- Unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing.
It provides high-level APIs in Java, Scala, Python and R, and an optimized engine that supports general execution graphs
-
MLLib
-
GraphX
-
Spark SQL
-
Structured Streaming
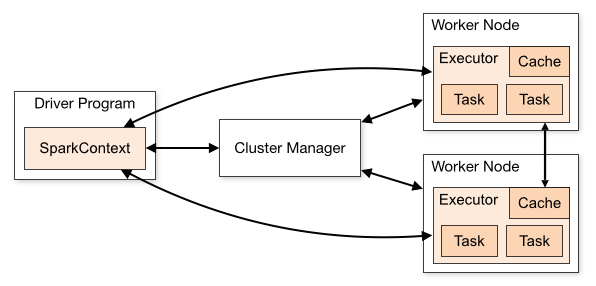
- SparkContext
Spark reads from a file on HDFS, S3 or another filestore, into an established mechanism called SparkContext.
- Resilient Distributed Dataset (RDD)
It represents an immutable collection of elements that can be operated on in parallel.
You can perform transformation, intermedidate steps, actions, or final steps on RDDs.
The result of a given transformation goes into the DAG bug doesn't persist to disk, but the result of an action persists all the data in memory to disk.
- DataFrames
A new abstraction in Spark is DataFrames, which were developed in Spark 2.0 as a companion interface to RDDs. The two are extremely similar, but DataFrames organize data into named columns, similar to Python's pandas. This makes them more user-friendly than RDDs.
SparkSQL also allows users to query DataFrames much like SQL tables in relational data stores.
- DAG
As the RDD and related actions are being created, Spark also created a DAG, or Directed Acyclic Graphic, to visualize the order of operations and the relationship between the operations in the DAG.
-
SparkQL
-
ML
MLLib
-
2x performance improvement on TPC-DS over Spark 2.4, enabled by adaptive query execution, dynamic partition pruning and other optimizations
-
ANSI SQL compliance
-
Significant improvements in pandas APIs, including Python type hints and additional pandas UDFs
-
Better Python error handling, simplifying PySpark exceptions
-
New UI for structured streaming
-
Up to 40x speedups for calling R user-defined functions
- TODO: Twitter streaming