Loan Broker application with AWS Step Functions, DynamoDB, Lambda, SQS, and SNS
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| Environment |   |
| Services | Step Functions, SQS, SNS, Lambda, DynamoDB, EventBridge |
| Integrations | CDK, AWS CLI |
| Categories | Serverless; Event-Driven architecture |
| Level | Intermediate |
| GitHub | Repository link |
Introduction
The Loan Broker application with AWS Step Functions, DynamoDB, Lambda, SQS, and SNS demonstrates Gregor Hohpe's Loan Broker example. The sample application implements a Recipient List pattern and a Scatter Gather pattern to retrieve a list of banks and dynamically route loan application to multiple banks respectively. The sample application implements the following integration among the various AWS services:
- User submits a loan application with personal data, desired terms, loan amount, and duration.
- Loan Broker fetches information from Credit Bureau and adds it to the loan application submitted earlier.
- Loan Broker routes the application to multiple banks, and the banks reply if they are willing to offer.
- Loan Broker aggregates all the result(s) and returns the result(s) to the user.
Users can deploy this application on LocalStack and AWS with no changes using Cloud Development Kit (CDK). To test this application sample, we will demonstrate how you use LocalStack to deploy the infrastructure on your developer machine and your CI environment. Furthermore, we will showcase how you can use Cloud Pods Launchpad to inject a Cloud Pod into your running LocalStack container to test the application without creating your infrastructure again!
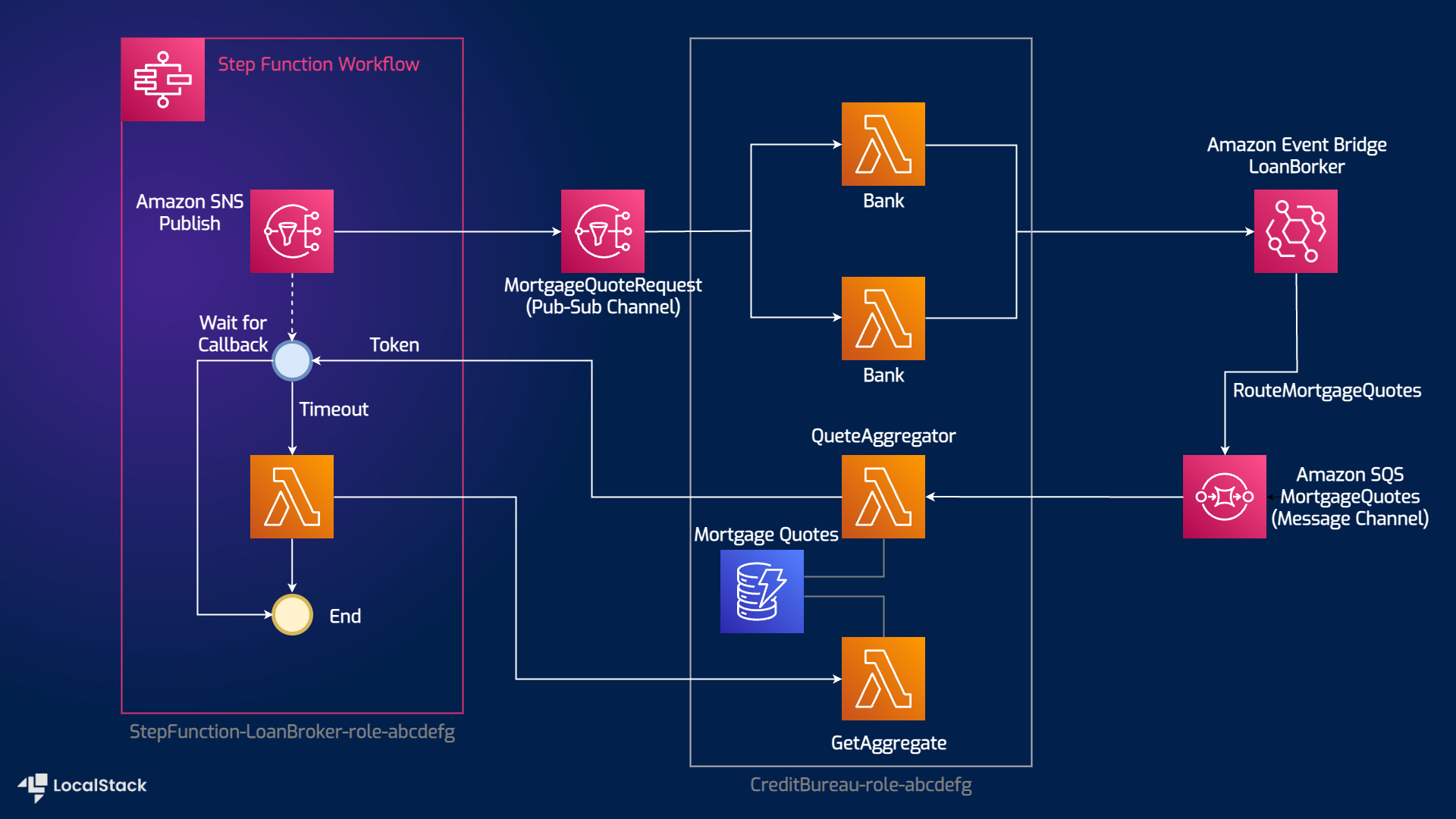
Architecture diagram
The following diagram shows the architecture that this sample application builds and deploys:
- Step Functions to controls the sequence of activities and transfer data between components for the Loan Broker.
- Lambda functions to implement the business logic for the Loan Broker, Banks and Aggregator in the application.
- SNS to publish messages and broadcasts loan quote requests to any subscribing banks.
- SQS to ferry loan quotes from the banks to the Aggregator.
- DynamoDB as a key-value and document database to persist the Aggregator's state.
Prerequisites
- LocalStack Pro with the
localstackCLI. - Cloud Development Kit with the
cdklocalinstalled. - AWS CLI with the
awslocalwrapper. - Node.js, and
yarn.
Start LocalStack Community edition:
DEBUG=1 localstack startWe specified DEBUG=1 to get the printed LocalStack logs directly in the terminal to help us see the event-driven architecture in action. If you prefer running LocalStack in detached mode, you can add the -d flag to the localstack start command, and use Docker Desktop to view the logs.
Instructions
You can build and deploy the sample application on LocalStack by running our Makefile commands. To deploy the infrastructure, you can run make deploy after installing the application dependencies, and run the test steps manually. Here are instructions to deploy and test it manually step-by-step.
Deploying the application
To create the AWS infrastructure locally, you can use CDK and our cdklocal wrapper. Before you can deploy the infrastructure, you need to install the application dependencies:
yarnTo deploy the infrastructure, you can run the following command:
cdklocal bootstrap
cdklocal deploy --allThis will deploy the LoanBroker-RecipientList-Stack and LoanBroker-PubSub-Stack stacks. You will see the following output:
Outputs:
LoanBroker-RecipientList-Stack.LoanBrokerArn = arn:aws:states:us-east-1:000000000000:stateMachine:LoanBroker-RecipientList-Stack-LoanBroker641FC9A8-dd79232c
Stack ARN:
arn:aws:cloudformation:us-east-1:000000000000:stack/LoanBroker-RecipientList-Stack/e7929928Take a note of the LoanBroker-RecipientList-Stack.LoanBrokerArn output. You will need it to test the application.
Testing the application
Before you can test the application, you need to pre-populate the LoanBrokerBanksTable for the RecipientsList stack:
awslocal dynamodb put-item \
--table-name=LoanBrokerBanksTable \
--item='{ "Type": { "S": "Home" }, "BankAddress": {"L": [ { "S": "BankRecipientPremium" }, { "S": "BankRecipientUniversal" }, { "S": "BankRecipientPawnshop" } ] } }'We can start the State Machine execution to get quotes from the banks after submitting a loan application. Run the following command:
awslocal stepfunctions start-execution \
--name=cli-test-run \
--state-machine-arn=<STATE_MACHINE_ARN> \
--input="{\"SSN\": \"123-45-6789\", \"Amount\": 500000, \"Term\": 30 }"Replace <STATE_MACHINE_ARN> with the LoanBroker-RecipientList-Stack.LoanBrokerArn output from the previous step. The result will contain the Execution ARN and the start date:
{
"executionArn": "arn:aws:states:us-east-1:000000000000:execution:LoanBroker-RecipientList-Stack-LoanBroker641FC9A8-dd79232c:cli-test-run",
"startDate": "2023-04-24T21:08:35.434000+05:30"
}You can use the Execution ARN to see the output of the State Machine execution:
awslocal stepfunctions describe-execution \
--execution-arn=<EXECUTION_ARN> \
--query="output" | jq -r '. | fromjson'Replace the <EXECUTION_ARN> with the executionArn output from the previous step. The result will contain the output of the State Machine execution:
{
"SSN": "123-45-6789",
"Amount": 500000,
"Term": 30,
"Credit": {
"Score": 861,
"History": 15
},
"Banks": {
"BankAddress": [
"BankRecipientPremium",
"BankRecipientUniversal",
"BankRecipientPawnshop"
]
},
"Quotes": [
{
"Quote": {
"rate": 3.881919225968371,
"bankId": "Premium"
}
},
{
"Quote": {
"rate": 5.032719931679686,
"bankId": "Universal"
}
},
{
"Quote": {
"rate": 6.019381689166033,
"bankId": "PawnShop"
}
}
]
}GitHub Action
This application sample hosts an example GitHub Action workflow that starts up LocalStack, builds the Lambda functions, and deploys the infrastructure on the runner. You can find the workflow in the .github/workflows/main.yml file. To run the workflow, you can fork this repository and push a commit to the main branch.
Users can adapt this example workflow to run in their own CI environment. LocalStack supports various CI environments, including GitHub Actions, CircleCI, Jenkins, Travis CI, and more. You can find more information about the CI integration in the LocalStack documentation.
Cloud Pods
Cloud Pods are a mechanism that allows you to take a snapshot of the state in your current LocalStack instance, persist it to a storage backend, and easily share it with your team members.
You can convert your current AWS infrastructure state to a Cloud Pod using the localstack CLI. Check out our Getting Started guide and LocalStack Cloud Pods CLI reference to learn more about Cloud Pods and how to use them.
To inject a Cloud Pod that contains the infrastructure for this application, you can run the following command:
localstack pod load file://$(pwd)/cloud-pod/loan-broker-applicationAlternatively, you can use Cloud Pods Launchpad to quickly inject Cloud Pods into your running LocalStack container. Click on the [badge] to launch Cloud Pods Launchpad and inject the Cloud Pod for this application by clicking the Inject button.
You can use the LocalStack Web Application to view the Step Functions Resource Browser and see the State Machine that the Cloud Pod injected. Similarly, you can navigate to the DynamoDB to see the LoanBrokerBanksTable table, alongside Lambda functions, SNS topic, SQS queue, and more that the Cloud Pod injected.