NPHardEval4V serves as a comprehensive benchmark for assessing the reasoning abilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) through the lens of computational complexity classes. This repository contains datasets and experimental procedures designed to evaluate LLMs in various reasoning tasks.
Our benchmark offers several advantages compared with current benchmarks:
- A comprehensive and automatic data generation (transformation) mechnism:
- Data construction grounded in the established computational complexity hierarchy
- Automatic checking mechanisms
- Automatic generation of datapoints
- An authentic focus on visual reasoning, with comparability to textual reasoning
- Complete focus on reasoning while exclude numerical computation
- Disentangle recognition and instruction following from reasoning
- Direct comparison with the NPHardEval Benchmark
conda create --name llm_reason python==3.10
conda activate llm_reason
git clone https://github.com/casmlab/NPHardEval.git
pip install -r requirements.txtPlease set up your API keys in each of the run files. Please don't directly upload your keys to any public repository.
For close source model GPT4V (please add your Openai API key in the file):
cd Close/run_fewtext_figure
python run_gpt4v_BSP.py
For close source model Gemini (please add your Google Gemeni API key in the file) :
cd Close/run_fewtext_figure
python run_gemeni_BSP.py
For all other open source models (please edit which model to run in the file):
cd Open/run
python run_all_models.py
Please also set up your file paths in the run files.
Directory: summary
Here are concise debugging tips for visualization:
- Result JSON Structure: Ensure the output JSON contains a single object or list. Remove any extraneous elements and keep the last element to prevent parsing issues.
- File Naming Convention: Rename result files using the format questionname_modelname_result.json. This aids dict key not found issue.
- Consistent Terminology: Please rename "decision" or "Decision" to "D" throughout the code.
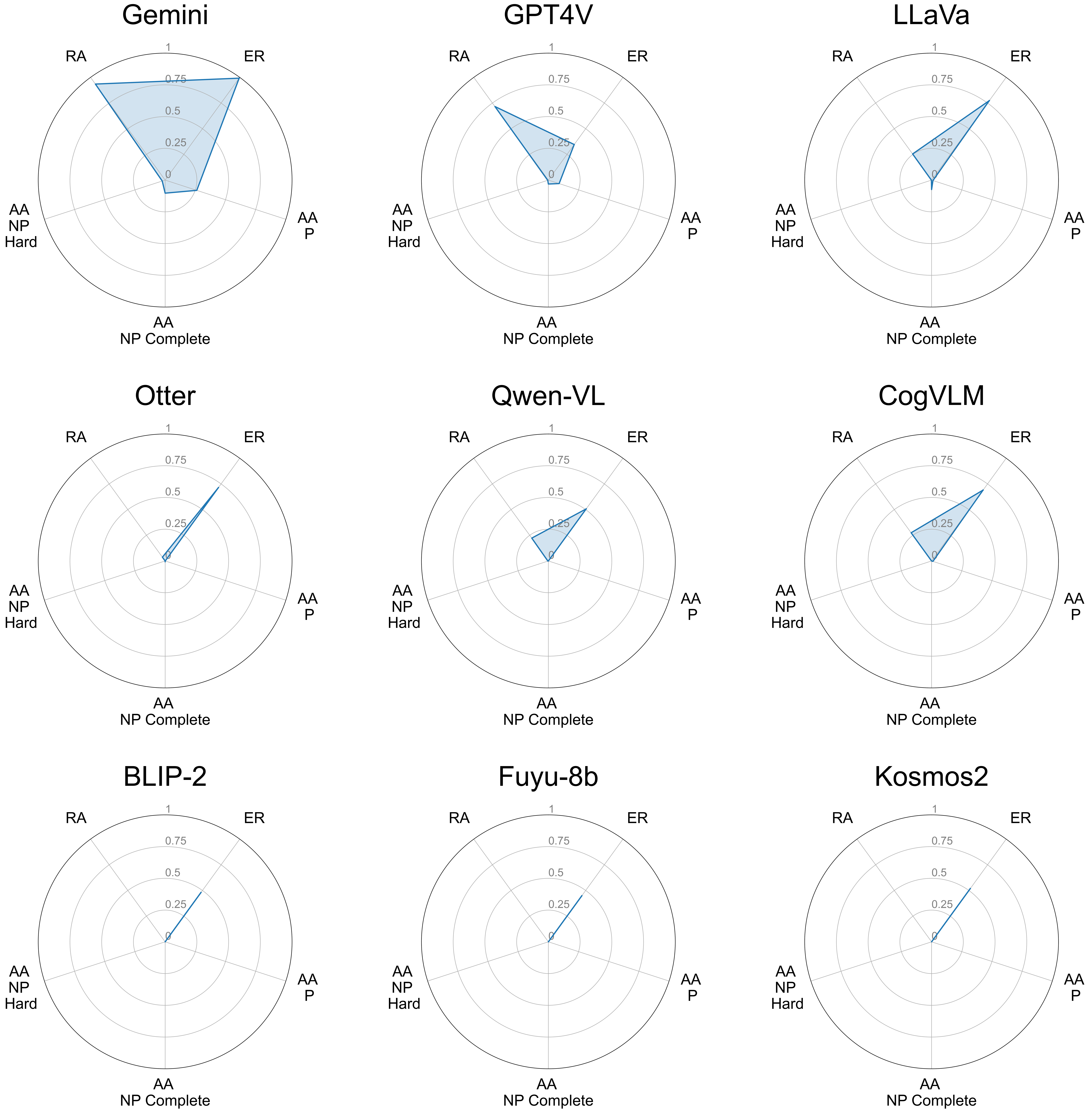
| Model | ER | AA P | AA NP-Complete | AA NP-Hard | RA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gemini | 0.99259 | 0.26801 | 0.10183 | 0.00788 | 0.93489 |
| GPT4V | 0.41296 | 0.08963 | 0.04115 | 0.01026 | 0.71622 |
| LLaVa | 0.77370 | 0.01123 | 0.07457 | 0.00166 | 0.25444 |
| Otter | 0.71444 | 0.00073 | 0.00691 | 0.00000 | 0.03667 |
| Qwen-VL | 0.50704 | 0.00000 | 0.00061 | 0.00384 | 0.22244 |
| CogVLM | 0.69000 | 0.01091 | 0.00000 | 0.00040 | 0.27444 |
| BLIP-2 | 0.48037 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 |
| Fuyu-8b | 0.44852 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 |
| Kosmos2 | 0.51852 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 |
Metrics include Recognition accuracy (RA), Instruction-following effective rate (ER), and aggregated accuracy of reasoning (AA) on polynomial time, NP-complete, and NP-hard problems
- Close and Open Source Models: The comparison between close source and open source MLLMs is quite stark, with close source models exhibiting superior performance in all tasks, irrespective of complexity class.
- Complexity Classes: The reasoning performance are inversely proportional to the complexity of the tasks.
- Task Difficulties: We notice a degradation in performance in correlation with increasing question difficulty.
Directory: Data
The Data directory houses the datasets utilized in our study. Under each sub-folder of the question, there are textual data and a subsub-folder of Images, which provides the corresponding image data. The image data is a direct transformation from the text data, i.e., they are identical in contents while different in modality.
Structure:
$ tree -d Data
Data
├── BSP
├── EDP
├── GCP
├── GCP_Decision
├── KSP
├── MSP
├── SPP
├── TSP
└── TSP_DecisionThe data used is under data directory. You can find the zeroshot/fewshot under the corresponding directory. They are the data used in our report.
Directory: check
Contained within this directory are utility functions crucial for verifying answers provided by the LLMs. These functions are automatically invoked during experiments executed via each of the run files. As the experiment progresses, these utilities rigorously evaluate the responses from LLMs and compile the outcomes in the Results directory. This automated process ensures a comprehensive and objective assessment of the LLM's performance.
-[2024.3.7] 🔥 We release the default version (V0) of NPHardEval4V with data, answer-checking code, and example.
@article{fan2024nphardeval4v,
title={NPHardEval: A Dynamic Reasoning Benchmark of Multimodal Large Language Models},
author={Fan, Lizhou and Hua, Wenyue and Li, Xiang and Zhu, Kaijie and Jin, Mingyu and Li, Lingyao and Ling, Haoyang and Chi, Jinkui and Wang, Jindong and Ma, Xin and Zhang, Yongfeng},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.01777},
year={2024}
}