| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| Environment |   |
| Services | Kinesis Data Streams, Kinesis Data Firehose, DynamoDB, S3, Lambda |
| Integrations | CDK |
| Categories | Serverless; ETL; Analytics; Data Lake; Storage & Backup |
| Level | Advanced |
| GitHub | Repository link |
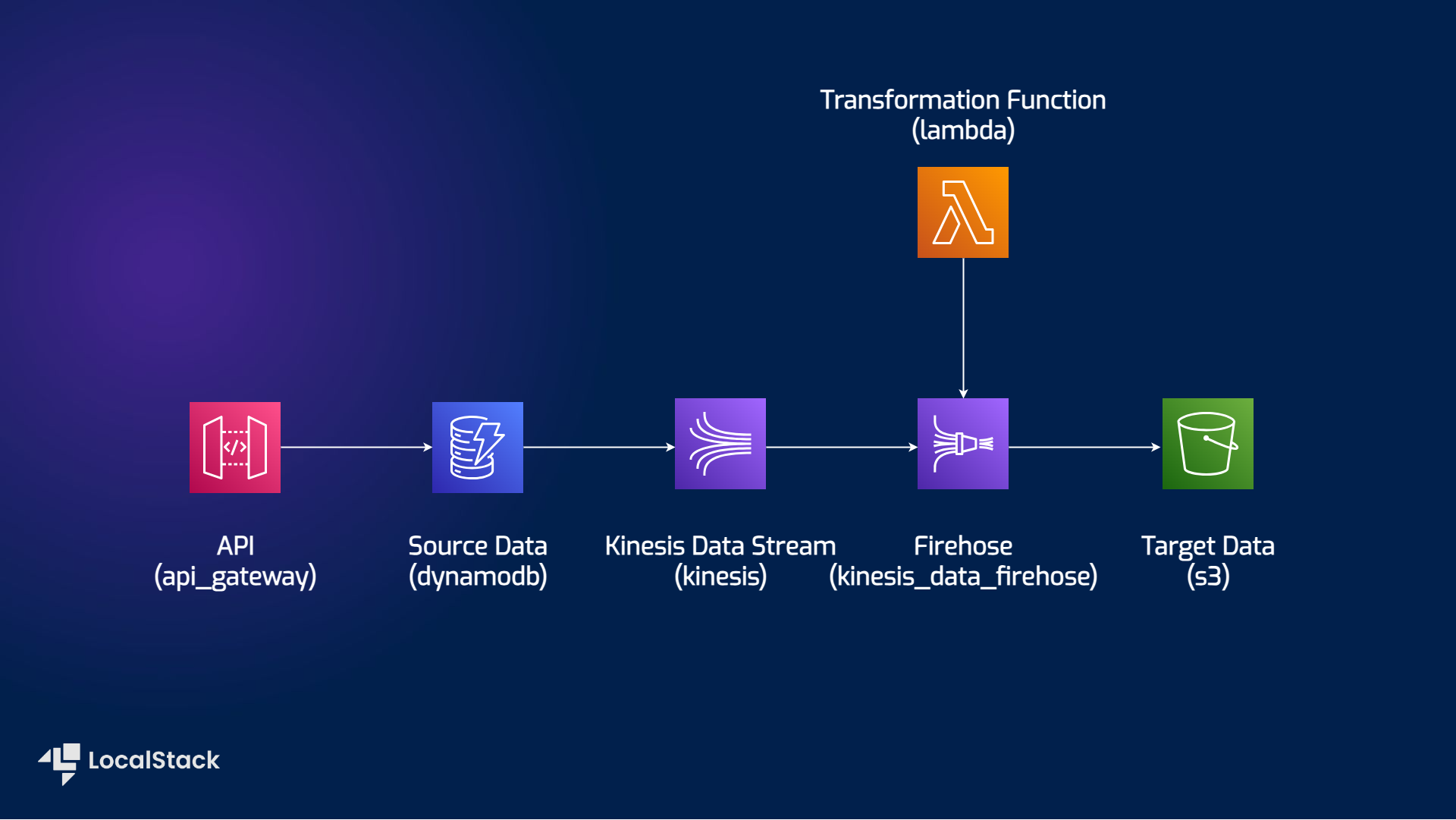
The sample applications delivers DynamoDB records to an S3 bucket using Kinesis Data Streams and Kinesis Data Firehose using Cloud Development Kit (AWS CDK) L3 constructs. The sample application implements the following integration among the various AWS services:
- The data is ingested using a REST API provided by an API Gateway as a proxy for DynamoDB.
- Item-level changes are generated in near-real time in Kinesis Data Streams for delivery to S3.
- Kinesis Data Streams sends the records to Kinesis Data Firehose for transformation & delivery.
- Lambda function converts the records from a DynamoDB record format to JSON format, which contains only the record item attribute names & values.
Users can deploy this application on LocalStack and AWS with no changes using Cloud Development Kit (CDK). To test this application sample, we will demonstrate how you use LocalStack to deploy the infrastructure on your developer machine and your CI environment.
The following diagram shows the architecture that this sample application builds and deploys:
We are using the following AWS services and their features to build our infrastructure:
- Kinesis Data Firehose to transform streaming data from the Kinesis Data Streams.
- Kinesis Data Streams to discover item-level changes in the DynamoDB table.
- S3 to store the data in the data lake from the Kinesis Data Firehose.
- DynamoDB to injest the data from the API Gateway proxy.
- API Gateway to provide a REST API as a proxy for the DynamoDB table.
- Lambda to convert the DynamoDB record format to JSON format.
- LocalStack Pro with the
localstackCLI. - Cloud Development Kit with the
cdklocalinstalled. - Node.js, and
yarn.
Start the LocalStack Pro container via the following command:
export LOCALSTACK_AUTH_TOKEN=<YOUR_AUTH_TOKEN>
DEBUG=1 localstack startWe specified DEBUG=1 to get the printed LocalStack logs directly in the terminal to help us visualize the background tasks in action. If you prefer running LocalStack in detached mode, you can add the -d flag to the localstack start command, and use Docker Desktop to view the logs.
You can install and build the code in pattern/aws-dynamodb-kinesisstreams-s3 and the root directories using the following commands:
pushd pattern/aws-dynamodb-kinesisstreams-s3
npm install
npm run build
popd
npm install
npm run buildThis will install & build the AWS CDK L3 construct aws-dynamodb-kinesisstreams-s3 and finally install/build the sample application.
To create the AWS infrastructure locally, you can use CDK and cdklocal wrapper. To deploy the infrastructure, you can run the following command from the sample-application directory:
cdklocal bootstrap
cdklocal deploy
popdThis will deploy the AwsDynamodbKinesisfirehoseS3IngestionStack stack on LocalStack. You will see the following output:
Outputs:
AwsDynamodbKinesisfirehoseS3IngestionStack.SourceDataRestApiEndpoint142D70D8 = https://ofw4fj46pe.execute-api.localhost.localstack.cloud:4566/prod/
Stack ARN:
arn:aws:cloudformation:us-east-1:000000000000:stack/AwsDynamodbKinesisfirehoseS3IngestionStack/8a300f0c
✨ Total time: 53.22sThe output will show the API Gateway URL endpoint to be used for testing. You will see a different URL endpoint in your output, and you can save it for later use.
The sample application creates a SourceData Service REST API with a POST method that you can see in the CDK output. Before testing the solution, navigate to the LocalStack Web Application and check-out the API Gateway Resource Browser.
You would be able to see the API Gateway Id on the Resource Browser. Click the Id and navigate to the Resources tab. Click the top-most Id available with the / path and navigate to the Methods tab. Click on POST, where you will be able to see the Authorization Type as AWS_IAM. Click on Edit Method and change the Authorization Type to NONE. Click on Submit. You are now ready to test the application.
You can use the following command to send a test event to the API Gateway:
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"data": {"CardID":"defaultname","Image":"defaulturl"}}' https://ofw4fj46pe.execute-api.localhost.localstack.cloud:4566/prod/Change the URL endpoint with the one you received in the CDK output. You will see the following response:
{}You can now verify the LocalStack logs to see the background tasks in action. Navigate to the DynamoDB Resource Browser to see two tables — AwsDynamodbKinesisfirehoseS3I-dynamodbKinesisS3DynamoT-639063f6 and AwsDynamodbKinesisfirehoseS3I-dynamodbKinesisS3streamf-371b758e-firehose. Click the tables, and navigate to the Items tab. Click on Switch to Scan. Select the Index as Whole Table before clicking Submit. You will be able to see the records in the table.
You can also view the S3 buckets in the S3 Resource Browser, and verify the records in the bucket. In the bucket awsdynamodbkinesisfirehoses3i-dynamodbkinesiss3streamf-d7c20afa you will be able to find an object with the following content:
{"SourceDataId":"e75ea050","MessageData":"{'CardID': 'defaultname', 'Image': 'defaulturl'}"}You can further send test events to the API Gateway to see the records in the DynamoDB table and S3 bucket. Here is an example event:
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"data": [{"CardID":"defaultname","Image":"defaulturl"},{"CardID":"defaultname","Image":"defaulturl"},{"CardID":"defaultname","Image":"defaulturl"},{"CardID":"defaultname","Image":"defaulturl"},{"CardID":"defaultname","Image":"defaulturl"}]}' \
https://ofw4fj46pe.execute-api.localhost.localstack.cloud:4566/prod/This application sample hosts an example GitHub Action workflow that starts up LocalStack, builds the Lambda functions, and deploys the infrastructure on the runner. You can find the workflow in the .github/workflows/main.yml file. To run the workflow, you can fork this repository and push a commit to the main branch.
Users can adapt this example workflow to run in their own CI environment. LocalStack supports various CI environments, including GitHub Actions, CircleCI, Jenkins, Travis CI, and more. You can find more information about the CI integration in the LocalStack documentation.
We appreciate your interest in contributing to our project and are always looking for new ways to improve the developer experience. We welcome feedback, bug reports, and even feature ideas from the community. Refer to the contributing guide for more details on how to get started.