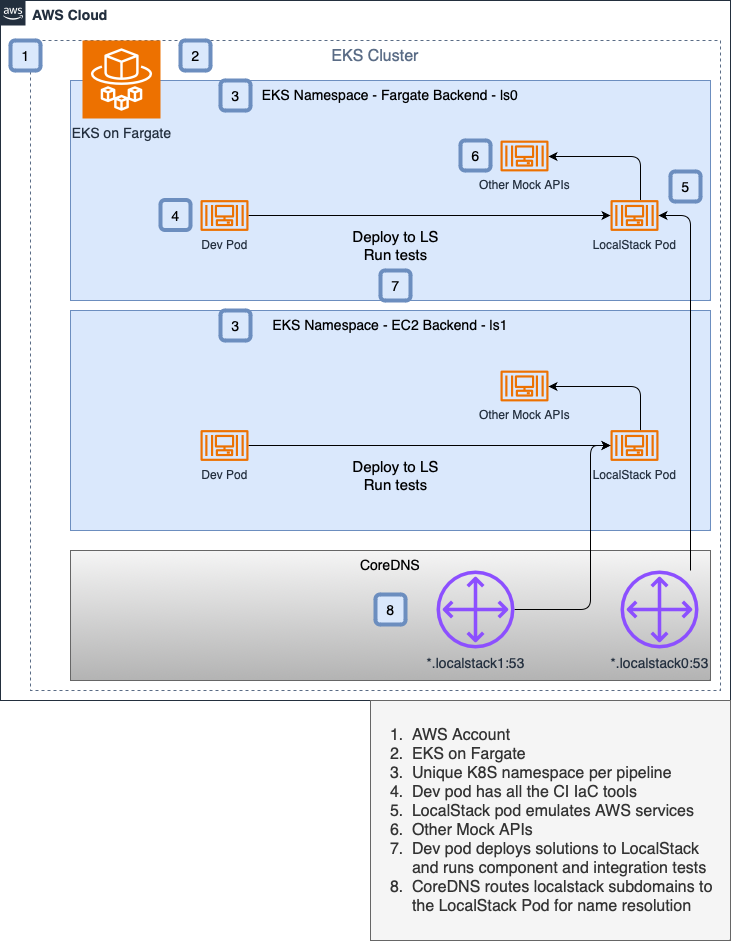
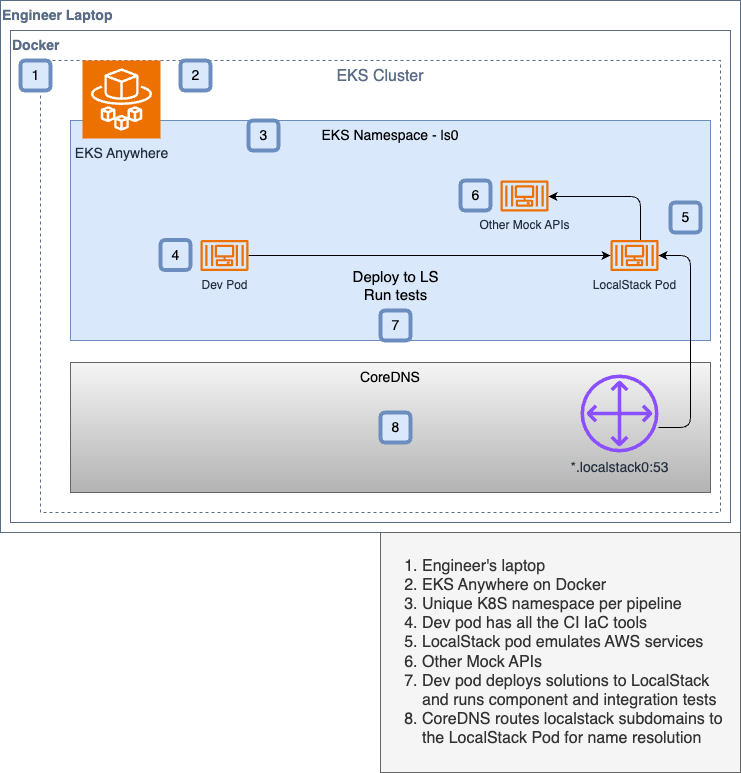
This blueprint has two solutions:
- Deploy LocalStack to AWS EKS with Fargate.
- Deploy LocalStack on an engineer's laptop on EKS Anywhere with Docker.
Solution-1 provides a hybrid integration environment where teams can run component/integration/system tests. The solution is managed in AWS to allow for easy management of the entire platform across multiple AWS accounts. This is further subdivided into two categories: workloads that run on Fargate backend and workloads that run on EC2 backend.
Solution-2 is identical to Solution-1 but it runs on engineers laptops with EKS Anywhere.
The two solutions having nearly identical tooling allows enterprise teams to create a manageable solution testing platform.
Multiple namespaces isolate testing of different solutions.
- LocalStack on K8S LocalStack provides AWS Service emulation to create aan amazing DevX with powerful solution testing.
- Dev Container Provides standard tooling to build, deploy, and test solutions.
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service K8S common platform for DevSecOps tooling to support unit, component, and integration testing.
This guide assumes that you have cloned this repository and are in the project root directory. The following steps will guide you through the process of building, deploying, and test Solution-1 (Solution-2 link). Solution-1 is not free. It will cost money to run EKS in AWS. Make sure to destroy your resources in the cleanup section to control your costs.
This solution has the EKS cluster deployed on AWS.
- install Helm
- install kubectl
- install eksctl
- AWS credentials for
eksctl. export LOCALSTACK_AUTH_TOKEN=<your LocalStack auth token>added to.env-local.- install localstack k8s operator.
Let's create the AWS cluster. This blueprint builds namespaces in the format of ls<NS_NUM>. So, we're going
to choose a namespace number for the following targets.
make aws-create-clusterLet's create a namespace ls0 of whose resources are deployed with Fargate:
export FARGATE_WORKLOAD=0
# Create the namespace and the Fargate profile.
make aws-create-fargate-profile NS_NUM=$FARGATE_WORKLOADNow let's create a namespace ls1 of whose resources are deployed on EC2 nodes:
export EC2_WORKLOAD=1
# Create the namespace for the workloads on EC2.
make create-namespace NS_NUM=$EC2_WORKLOADThen let's deploy Localstack on the namespace that runs its workloads on Fargate:
# Generate manifests and apply Localstack/DevPod deployments.
make deploy-localstack NS_NUM=$FARGATE_WORKLOAD
# Exec into dev environment
make exec-devpod-interactive NS_NUM=$FARGATE_WORKLOADOnce inside the DevPod environment, let's clone our Localstack sample project:
git clone https://github.com/localstack-samples/lambda-ddb.git
cd lambda-ddb
make integ-awscdk-bootstrap
make integ-awscdk-deploy
make integ-awscdk-testNow, let's deploy Localstack on the namespace that runs its workloads on EC2 nodes:
# Generate manifests and apply Localstack/DevPod deployments.
make deploy-localstack NS_NUM=$EC2_WORKLOAD
# Exec into dev environment
make exec-devpod-interactive NS_NUM=$EC2_WORKLOADAnd like before, once inside the DevPod environment, let's clone our Localstack sample project:
git clone https://github.com/localstack-samples/lambda-ddb.git
cd lambda-ddb
make integ-awscdk-bootstrap
make integ-awscdk-deploy
make integ-awscdk-testAfter the test passes, let's delete the EKS cluster from AWS:
make deploy-cleanup NS_NUM=$FARGATE_WORKLOAD
make deploy-cleanup NS_NUM=$EC2_WORKLOAD
make aws-delete-clusterThis solution has the EKS cluster deployed on your local machine, using the EKS anywhere plugin.
- Locally-accessible machine.
- install Helm
- install kubectl
- install eksctl
- install eksanywhere plugin
- install localstack k8s operator.
Let's create the AWS cluster using EKS Anywhere locally. This blueprint builds namespaces in the format of ls<NS_NUM>. So, we're going to choose a namespace number for the following targets.
make local-create-cluster
# Create the namespace.
make create-namespace NS_NUM=0
# Generate manifests and apply Localstack/DevPod deployments.
make deploy-localstack NS_NUM=0
# Exec into dev environment
make exec-devpod-interactive NS_NUM=0Once inside the DevPod environment, let's clone our Localstack sample project:
git clone https://github.com/localstack-samples/lambda-ddb.git
cd lambda-ddb
make integ-awscdk-bootstrap
make integ-awscdk-deploy
make integ-awscdk-testAfter the test passes, let's delete the EKS cluster from the local machine:
make deploy-cleanup NS_NUM=0
make local-delete-clusterTo deploy multiple Localstack instances with their own dev environment, you can do something like this:
function create_environment () {
local namespace_idx="$1"
make create-namespace NS_NUM=$namespace_idx
make deploy-localstack NS_NUM=$namespace_idx
make exec-devpod-interactive NS_NUM=$namespace_idx
}
function check_localstack () {
local namespace_idx="$1"
make exec-devpod-noninteractive NS_NUM=$namespace_idx CMD="curl -i localstack$namespace_idx:4566"
}
# Create a 100 environments
for i in `seq 0 100`; do
create_environment "$i"
done
# Execute the `ls -la` command on all 1000
for i in `seq 0 100`; do
check_localstack "$i"
done