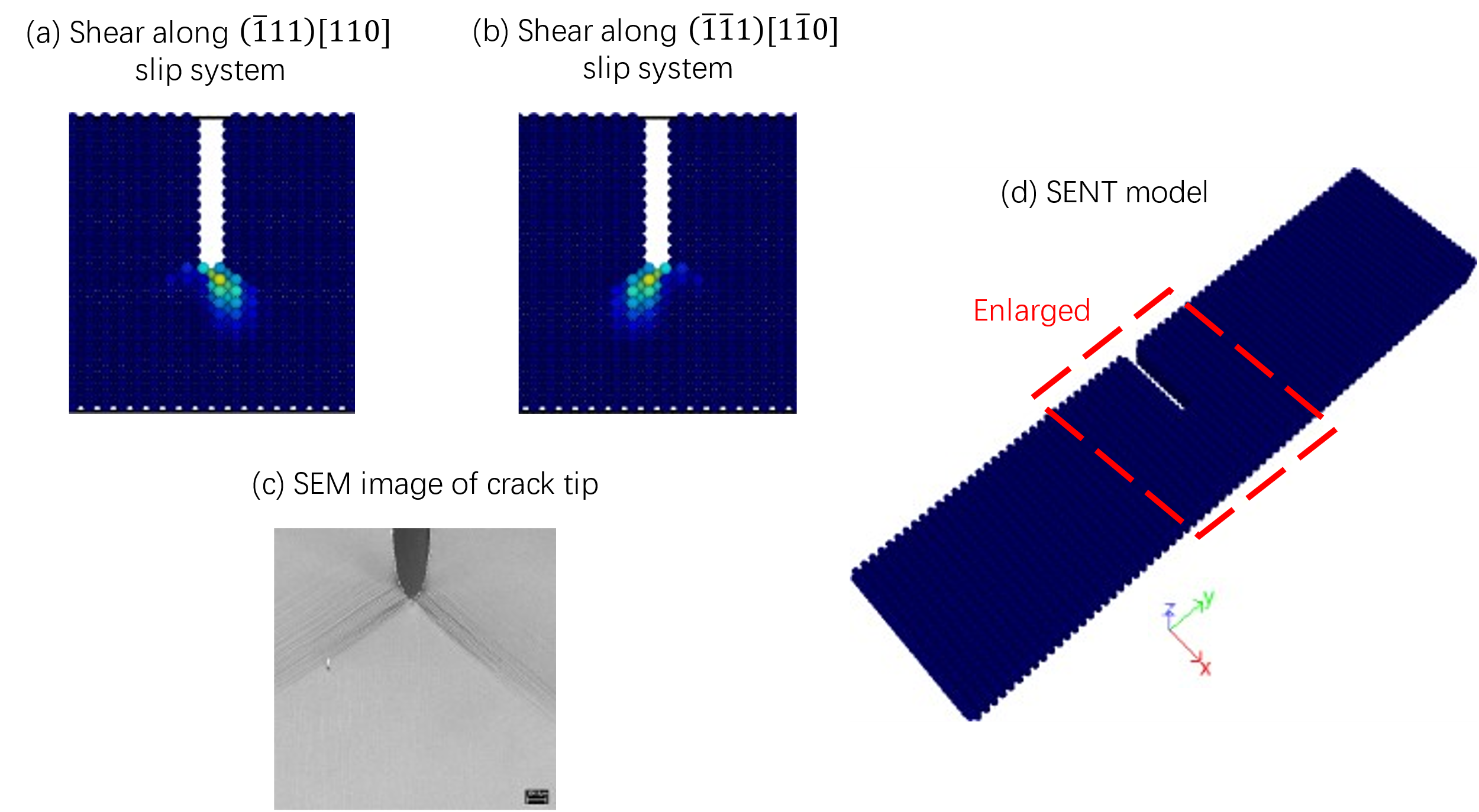
A multi-threaded implementation of a nonlocal lattice particle method (LPM) using an iterative solution procedure. The default force unit is N, displacement unit is mm, pressure unit is MPa. Below shows the image of slip system activation in a SENT sample [1].
- Install Homebrew from
https://brew.sh/ - Install LLVM and openmp:
brew install llvmandbrew install libomp, add into environment variables - Install CMake:
brew install cmake - Install OpenBLAS:
brew install openblas, exportOpenBLAS_DIRenvironment variables for OpenBLAS .cmake files - Install Boost:
brew install boost, exportOpenBLAS_DIRenvironment variables for Boost .cmake files - Download Eigen from
https://eigen.tuxfamily.org/ - Export Eigen root folder into
CPLUS_INCLUDE_PATHenvironment variable - Properly setup the IDE configuration
git pull https://github.com/longfish/LPM-CPP.gitunderLPM-CPPfolder if need an updated version of the codemkdir build && cd buildcmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release# change from Release to Debug for debugging (e.g., valgrind)cmake --build . -j 8
./lpmcpp
The results will be in the build folder.
There are some example files in the ./examples folder that contains additional numerical cases such as those in [1, 2]. They define the run() functions of the project. Please change/add the example file and also include them into src/lmpcpp.cpp to run the code. Please note that other code pieces, such as assembly.h, lpm.h, etc. may also need to be changed.
To ease some common geometries that often see in numerical simulations, customized loading and geometry codes are provided. The loading folder contains Jupyter code, while geometry folder contains cpp code.
- Meng C, Wei H, Chen H, et al. Modeling plasticity of cubic crystals using a nonlocal lattice particle method[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 385: 114069.
- Meng C, Liu Y. Damage-augmented nonlocal lattice particle method for fracture simulation of solids[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2022, 243: 111561.
- Valgrind command:
valgrind --leak-check=yes --show-leak-kinds=all --log-file=valgrind.rpt ./lpmcpp