| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| Environment | LocalStack |
| Services | EventBridge, Lambda, CloudWatch |
| Integrations | SAM |
| Categories | Serverless; Event-driven architecture |
| Level | Beginner |
| GitHub | Repository link |
The sample application create a Producer & Consumer using two Lambda functions. It is coupled with an EventBridge rule to determine events that are routed to the consumer. The example demonstrates how an ATM application at a bank could generate events, and the rule only passes Approved transactions to an event consuming application. Users can deploy this application sample on LocalStack & AWS using Serverless Application Model (SAM) without any changes. To test this application sample, we will demonstrate how you use LocalStack to deploy the infrastructure on your developer machine and in your CI environment. Furthermore, we will showcase how you can check out the event-driven architecture using LocalStack Web Application by verifying the logs.
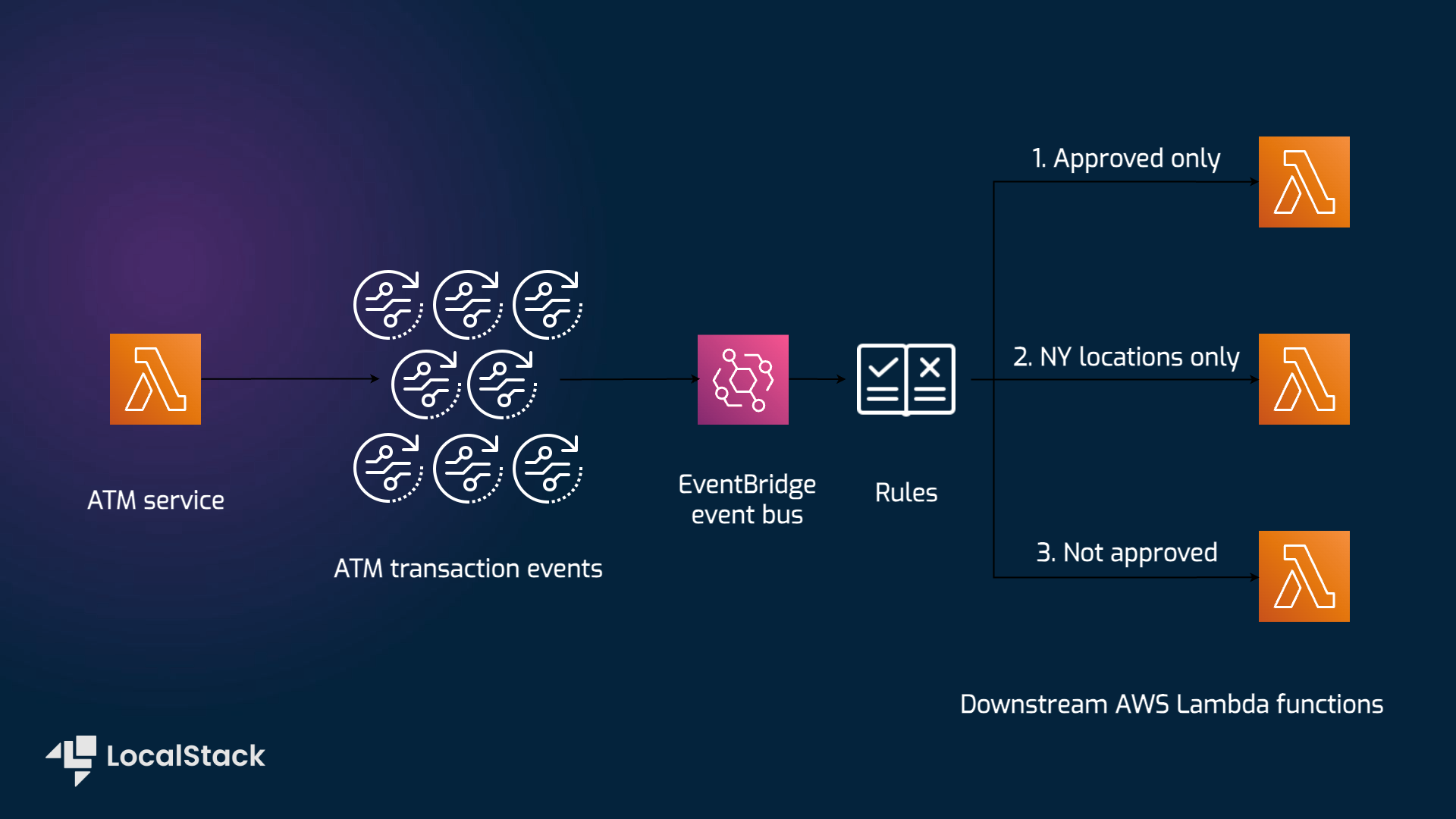
The following diagram shows the architecture that this sample application builds and deploys:
We are using the following AWS services and their features to build our infrastructure:
- EventBridge to create an event bus that filter the events based upon a specified criteria, and once validated route to the Consumer function.
- Lambda to create two functions, a producer and a consumer, that are triggered by events on the event bus which is further used to log the events.
- CloudWatch to create a log group to store the logs generated by the functions, allowing the users to view the logs in the LocalStack Web Application or through the AWS CLI.
- LocalStack Pro with the
localstackCLI. - Serverless Application Model with the
samlocalinstalled. - AWS CLI with the
awslocalwrapper. - Node.js 18.x with the
npmpackage manager.
Start LocalStack Pro with the LOCALSTACK_AUTH_TOKEN pre-configured:
export LOCALSTACK_AUTH_TOKEN=<your-auth-token>
DEBUG=1 localstack startWe specified DEBUG=1 to get the printed LocalStack logs directly in the terminal to help us see the event-driven architecture in action. If you prefer running LocalStack in detached mode, you can add the -d flag to the localstack start command, and use Docker Desktop to view the logs.
To install the dependencies, run the following command:
cd atmProducer
npm installTo build the SAM application, run the following command from the root directory of the application:
samlocal buildIf you see a Build Succeeded message, you can proceed to the next step.
To deploy the SAM application, run the following command:
samlocal deploy --guidedThe above command will create a new managed S3 bucket to store the artifacts of the SAM application. If you want to use an existing S3 bucket, you can use the --s3-bucket flag to specify the bucket name. Before being deployed, the CloudFormation changeset will be displayed in the terminal. If you want to deploy the application without confirmation, you can use the --no-confirm-changeset flag.
To view the created resources, check out the CloudFormation outputs from deployed stack or run the following commands:
awslocal lambda list-functions
awslocal events list-rulesYou can now invoke the Producer function. This places the events in events.js onto the default event bus in EventBridge. To invoke the function, run the following command:
output=$(awslocal lambda list-functions | grep 'sam-app-atmProducerFn-')
function_name=$(echo "$output" | awk -F'"' '/"FunctionName"/ {print $4}')
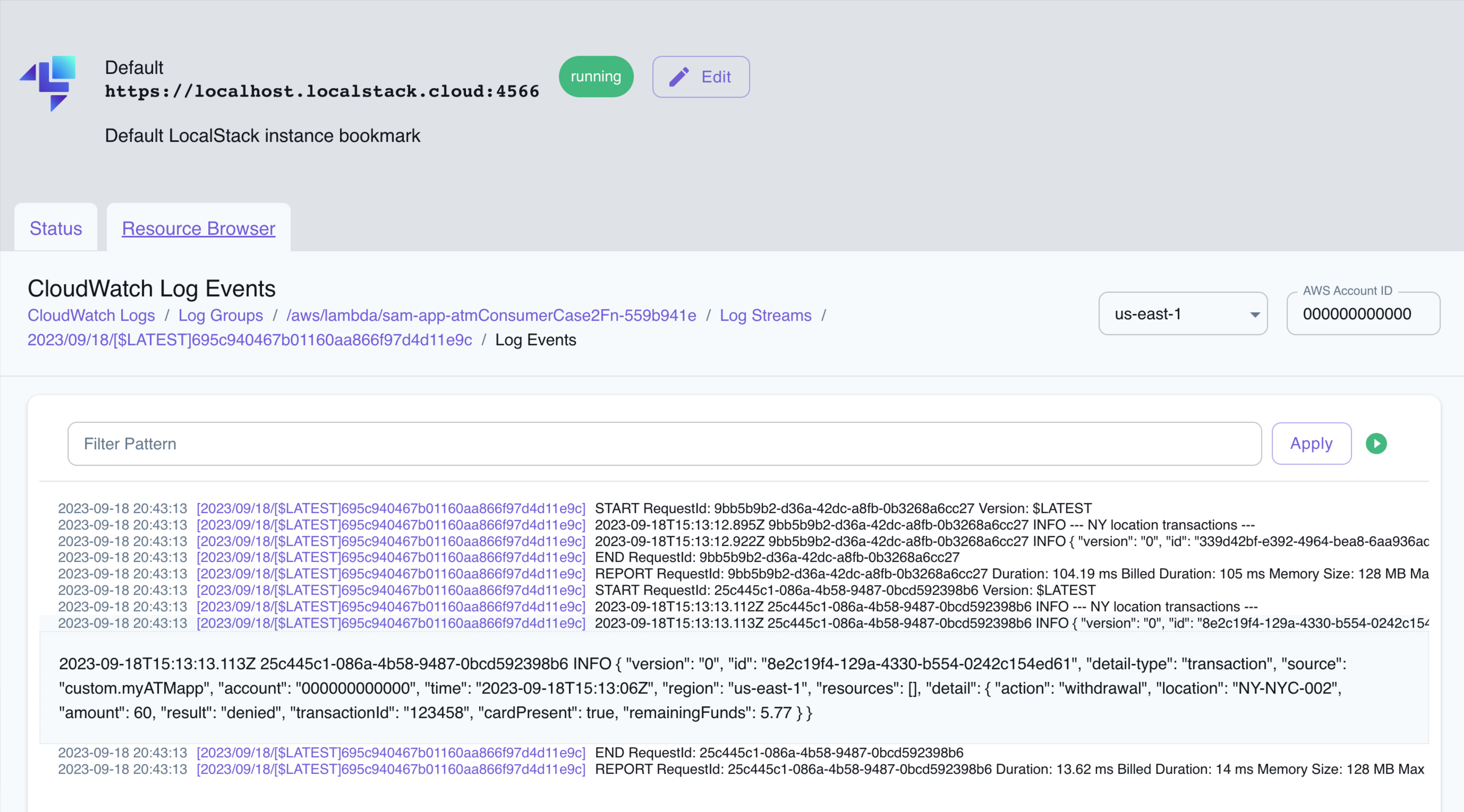
awslocal lambda invoke --function-name $function_name --payload '{}' output.txtNavigate to the CloudWatch Resource Browser to view the logs generated by the functions:
You can click on the individual Log groups to view the logs. You can also apply custom filters to the logs, or navigate to the Resource Browsers for other AWS services to view the resources created by the sample application.
This application sample hosts an example GitHub Action workflow that starts up LocalStack, builds the Lambda functions, and deploys the infrastructure on the runner. You can find the workflow in the .github/workflows/main.yml file. To run the workflow, you can fork this repository and push a commit to the master branch.
Users can adapt this example workflow to run in their own CI environment. LocalStack supports various CI environments, including GitHub Actions, CircleCI, Jenkins, Travis CI, and more. You can find more information about the CI integration in the LocalStack documentation.
The sample application is based on a public AWS sample app that deploys an event producer and consumer in Lambda, and creates an EventBridge rule to route events.
We appreciate your interest in contributing to our project and are always looking for new ways to improve the developer experience. We welcome feedback, bug reports, and even feature ideas from the community. Please refer to the contributing file for more details on how to get started.