λλλλλλ\ λλλλλλ\ λλ\ λλ\ λλλλλλλ\
λλ __λλ\ λλ __λλ\ λλλ\ λλλ |λλ __λλ\
λλ / \__|λλ / λλ |λλλλ\ λλλλ |λλ | λλ |
\λλλλλλ\ λλλλλλλλ |λλ\λλ\λλ λλ |λλλλλλλ |
\____λλ\ λλ __λλ |λλ \λλλ λλ |λλ ____/
λλ\ λλ |λλ | λλ |λλ |\λ /λλ |λλ |
\λλλλλλ |λλ | λλ |λλ | \_/ λλ |λλ |
\______/ \__| \__|\__| \__|\__|
serverless pattern generator | local debugging | iam policy builder | console navigation helper | and more
CLI tool that takes your AWS SAM development to the next level
This is the continuation of the now deprecated sam-patterns-cli tool. It has been renamed to Sam Plus (samp) which better reflects the direction of the tool, namely to offer additional developer tooling beyond the realm of sam-cli. Please note that this is not a replacement for sam-cli.
- Installation
- Usage
- samp init - initalises a SAM project based on cookiecutter templates
- samp import - imports a serverless pattern from serverlessland.com into an existing template
- samp invoke - invokes a Lambda function or StepFunctions state machine in your CloudFormation stack
- samp local - test your Lambda functions locally with real events from your AWS account
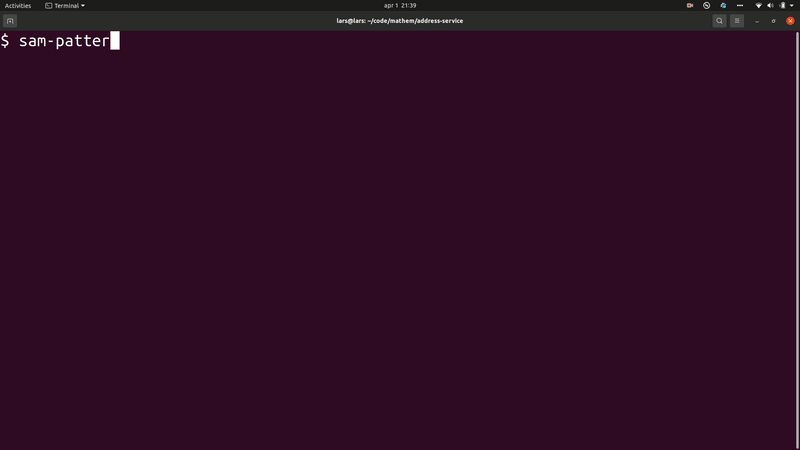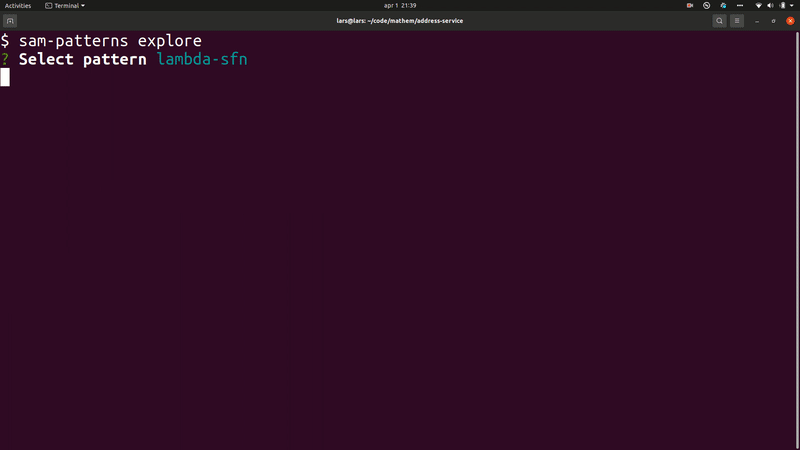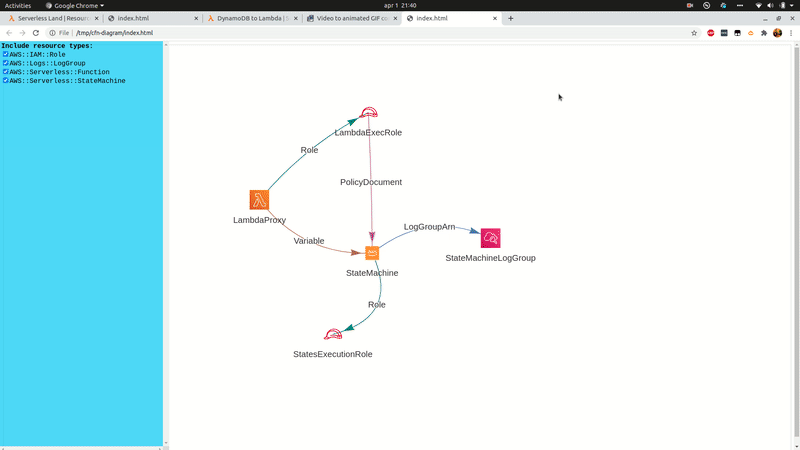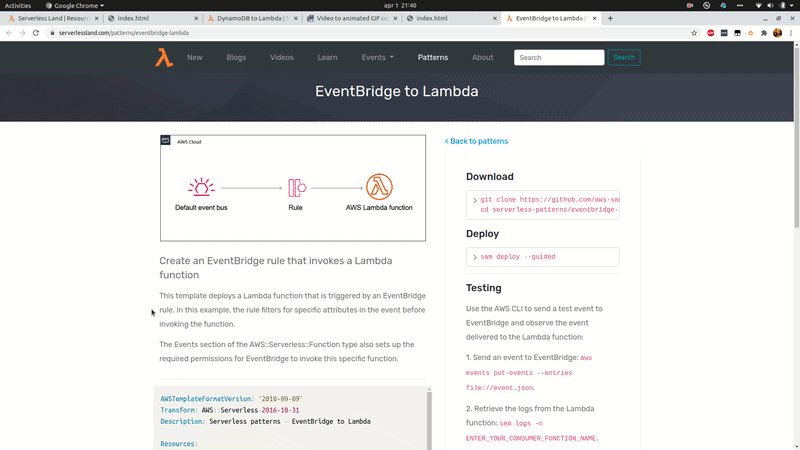
- samp explore - explore patterns on serverlessland.com
- samp console - open the AWS console for a resource in your stack
- samp generate - generate a SAM resources with the help of ChatGPT prompts
- samp describe - describe a SAM resource using ChatGPT
- samp source - add additional sources for init templates and pattern imports
- samp policy - generate IAM policies for your Lambda functions, state machines and IAM roles
- samp return-values - get the return values of a SAM/CloudFormation resource
- samp share - share a serverless pattern with your team or the community
- samp powertools - quickly finds and installs the latest version of AWS Lambda Powertools
- Customise pattern imports using placeholders and property manipulation
- Known issues and limitations
npm install -g samp-cli
Acquire a Github access token from here and either store it in environment variable GITHUB_TOKEN or configure the tool using samp configure --github-token <token> (recommended). This is not strictly required, but if you don't you'll be rate limited to 60 requests per hour. Note that SSH auth is not supported by by the OctoKit SDK.
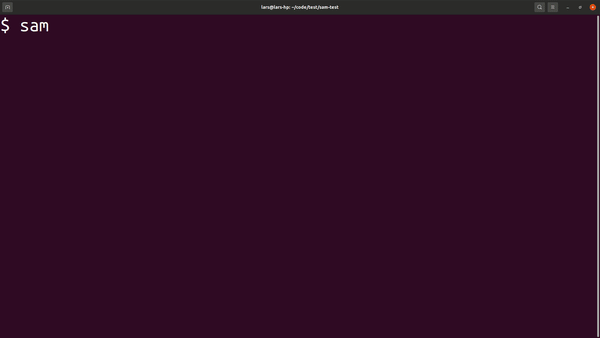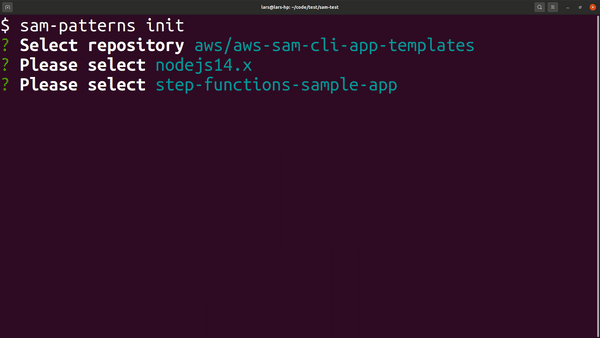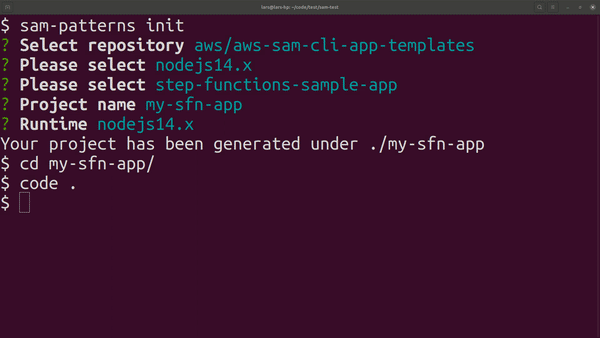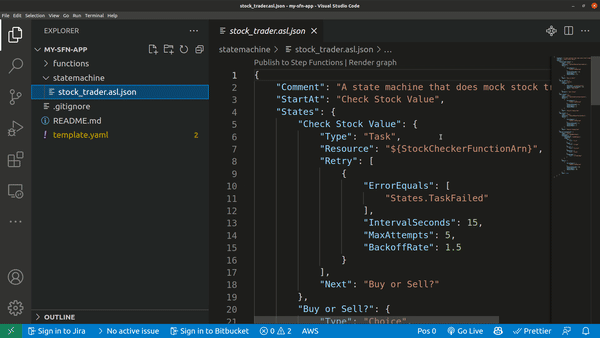
Initialises a SAM project based on a cookiecutter template. By default the tool gives access to the same AWS managed templates that are used by sam-cli.
You can add custom template locations by using the --add-repository flag.
Usage: samp init [options]
Initialises a SAM project from a quick-start template. See https://github.com/aws/aws-sam-cli-app-templates for examples and structure.
Options:
-r, --add-repository GitHub repository where your templates are located (default: false)
-h, --help display help for command
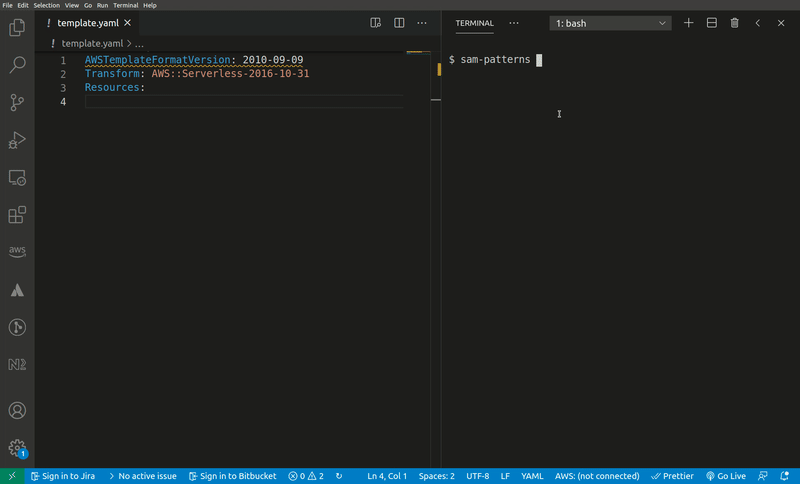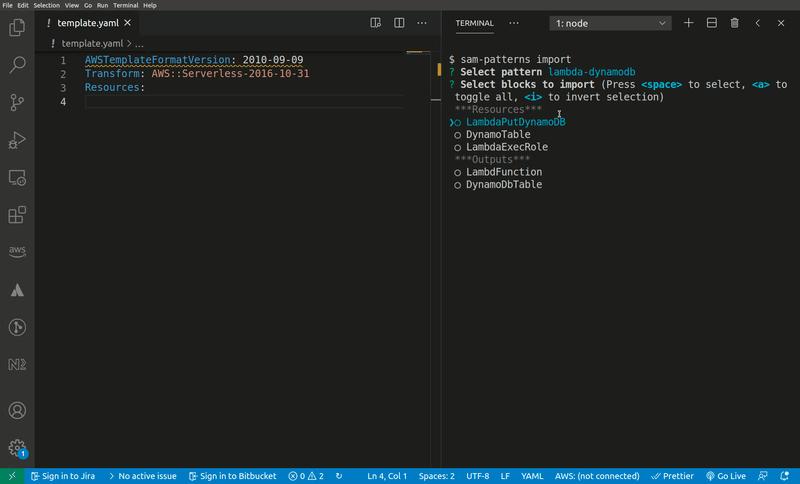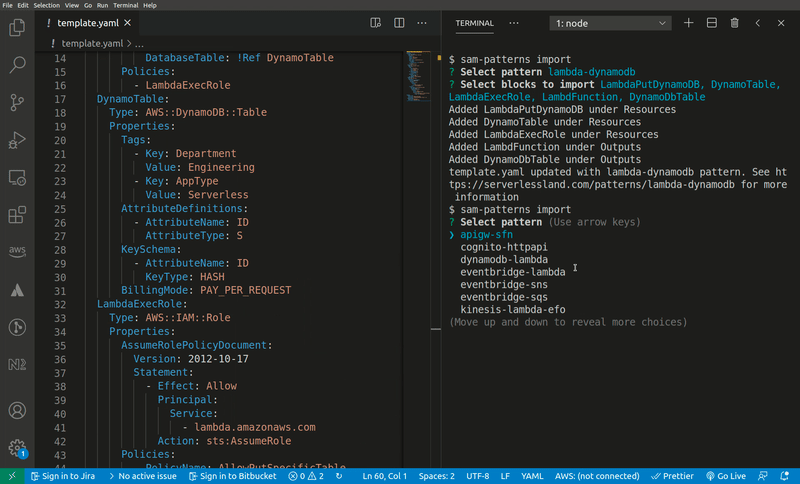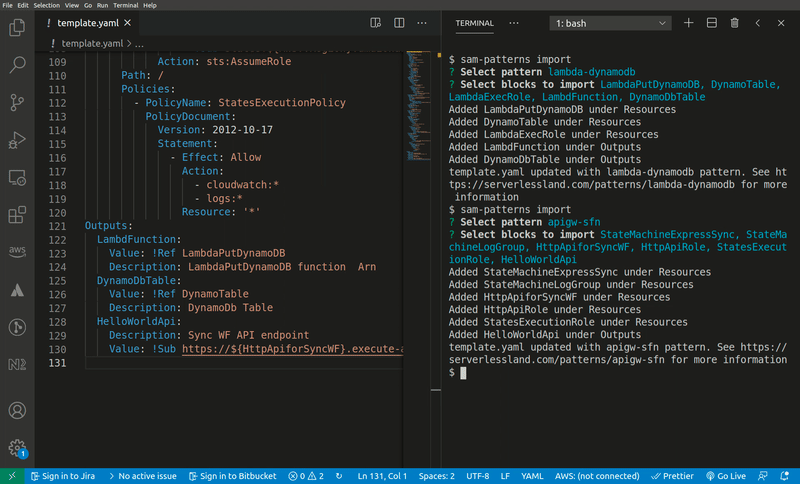
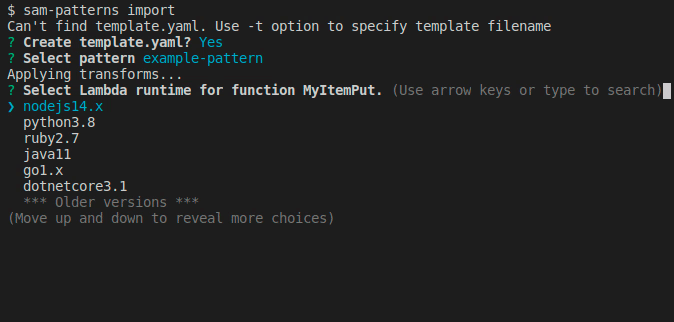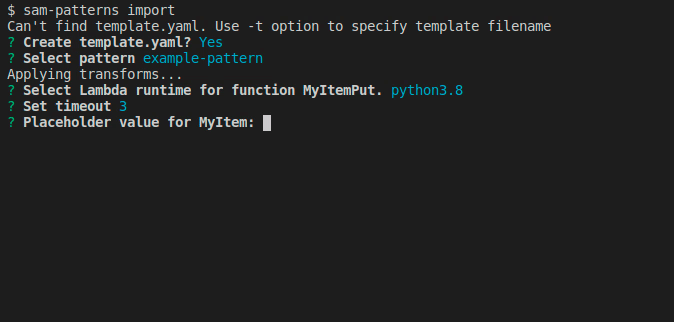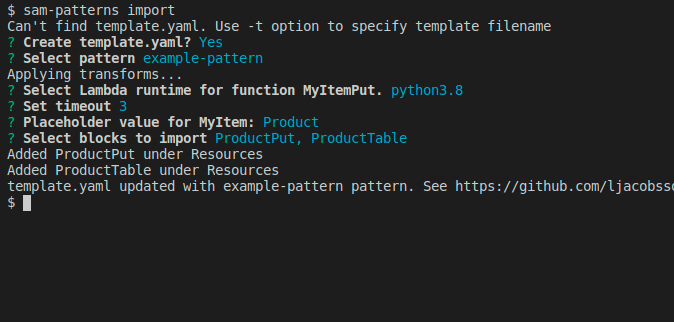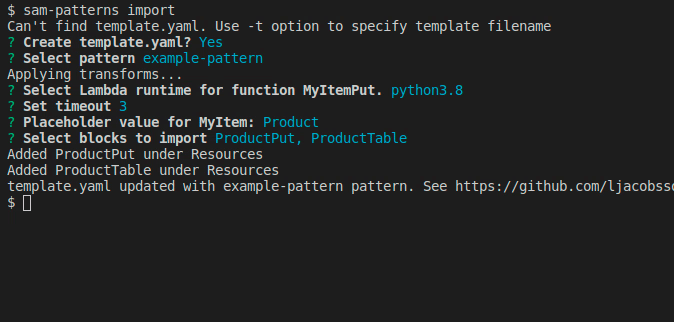
Imports a serverless pattern into an existing template. You can merge one or more resources in the imported pattern with existing resources in your template by adding the --merge flag to, for example, combine sqs-lambda and lambda-dynamodb as one sqs-lambda-dynamodb pattern.
Usage: samp import|i [options]
Imports a pattern from https://github.com/aws-samples/serverless-patterns/
Options:
-t, --template [template] SAM template file (default: "template.yaml")
-m, --merge Merge pattern with existing template resource(s) (default: false)
-a, --asl-format [asl-format] Output format for StepFunctions ASL definitions (YAML or JSON) (default: "YAML")
-f, --source-filter [source-filter] Filter text to match against source collection names. Optional (default: "")
-h, --help display help for command
Invokes a Lambda function or StepFunctions state machine in your CloudFormation stack. If a samconfig.[toml/yaml] file is present, it will use the stack name and region from that file. Otherwise you will have to specify them using the --stack-name and --region flags.
You can pass a variety of inputs to the function / state machine:
- A path to a local JSON file
- JSON string
- Shared Lambda test event. These test events become available for other developers with access to the same AWS account. This command also introduces the same sharable test events for StepFunctions.
- For StepFunctions, you can select to re-run the input from a recent execution from the state machine.
Usage: samp invoke|in [options]
Invokes a Lambda function or a StepFunctions state machine
Options:
-s, --stack-name [stackName] The name of the deployed stack
-r, --resource [resource] The resource (function name or state machine ARN) to invoke. If not specified, you will be prompted to select one
-pl, --payload [payload] The payload to send to the function. Could be stringified JSON, a file path to a JSON file or the name of a shared test event
-l, --latest Invokes the latest request that was sent to the function (default: false)
-p, --profile [profile] AWS profile to use (default: "default")
--region [region] The AWS region to use. Falls back on AWS_REGION environment variable if not specified
-h, --help display help for command
This feature is inspired by and works similarly to SST's Live Lambda Development.
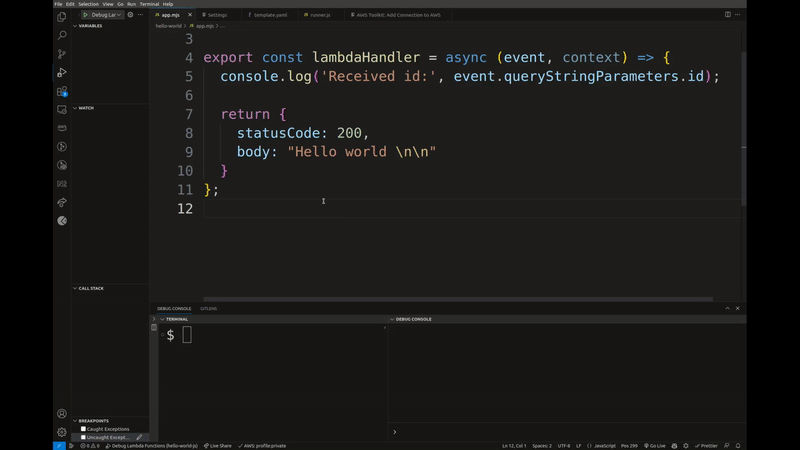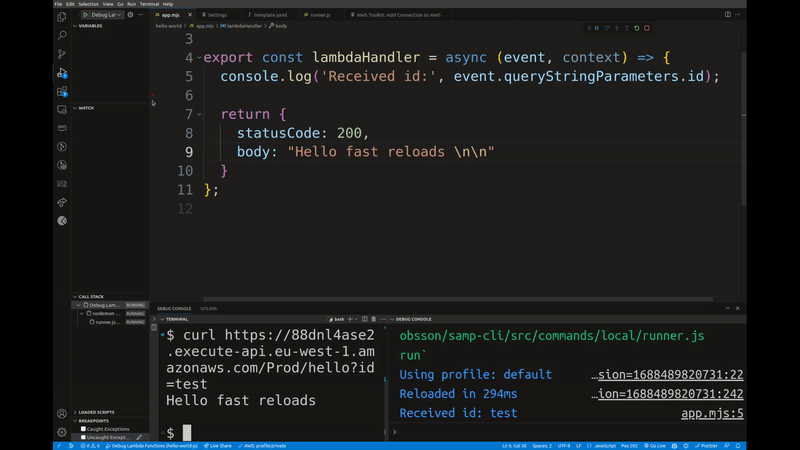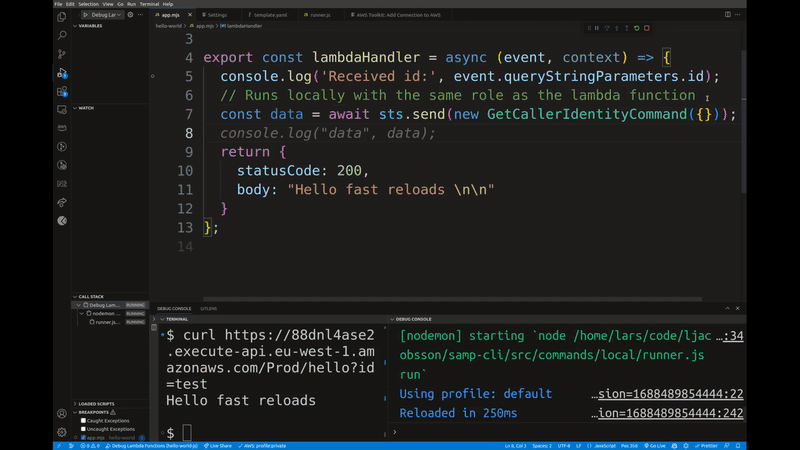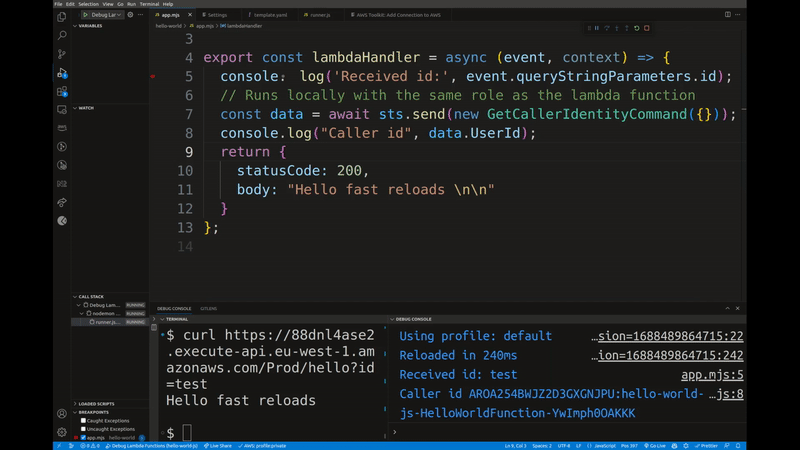
It lets you test your Lambda functions locally with real events from your AWS account. You can step through your code using breakpoints and get sub-second code reloads on changes. If a samconfig.[toml/yaml] file is present, it will use the stack name and region from that file. Otherwise you will have to specify them using the --stack-name and --region flags.
- NOTE #1: this command temporarily replaces your function code in the cloud with a proxy function that relays events to your local machine over AWS IoT (MQTT). Please only use on development stacks. Never use on production functions! *
- NOTE #2: this command does not fully support Lambda layers. If you use layers to bundle your dependencies, you will have to manually install them locally as well. If you use layers to share custom code between functions, create a symlink from
/opt/nodejsto the layer folder in your function folder.
Usage: samp local|l [options]
Sets up a debugging session where the Lambda invocations in the cloud gets executed on your local machine
Options:
-s, --stack-name [stackName] The name of the deployed stack
--force-restore Force restore of the original Lambda code (default: false)
--merge-package-jsons For projects that use one project.json per function subfolder, this merges them into one to enable package resolution whilsh running this command (default: false)
-f, --functions [functions] Select which functions to be part of the debugging session. Comma separated list of logical IDs. (default: "ALL")
-d, --debug Configure debug for vscode. This only needs to be run once per project (default: false)
-p, --profile [profile] AWS profile to use
--region [region] The AWS region to use. Falls back on AWS_REGION environment variable if not specified
-h, --help display help for command
The --force-restore flag is useful if you want to restore the original Lambda code in the cloud after you've finished debugging. This is normally done automatically when you finish your session (CTRL+C), but in the case of a crash or unexpected exit, you can use this flag to restore the original code.
Big thanks to Jason Wadsworth for all the early feedback on this feature <3
- Create a launch configuration (and shutdown task if you're on VS Code using NodeJS). This command will automate it for you:
sam local --debug
- Set breakpoints in your code
- Select your debug configuration and start debugging
- When you're done debugging, make sure you kill the
samp localprocess. For NodeJS it's enough to stop the debugger.
Note that you can create multiple configurations for different functions / group of functions. You can pass these as a comma separated list to the --functions flag.
- NodeJS (JavaScript and TypeScript)
- .NET (only tested on v6.0)
- Python
Java and Go are not supported at this time, but will be added in the future.
- VsCode (All runtimes)
- Visual Studio (.NET only)
- Rider (.NET only)
- PyCharm (Python only)
| NodeJS (JS/TS) | .NET | Python | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VS Code | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Visual Studio | ✓ | ||
| JetBrains Rider | ✓ | ||
| JetBrains PyCharm | ✓ | ||
| JetBrains WebStorm | ✓ |
The tool temporarily replaces your function code in the cloud with a proxy function that relays events to your local machine over AWS IoT (MQTT). The functions are automatically restored when you exit the debugging session with the values in your processed CloudFormation tempate. The tool also sets the MemorySize to 128MB and Timeout to 60 seconds to avoid timeouts during debugging as well as saving cost.
Should you encounter any issues during the restoration of the original function code, you can use the --force-restore flag to restore the original code manually. Failing that, you can always redeploy your stack to restore the original code.
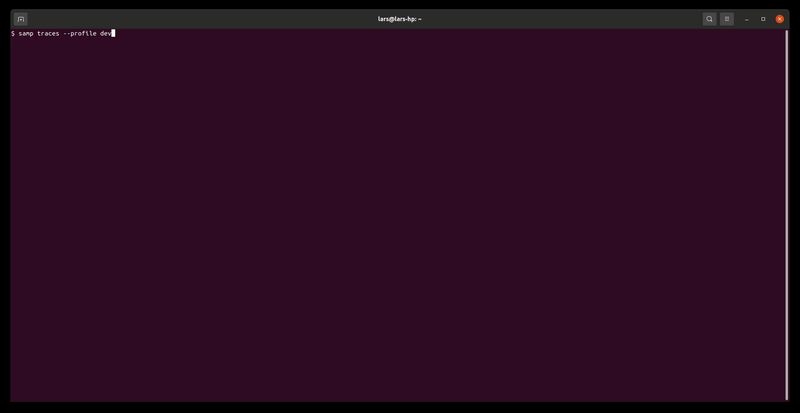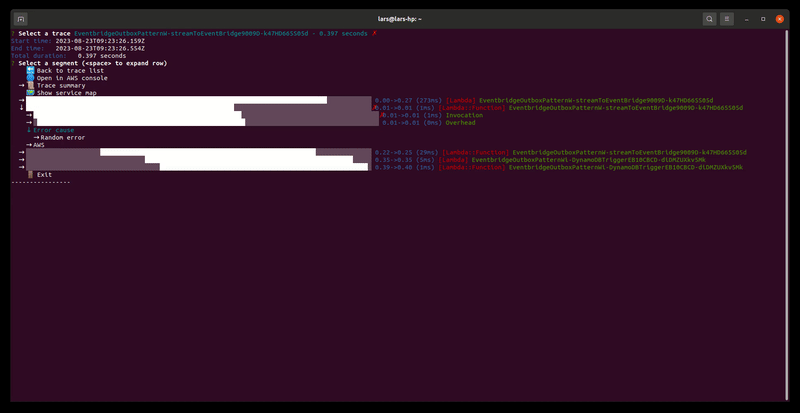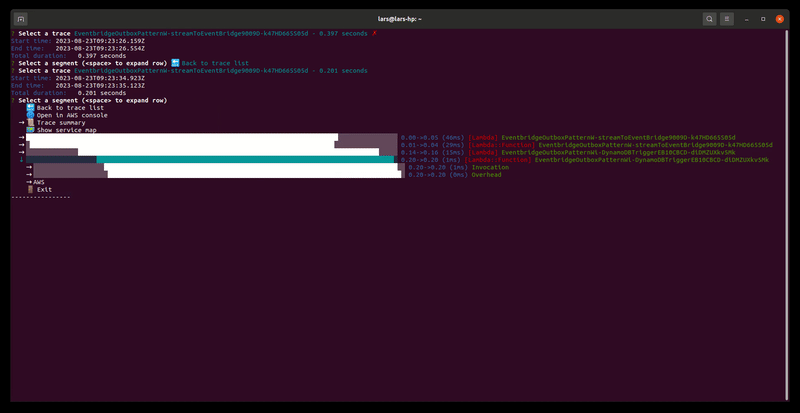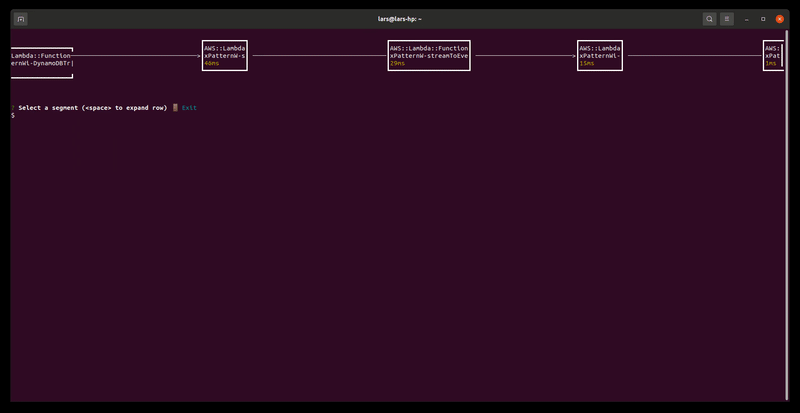
Lets you browse and explore the AWS X-Ray traces in your AWS account
Usage: samp traces|t [options]
Browses and renders AWS X-Ray traces in your account
Options:
-s, --start <start> Start time (minutes ago) (default: 5)
-e, --end <end> End time (minutes ago) (default: 0)
-as, --absolute-start <start> Start time (ISO 8601)
-ae, --absolute-end <end> End time (ISO 8601)
-f, --filter-expression <filter> Filter expression. Must be inside double or single quotes ("/')
-p, --profile <profile> AWS profile to use (default: "default")
-r, --region <region> AWS region to use
This command consists of two sub commands: init and sync
Initiates a new StepFunctions resource and ASL file to your SAM project.
Establishes a live sync between your ASL file(s) and their corresponding state machine in the cloud. This enables you to write ASL with a fast feedback loop without the wait time of deploying the state machine to the cloud.
Usage: samp stepfunctions|sfn stepfunctions [init|sync] [options]
Initiates a state machine or sets up a live sync between your local ASL and the cloud
Options:
-t, --template-file [templateFile] Path to SAM template file (default:
"template.yaml")
-s, --stack-name [stackName] [Only applicable when syncing] The name of
the deployed stack
-p, --profile [profile] [Only applicable when syncing] AWS profile
to use (default: "default")
--region [region] The AWS region to use. Falls back on
AWS_REGION environment variable if not
specified
-h, --help display help for command
Lets you interact with StepFunction's TestState API. Read more here and here
Lets you browse and explore your serverless patterns repositories.
Usage: samp explore|e [options]
Explores and visualises patterns from https://github.com/aws-samples/serverless-patterns/
Options:
-h, --help display help for command
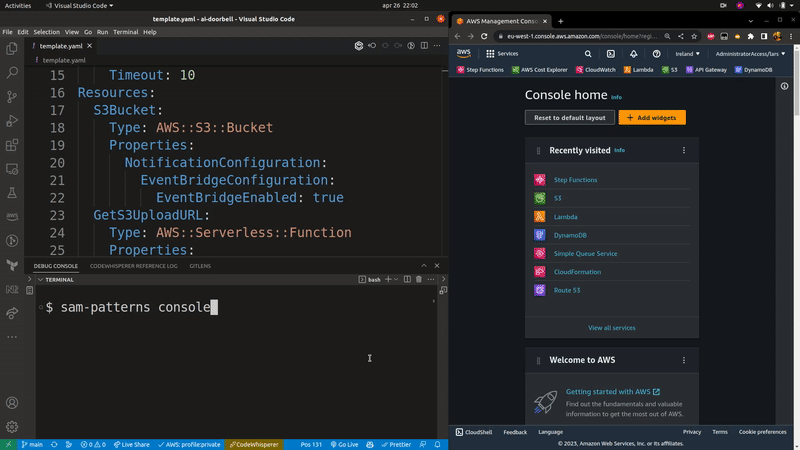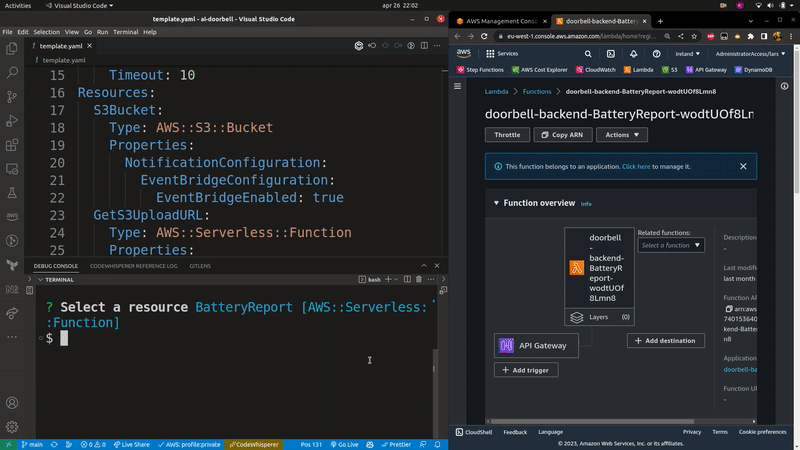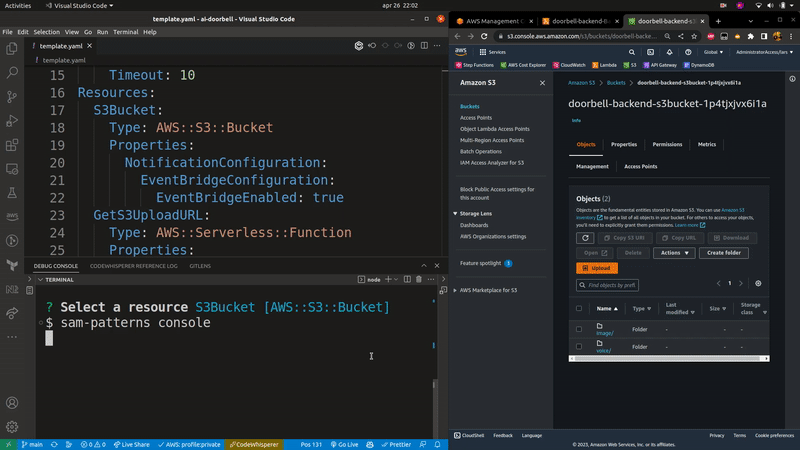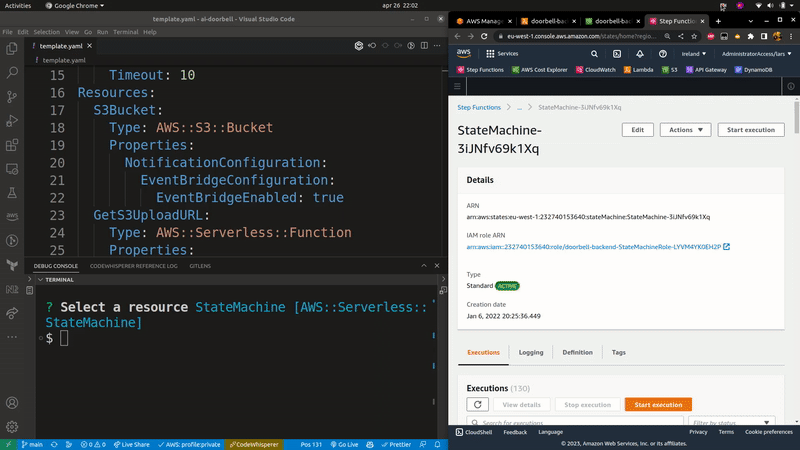
Launches the AWS console for the selected SAM resource. If a samconfig.[toml/yaml] file is present, it will use the stack name and region from that file. Otherwise you will have to specify them using the --stack-name and --region flags.
Usage: sampat console|c [options]
Opens the AWS console for a deployed resource in your SAM template.
Options:
-t, --template-file [templateFile] Path to SAM template file (default: "template.yaml")
-s, --stack-name [stackName] The name of the deployed stack
-p, --profile [profile] AWS profile to use (default: "default")
--region [region] The AWS region to use. Falls back on AWS_REGION environment variable if not specified
-h, --help display help for command
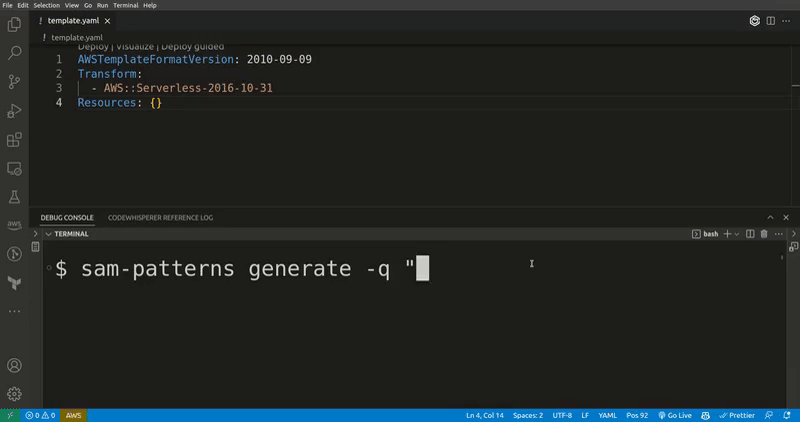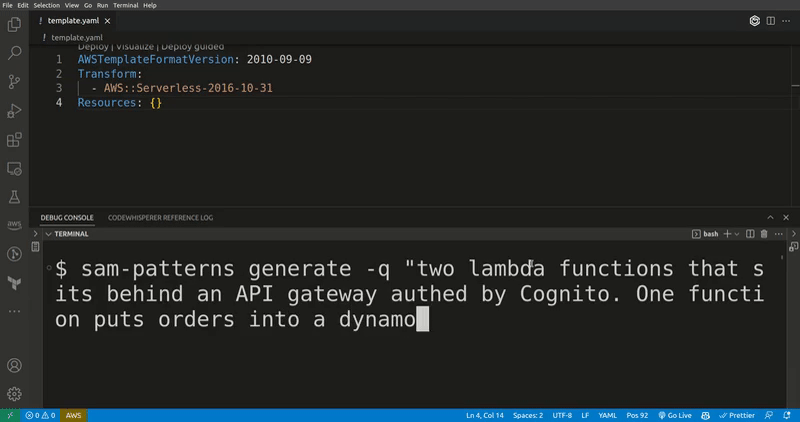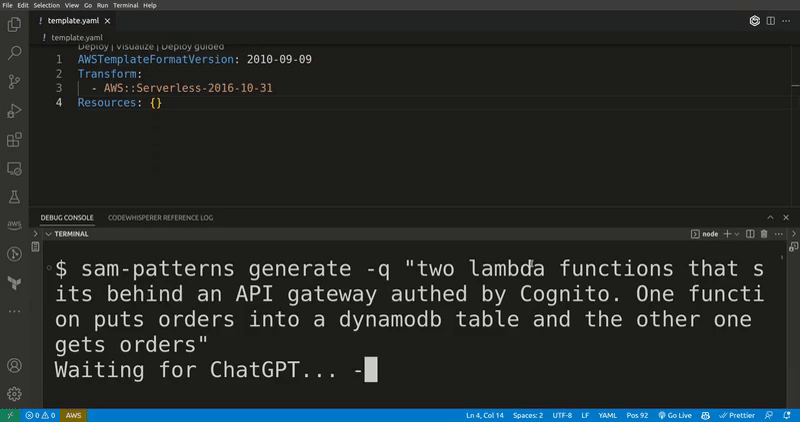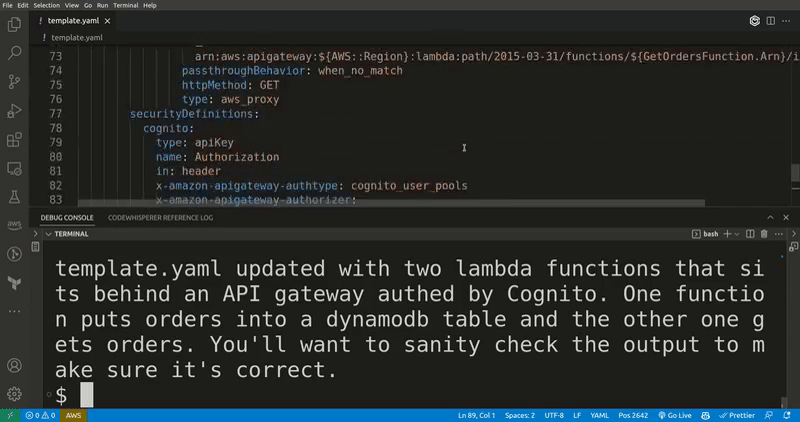
Generates SAM resources, CDK code, StepFunctions ASL and Lambda functions in any language based on a query to ChatGPT. If you ask for SAM resources, it will merges them into your existing template.
This is an experimental feature and requires a ChatGPT API key. You can get one here. Make sure to validate the output before deploying your template as it might contain errors or things that could incur cost
Usage: sampat generate|g [options]
Generates resources from a ChatGPT response
Options:
-t, --template [template] SAM template file (default: "template.yaml")
-q, --query [query] Question to ask ChatGPT. I.e "a lambda function that's triggered by an S3 event"
-m, --model [model] OpenAI model to use. Valid values are 'gpt-3.5-turbo' and 'gpt-4'. Note that gpt-3.5-turbo is fine for
most use cases and that gpt-4 is slower and more expensive (default: "gpt-3.5-turbo")
-o, --output [output] Output feature. Valid values are 'SAM', 'CDK', 'lambda-<language>' or 'ASL'. If not 'SAM', set
--output-file (default: "SAM")
-of, --output-file [output-file] Output file. Only applicable if --output is CDK
-h, --help display help for command
- To generate SAM resources for a Lambda function that reads off a DynamoDB table:
samp generate -q "a lambda function that reads off a dynamodb table" - To generate a CDK stack for the same:
samp generate -q "a lambda function that reads off a dynamodb table" --output CDK --output-file cdk-stack.ts - To generate a Lambda function in Rust that reads off a DynamoDB table:
samp generate -q "a lambda function that reads off a dynamodb table" --output lambda-rust --output-file lambda.py - To generate a StepFunctions ASL definition that reads off a DynamoDB table:
samp generate -q "a lambda function that reads off a dynamodb table" --output ASL --output-file asl.yaml
Note that quality of results may vary and that you sometimes have to run the command a few times to get a good result.
Describes a pattern using ChatGPT and gives suggestions on how to improve security.
Usage: sampat describe|d [options]
Describes a SAM template using ChatGPT
Options:
-t, --template [template] SAM template file (default: "template.yaml")
-r, --repository-path [repository] Github repository path, i.e "aws-samples/serverless-patterns/apigw-sfn"
-m, --model [model] OpenAI model to use. Valid values are 'gpt-3.5-turbo' and 'gpt-4'. Note that gpt-3.5-turbo is fine for most use cases and that gpt-4 is slower and more expensive (default: "gpt-3.5-turbo")
-h, --help display help for command
Lets you add more sources. This could be public repositories, such as Jeremy Daly's Serverless Reference Architectures or a private repository for company specific patterns.
Example how to add Jeremy Daly's reference architectures as a source:
? GitHub owner: serverless-architecture
? GitHub repo: reference-architectures
? Root: folder /
? Relative path to template file: /sam
? Template filename(s): template.yaml,template.yml
? URL (use #PATTERN_NAME# as placeholder): https://jeremydaly.com/the-#PATTERN_NAME#-pattern
The configuration gets stored in ~/.samp-cli/settings.json
If you create your own collection you need to follow this structure:
The repository should follow the following structure. (README.md is optional):
├── pattern-1
| ├── README.md
│ └── template.yaml
├── pattern-2
| ├── README.md
│ └── template.yaml
└── pattern-3
├── README.md
└── template.yaml
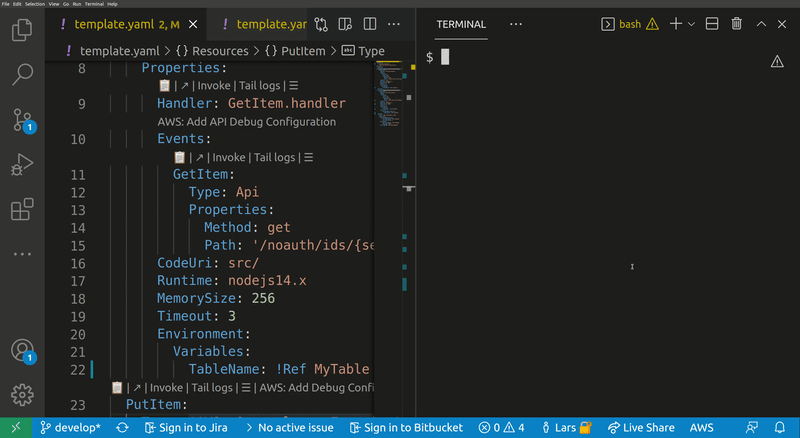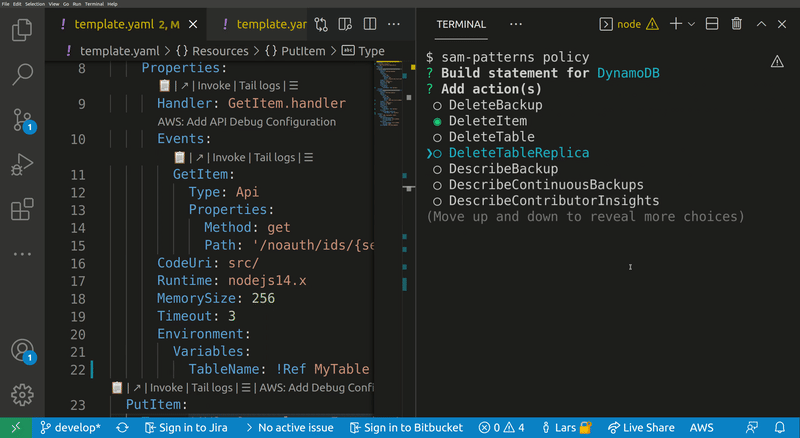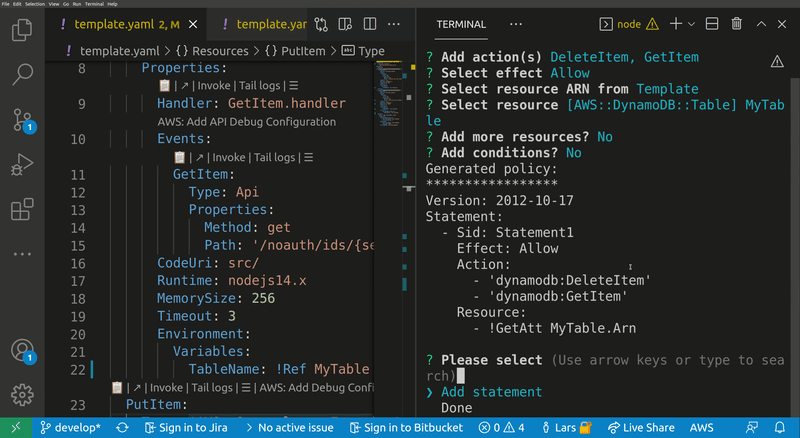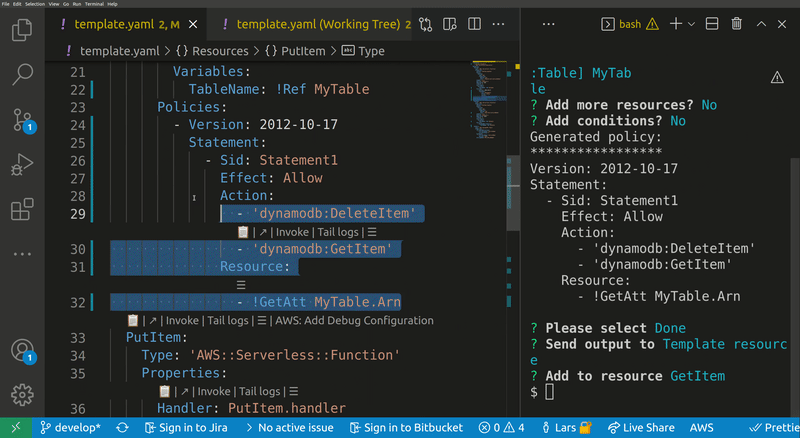
Lets you quickly build IAM polices, find SAM policy templates or generate SAM Connectors based on the resources you have in your template. The generated policy can be attached to supported resource types.
Usage: samp policy|p [options]
Opens a wizard that helps you to create and attach a new IAM policy to a resource in your template
Options:
-t, --template <filename> Template file name (default: "template.yaml")
-f, --format <JSON|YAML> Output format (default: "JSON")
-o, --output <console|clipboard> Policy output (default: "console")
-h, --help display help for command
Lets you browse the return values of a resource and send the intrinsic function that retrieves it to your stdout or clipboard
Usage: sampat return-values|rv [options]
Browses the return values and the intrinsic functions of a CloudFormation/SAM resource
Options:
-t, --template [template] SAM template file (default: "template.yaml")
-c, --clipboard Send the return value's intrinsic function to the clipboard (default: false)
-h, --help display help for command
Converts samconfig.toml to yaml format
Usage: samp convert-samconfig|cs [options]
Converts samconfig.toml to samconfig.yaml
Options:
-h, --help display help for command
Quickly Lambda Powertools modules and installs them in your project.
Usage: samp powertools|pt [options]
Adds Lambda Powertools to your project
Options:
-h, --help display help for command
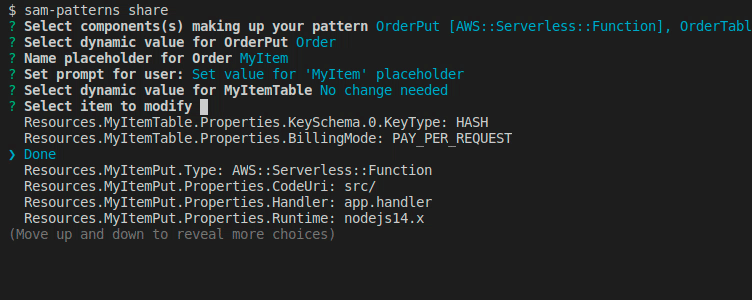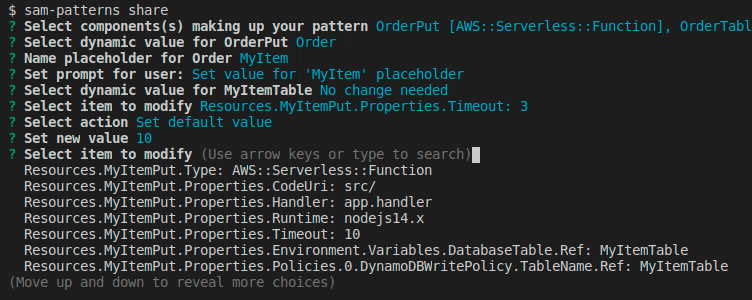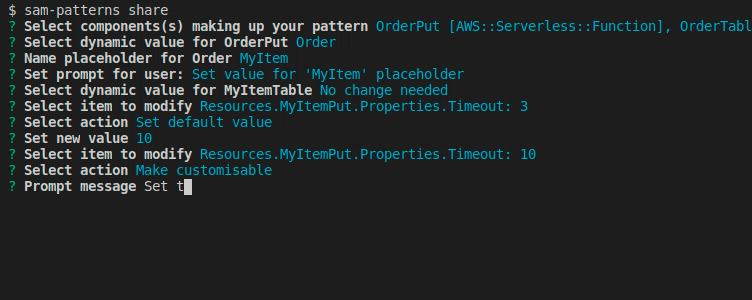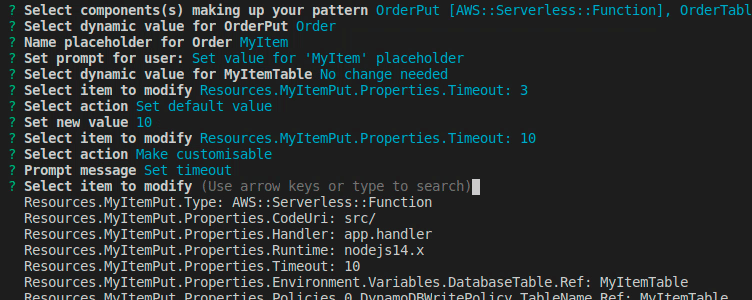
Lets you share patterns from an existing CloudFormation/SAM template with the world or your colleagues.
In this example we have a stack with the following resources:
- OrderPutFunction [AWS::Serverless::Function]
- OrderTable [AWS::DynamoDB::Table]
- MySnsTopic [AWS::SNS::Topic]
- EventRule [AWS::Events::Rule]
- EventBridgeToToSnsPolicy [AWS::SNS::TopicPolicy]
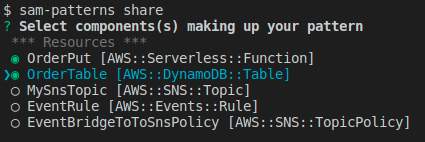
We've identified that OrderPutFunction and OrderTable together make up a reusable pattern that we want to share, so we run samp share:
We select the components making up our pattern and hit .
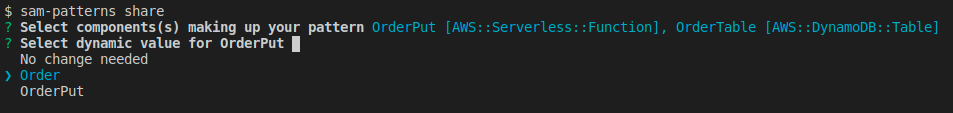
Next, we want to make the pattern generic so the developer importing it can customise it their way. In this case we created the pattern from an stack dealing with 'order' items. The next user of this pattern might work on a stack bound to 'products'.
From a quick look at the resources we can see a pattern that they both start with Order. The rest of their names are generic and is referring to the resource type, so we select Order.
Now we're prompted to name the placeholder for 'Order'. Here is a good idea to use something unique and not a short string like 'My'. This is because the import command will make a naive find/replace on the placeholder name.
Next we're asked to enter a string prompting the user to set the value. You can hit for the default string Set value for 'MyItem' placeholder.
We want to change some default values of some properties or make some values customisable for the user during import. Here we get prompted with a flattened list of the components we've chosen.
Once done, hit Done, select a name for the pattern and a source where to commit it to. Note that your GITHUB_TOKEN needs permission to push to the selected repository. Refer to samp source on how to link repositories.
The new pattern has now been pushed and is ready to be used by someone else using samp import
NOTE If you create patterns that aren't specific to your business use cases, please consider sharing them with the community over at Serverless Pattern Collection
Say you host a pattern that creates an SQS queue and a Lambda function and sets the queue as an event source:
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Transform:
- AWS::Serverless-2016-10-31
Resources:
The_Consumer:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
Runtime: nodejs14.x
CodeUri: src/
Handler: The_Consumer.handler
Timeout: 3
Events:
SQS:
Type: SQS
Properties:
BatchSize: 10
Queue: !GetAtt The_Queue.Arn
The_Queue:
Type: AWS::SQS::Queue
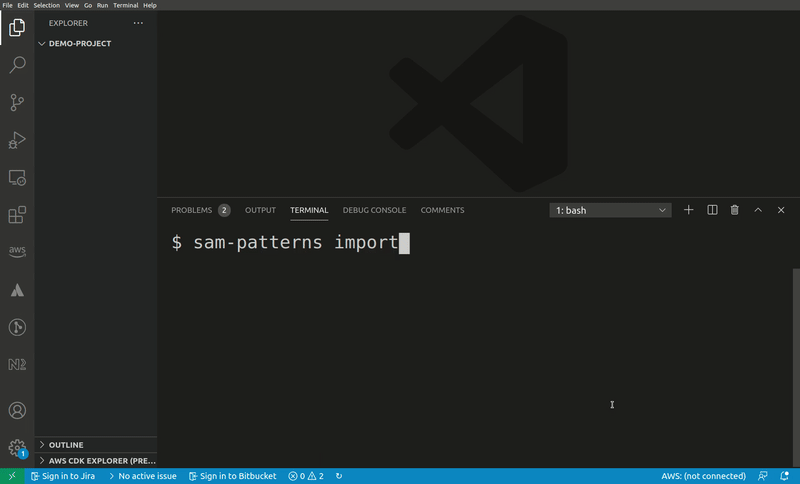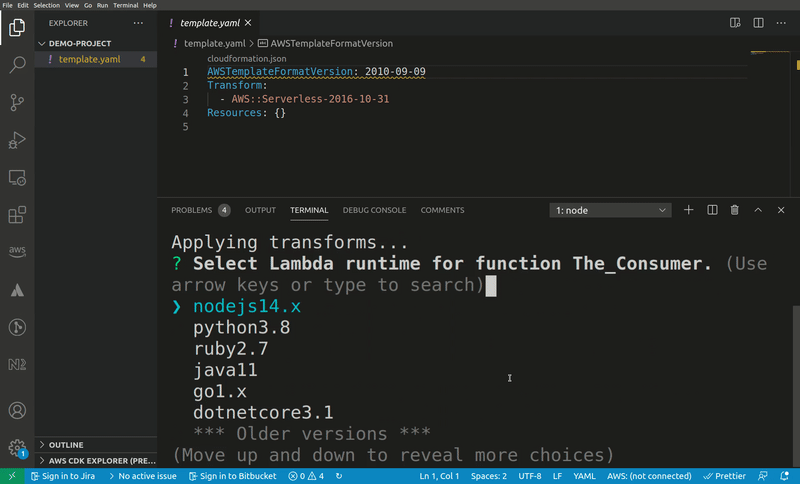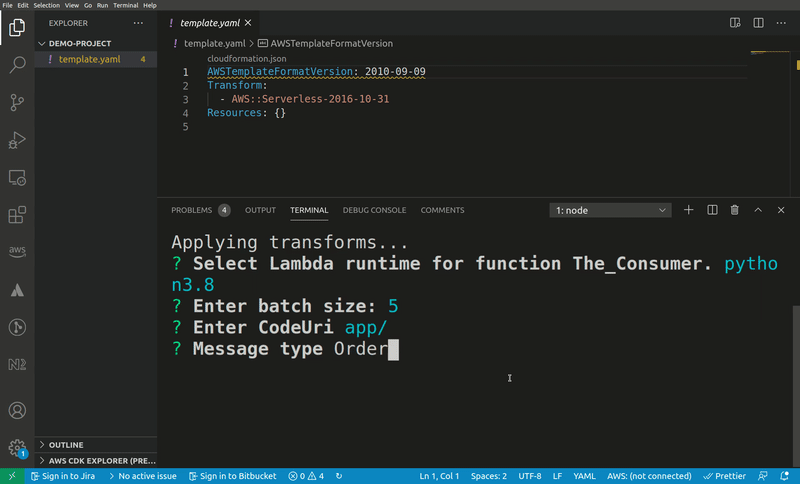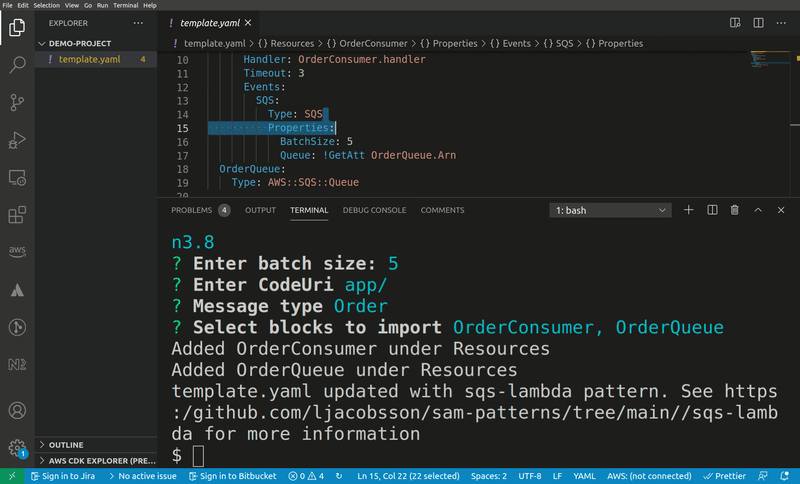
When a user of this snippet imports it into their template they are likely to jump straight at renaming the resources to something that semantically describes the type of messages the queue is handling. Also, the runtime is likely to be something different.
As a pattern producer you can help out with this by defining a Metadata object on the pattern template:
Metadata:
PatternTransform:
Placeholders:
- Placeholder: The_
Message: Message type
Properties:
- JSONPath: $.Resources.The_Consumer.Properties.Events.SQS.Properties.BatchSize
InputType: number
Message: Enter batch size
- JSONPath: $.Resources.The_Consumer.Properties.CodeUri
InputType: string
Message: Enter CodeUri
PatternTransform.Placeholders (array)
Placeholder: the string to be replacedMessage: A message to be displayed (optional)
PatternTransform.Properties (array)
JSONPath: The JSONPath to the property to be modifiedMessage: A message to be displayed (optional)InputType: The datatype. Currently supportsstring,numberorruntime-select
The input type runtime-select lets the user select a valid Lambda runtime. This metadata is automatically applied to all patterns, so there's no need to explicitly add it. If the user always writes code in a specific language they can export environment variable SAM_PATTERNS_DEFAULT_RUNTIME to a valid Lambda runtime identifier.
- Comments in YAML disappear when parsing the template
- Only content from the template.yaml file will be imported. Any supporting files like lambda functions or openapi schemas will be skipped.
- Only works with SAM templates