), BankAccount.class);
future.thenAccept(bankAccount -> {
bankAccount.commitTransactionPreparation(command.transactionId);
});
return future;
}
}领域事件和Sagas处理逻辑:
/**
* 银行存款交易流程管理器,用于协调银行存款交易流程中各个参与者聚合根之间的消息交互
* IMessageHandler<DepositTransactionStartedEvent>, //存款交易已开始
* IMessageHandler<DepositTransactionPreparationCompletedEvent>, //存款交易已提交
* IMessageHandler<TransactionPreparationAddedEvent>, //账户预操作已添加
* IMessageHandler<TransactionPreparationCommittedEvent> //账户预操作已提交
*/
@Event
public class DepositTransactionProcessManager {
@Resource
private CommandBus commandBus;
@Subscribe
public CompletableFuture<Boolean> handleAsync(DepositTransactionStartedEvent evnt) {
AddTransactionPreparationCommand command = new AddTransactionPreparationCommand(evnt.accountId, evnt.getAggregateRootId(), TransactionType.DEPOSIT_TRANSACTION, PreparationType.CREDIT_PREPARATION, evnt.amount);
command.setId(evnt.getId());
return commandBus.sendAsync(command);
}
@Subscribe
public CompletableFuture<Boolean> handleAsync(TransactionPreparationAddedEvent evnt) {
if (evnt.transactionPreparation.transactionType == TransactionType.DEPOSIT_TRANSACTION && evnt.transactionPreparation.preparationType == PreparationType.CREDIT_PREPARATION) {
ConfirmDepositPreparationCommand command = new ConfirmDepositPreparationCommand(evnt.transactionPreparation.transactionId);
command.setId(evnt.getId());
return commandBus.sendAsync(command);
}
return Task.completedTask;
}
@Subscribe
public CompletableFuture<Boolean> handleAsync(DepositTransactionPreparationCompletedEvent evnt) {
CommitTransactionPreparationCommand command = new CommitTransactionPreparationCommand(evnt.accountId, evnt.getAggregateRootId());
command.setId(evnt.getId());
return (commandBus.sendAsync(command));
}
@Subscribe
public CompletableFuture<Boolean> handleAsync(TransactionPreparationCommittedEvent evnt) {
if (evnt.transactionPreparation.transactionType == TransactionType.DEPOSIT_TRANSACTION && evnt.transactionPreparation.preparationType == PreparationType.CREDIT_PREPARATION) {
ConfirmDepositCommand command = new ConfirmDepositCommand(evnt.transactionPreparation.transactionId);
command.setId(evnt.getId());
return (commandBus.sendAsync(command));
}
return Task.completedTask;
}
}目前支持三种
bin/pulsar standalone
https://kafka.apache.org/quickstart
bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh config/zookeeper.properties
bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server.propertieshttps://rocketmq.apache.org/docs/quick-start/
启动RocketMQ服务:
nohup sh bin/mqnamesrv &
nohup sh bin/mqbroker -n 127.0.0.1:9876 &CQRS架构中的Command端应用
主要用来接收
Command,将Command发送到消息队列。
- 消费
Command队列中的消息的服务
将领域事件消息持久化才算是
Command执行成功,Command执行的结果可以通过发送命令时注册的监听器获取。
- 领域事件处理服务
事件可能会多次投递,所以需要消费端逻辑保证幂等处理,这里框架无法完成支持,需要开发者自己实现。
转账的业务场景,涉及了三个聚合根:
- 银行存款交易记录,表示一笔银行存款交易
- 银行转账交易记录,表示一笔银行内账户之间的转账交易
- 银行账户聚合根,封装银行账户余额变动的数据一致性
- 接入了
OpenApi 3.0,打开swagger-ui即可。
http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
聚合根需要定义一个无参构造函数,因为聚合根初始化时使用了:
aggregateRootType.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();因为服务的现状大都是服务提供者少,通常只有几台机器,而服务的消费者多,可能整个网站都在访问该服务。
在我们的这个场景里面,command-web只需要很少的机器就能满足前端大量的请求,command-consumer和event-consumer的机器相对较多些。
如果采用常规的“单请求单连接”的方式,服务提供者很容易就被压跨,通过单一连接,保证单一消费者不会压死提供者,长连接,减少连接握手验证等,并使用异步IO,复用线程池,防止C10K问题。
CommandHandler是为了操作内存中的聚合根的,所以不会有异步操作,但后来CommandHandler的Handle方法也设计为了handleAsync了,目的是为了异步到底,否则异步链路中断的话,异步就没效果了CommandAsyncHandler是为了让开发者调用外部系统的接口的,也就是访问外部IO,所以用了`Async
CommandHandler,CommandAsyncHandler这两个接口是用于不同的业务场景,CommandHandler.handleAsync方法执行完成后,框架要从context中获取当前修改的聚合根的领域事件,然后去提交。而CommandAsyncHandler.handleAsync方法执行完成后,不会有这个逻辑,而是看一下handleAsync方法执行的异步消息结果是什么,也就是IApplicationMessage。 目前已经删除了CommandAsyncHandler,统一使用CommandHandler来处理,异步结果会放在context中,通过访问#setResult设置
sendAsync只关注发送消息的结果
executeAsync发送消息的同时,关注命令的执行结果,返回的时机如下:
CommandReturnType.CommandExecuted:Command执行完成,Event发布成功后返回结果CommandReturnType.EventHandled:Event处理完成后才返回结果
event的订阅者可能有很多个,所以enode只要求有一个订阅者处理完事件后发送结果给发送命令的人即可,通过defaultDomainEventMessageHandler中sendEventHandledMessage参数来设置是否发送,最终来决定由哪个订阅者来发送命令处理结果。