English | 简体中文
- 1 Change History
- 2 About This Document
- 3 SDK Overview
- 4 Preparations
- 5 Typical Access Scenarios
- 6 SDK APIs
- 7 Generating an SDK Library File
- 8 Open-Source Protocols
Click here to download earlier versions of source code.
This document uses an example to describe how to use iot-device-sdk-cSharp (SDK for short) to quickly connect MQTT devices to the HUAWEI CLOUD IoT platform. The SDK is designed for embedded devices with powerful computing and storage capabilities. You can call SDK APIs to implement communication between devices and the platform. The SDK currently supports:-
Product model: reporting device messages/properties/events and receiving the platform's commands/messages/events/requests for setting properties
-
Child device message forwarding and child device management
-
Over-the-air (OTA) upgrades
-
Secret authentication and certificate authentication for device access
-
Topic customization
-
Device shadow query
-
Custom log collection
SDK Directory Structure
* Linux operating system * GCC (V4.8 or later) The SDK depends on the OpenSSL, Paho, and zlib libraries. If you have your own compilation chains, compile these library files.- Compiling the OpenSSL Library
-
Visit the OpenSSL website and download the latest version. (This document uses openssl-1.1.1d.tar.gz as an example.)
-
Upload the OpenSSL package to a directory (for example, /home/test) on the Linux compiler.
-
Run the tar -zxvf openssl-1.1.1d.tar.gz command to decompress the package.

-
Run the cd openssl-1.1.1d command to access the OpenSSL source code directory.
-
Run the ./config shared --prefix=/home/test/openssl --openssldir=/home/test/openssl/ssl command to generate a Makefile. prefix is a custom installation directory, openssldir is a custom directory that stores configuration files, and shared is used to generate a dynamic link library (.so library).
If the compilation goes wrong, add **no-asm** to the configuration command, indicating that no assembly code is used../config no-asm shared --prefix=/home/test/openssl --openssldir=/home/test/openssl/ssl

-
In the OpenSSL source code directory, run the make depend command to add dependencies.
-
Run the make command to start compilation.
-
Run the make install command to install OpenSSL.
In the OpenSSL installation directory (home/test/openssl), find the lib folder, which stores the library files (libcrypto.so.1.1 and libssl.so.1.1) and soft links (libcrypto.so and libssl.so).
-
Copy these files to the lib folder of the SDK and copy the openssl folder in the home/test/openssl/include directory to the include folder of the SDK.

-
Compiling the Paho Library
-
Click here to download the paho.mqtt.c source code.
-
Decompress the package and upload it to the Linux compiler.
-
Run the vim Makefile command to edit Makefile.
-
Run the :set nu command to display the number of lines.
-
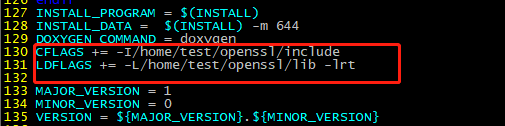
Add CFLAGS += -I/home/test/openssl/include and LDFLAGS += -L/home/test/openssl/lib -lrt to the end of line 129. (The /home/test/openssl/include directory stores OpenSSL header files, and the /home/test/openssl/lib directory stores OpenSSL library files, as customized in 4.2 Compiling Library Files)
-
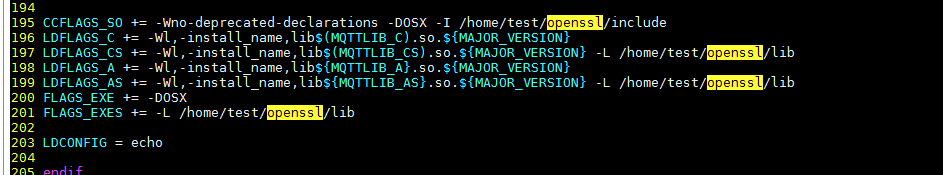
Change the addresses in lines 195, 197, 199, and 201 as follows.
-
Run the make clean command.
-
Run the make command.
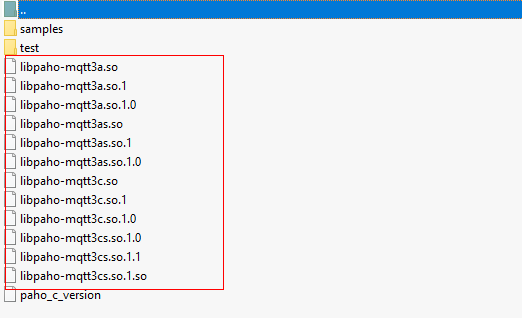
After the compilation is complete, check the compiled libraries in the build/output directory.
-
Copy the Paho library. Currently, the SDK uses only libpaho-mqtt3as. Copy the libpaho-mqtt3as.so and libpaho-mqtt3as.so.1 files to the lib folder of the SDK, and copy the header files (MQTTAsync.h, MQTTClient.h, MQTTClientPersistence.h, MQTTProperties.h, MQTTReasonCodes.h, and MQTTSubscribeOpts.h) in the src folder of the Paho source code directory to the include/base directory of the SDK.
-
-
Compiling the zlib Library
-
Download the zlib source code package.
-
Run the unzip zlib-1.2.11.zip command to decompress the package.
-
Run the cd zlib-1.2.11 command to access the source code directory.
-
Run the ./configure command to generate a Makefile.
-
Run the Makefile.
-
Copy .so library files. Copy the libz.so, libz.so.1, and libz.so.1.2.11 files generated in the source code directory to the lib folder of the SDK.
-
Visit IoT Device Access (IoTDA) and click Use Now to access the IoTDA console.
-
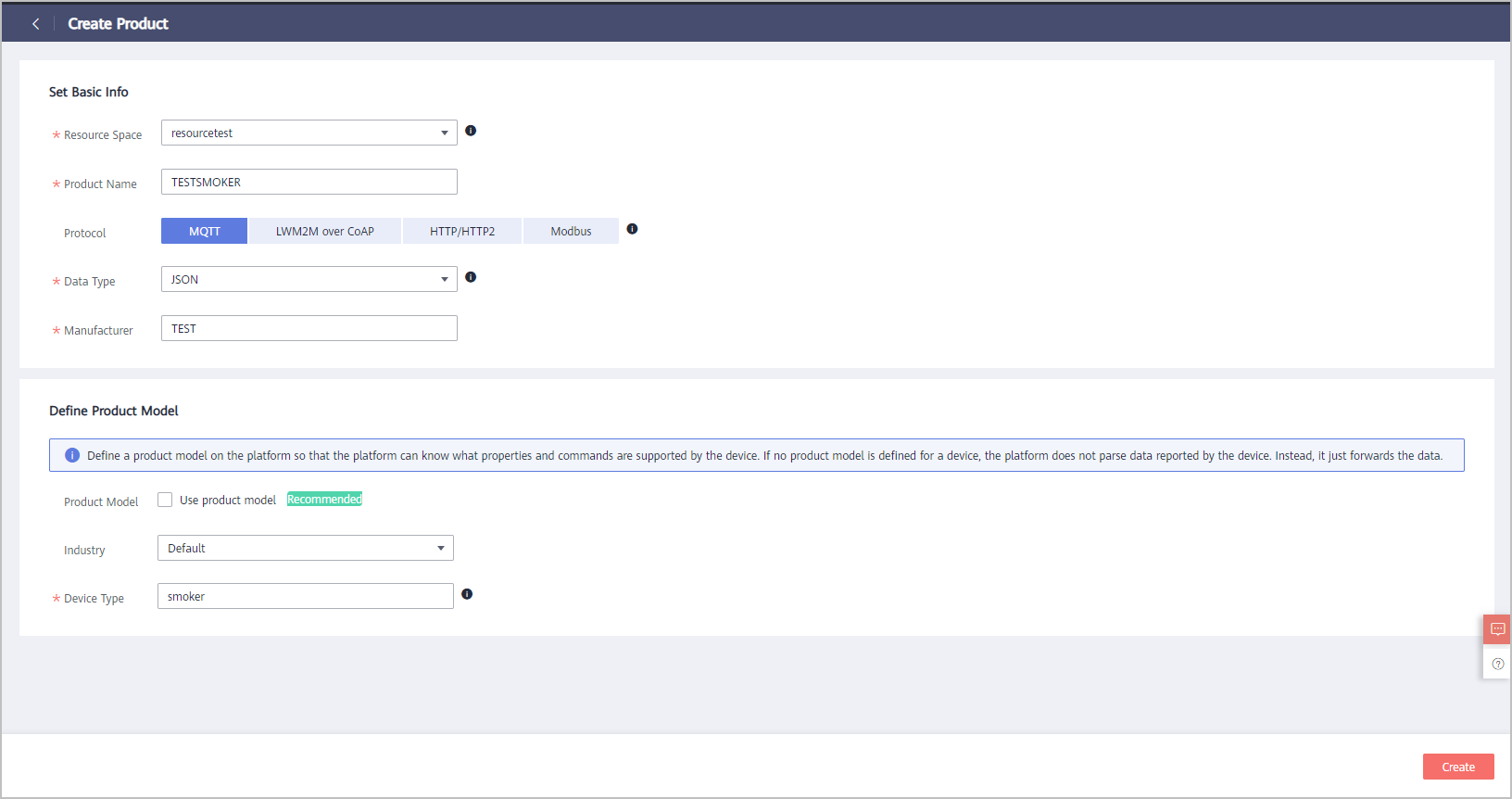
On the IoTDA console, choose Products in the navigation pane, and click Create Product in the upper right corner. On the displayed page, specify the product name, protocol, data type, manufacturer, industry, and device type, and click Create.
-
After the product is created, click View to access its details. On the Model Definition page, click Import Local Profile to upload the developed product model.
-
In the navigation pane, choose Device > All Devices. On the page displayed, click Individual Register in the upper right corner. On the page displayed, set the device registration parameters and click OK.
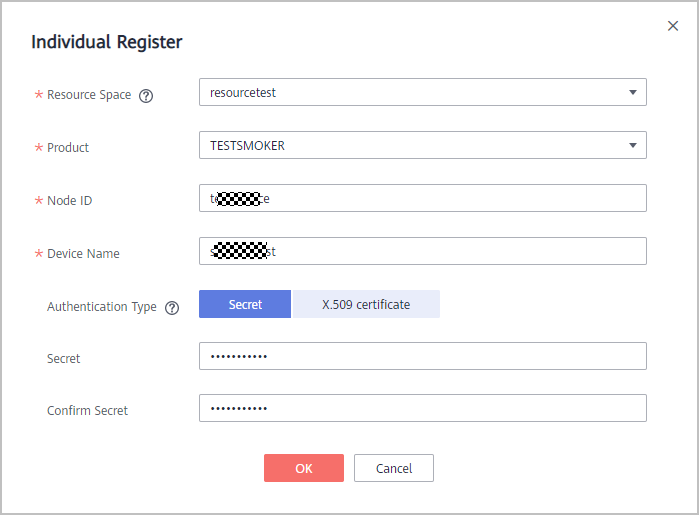
After the device is registered, save the node ID, device ID, and secret.
-
Access Using a Device ID (Username)/Secret
-
Register a device on the platform and obtain the device ID and secret.
-
Set a mode for the device to access using a secret.
void SetAuthConfig() { IOTA_ConfigSetStr(EN_IOTA_CFG_MQTT_ADDR, serverIp_); IOTA_ConfigSetUint(EN_IOTA_CFG_MQTT_PORT, port_); IOTA_ConfigSetStr(EN_IOTA_CFG_DEVICEID, username_); IOTA_ConfigSetStr(EN_IOTA_CFG_DEVICESECRET, password_); IOTA_ConfigSetUint(EN_IOTA_CFG_AUTH_MODE, EN_IOTA_CFG_AUTH_MODE_SECRET); //IOTA_ConfigSetUint(EN_IOTA_CFG_AUTH_MODE, EN_IOTA_CFG_AUTH_MODE_CERT); //IOTA_ConfigSetStr(EN_MQTT_CFG_PRIVATE_KEY_PASSWORD, "yourPassword"); }
-
Copy the SDK package to the Linux environment and run the unzip huaweicloud-iot-device-sdk-c-master.zip command to decompress the package.
-
Run the cd huaweicloud-iot-device-sdk-c-master command to access the decompressed folder.
-
Modify parameters in the src/device_demo/device_demo.c file:
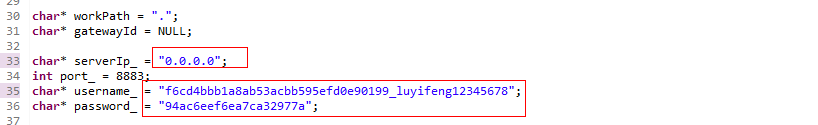
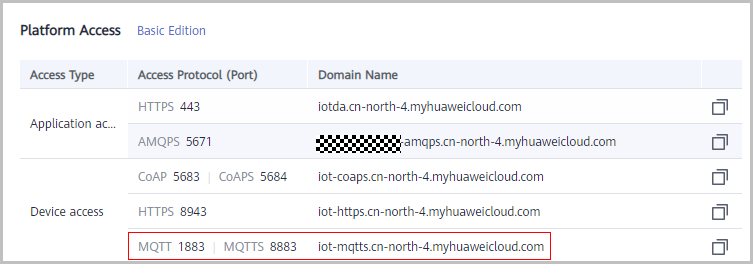
serverIp: indicates the application access address, which can be viewed on the Overview page of the console.
username: indicates the device ID, which is returned after the device is registered. The MQTT protocol requires writing into a username.
password: indicates the device secret, which is returned after the device is registered.
-
Run the make command to perform compilation. (For a 32-bit operating system, delete -m64 from Makefile.)
-
Run the export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=./lib/ command to load the library files.
-
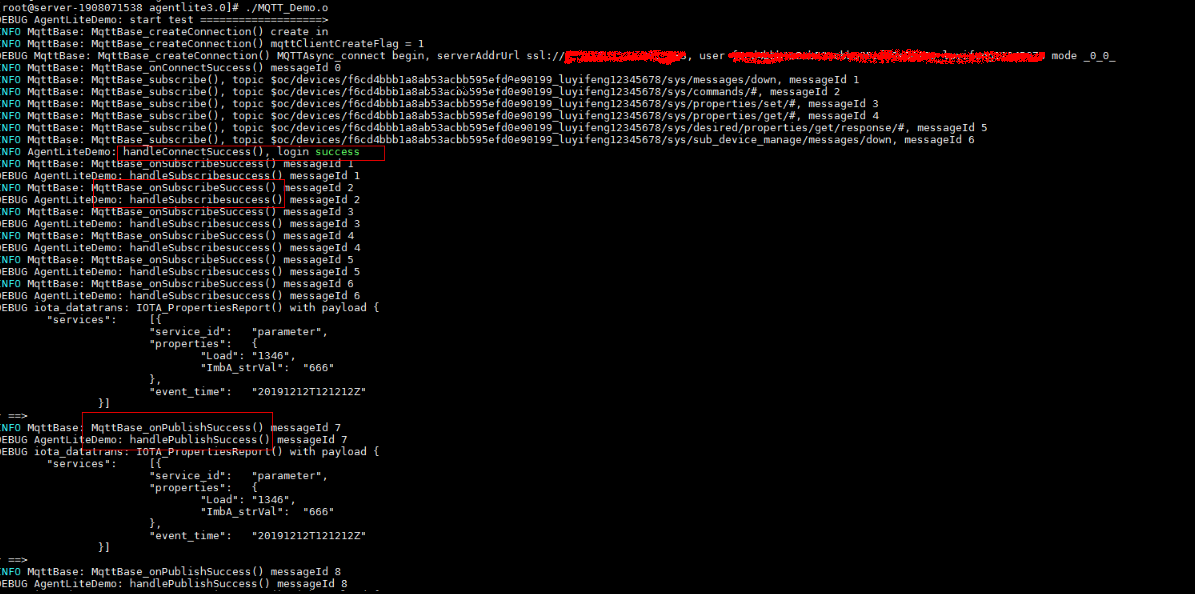
Run the ./MQTT_Demo.o command. The following logs are displayed on the console: login success indicates that a device is authenticated. MqttBase_onSubscribeSuccess indicates that a topic is subscribed, MqttBase_onPublishSuccess indicates that device data is published.
-
Check the running state of the device.
-
Gateway (online): Access the console and choose All Devices > Device List to check whether the gateway is online.
-
Gateway (reporting data): Access the console and choose All Devices > Device List, and click View to view the reported data.
-
Child device
-
A gateway receives the platform's notification of adding a child device.
-
A child device reports data.
-
Check the state of the child device.
- Online: Access the console and choose All Devices > Device List to check whether the child device is online.
- Reporting data: Access the console and choose All Devices > Device List, and click View to view the reported data.
-
-
-
Access Using a Certificate
-
- Create and upload a device certificate. For details, see Registering a Device Authenticated by an X.509 Certificate.
-
Change the certificate and secret file names to deviceCert.pem and deviceCert.key respectively, and place the two files in the conf directory of the SDK.
-
Set a mode for the device to access using a certificate.
void SetAuthConfig() { IOTA_ConfigSetStr(EN_IOTA_CFG_MQTT_ADDR, serverIp_); IOTA_ConfigSetUint(EN_IOTA_CFG_MQTT_PORT, port_); IOTA_ConfigSetStr(EN_IOTA_CFG_DEVICEID, username_); // IOTA_ConfigSetStr(EN_IOTA_CFG_DEVICESECRET, password_); // IOTA_ConfigSetUint(EN_IOTA_CFG_AUTH_MODE, EN_IOTA_CFG_AUTH_MODE_SECRET);
IOTA_ConfigSetUint(EN_IOTA_CFG_AUTH_MODE, EN_IOTA_CFG_AUTH_MODE_CERT); IOTA_ConfigSetStr(EN_MQTT_CFG_PRIVATE_KEY_PASSWORD, "yourPassword"); }4. For details about subsequent access steps, see steps 3 to 9 in **Access Using a Device ID (Username)/Secret**. Note: You do not need to enter the secret. -
The SDK provides a demo of generic-protocol access (TCP). Go to the src/gateway_demo directory and you will see the following files:
- gateway_server_demo.c: provides a demo related to a generic-protocol gateway, which is used to receive device data, decode the data, and report it to the platform. In addition, this gateway can be used to encode and deliver the platform's commands to devices.
- generic_tcp_protocol.c: provides custom encoding and decoding rules of the TCP protocol, so that the data from the platform can be encoded and then sent to a device, and the device data is decoded and then sent to the platform.
- gateway_client_demo.c: provides a demo related to a TCP device (simulating a client), which is used to report data and receive commands. After being decoded based on the rules defined in generic_tcp_protocol.c, the data is reported to the platform from the TCP device. After being encoded based on the rules defined in generic_tcp_protocol.c, the platform's commands are delivered to the TCP device.
** Access Procedures**
-
Refer to 4.2 Compiling Library Files to compile the library files. (Go to the next step if the library files have been compiled.)
-
Register a device and save the device ID and secret.
-
Update the device ID and secret in gateway_server_demo.c.
-
Comment out device_demo.o from OBJS in Makefile and uncomment generic_tcp_protocol.o gateway_server_demo.o.
-
Run the make command to perform compilation.
-
After the compilation is complete, run the **export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=./lib/ ** command to import the library files to the lib folder.
-
Run the ./MQTT_Demo.o command to run a gateway.
-
Run the gcc -o client.o gateway_client_demo.c command to access the src/gateway_demo directory and compile the client.
-
Run the ./client.o command to run the client.
-
Report data.
After the client is started, enter **123** on the client console. The decoded data is displayed on the gateway console and the reported device data can be viewed on the platform.
For details about the decoding rules, see generic_tcp_protocol.c.
You can provision devices to different regions. For details, see the access examples in Getting StartedNote: The SDK has automatically implemented the bootstrap device in the example. For details, see the User Guide</a.Comment out device_demo.o from OBJS in Makefile and uncomment bootstrap_demo.o.

- Compiling and Running the Program
-
Copy the huaweicloud-iot-device-sdk-c-master.zip package to the Linux environment and run the unzip huaweicloud-iot-device-sdk-c-master.zip command to decompress the package.
-
Run the cd huaweicloud-iot-device-sdk-c-master command to access the folder.
-
Run the make command to perform compilation.
-
Run the ./MQTT_Demo.o command to run the SDK demo.
void IOTA_SetPrintLogCallback(PFN_LOG_CALLBACK_HANDLER pfnLogCallbackHandler)
To print logs on the console, refer to vprintf(format, args) set in the myPrintLog function in the demo.
To print logs to the system log file, refer to the vsyslog(level, format, args) set in the myPrintLog function in the demo. In addition, #include "syslog.h" and #define _SYS_LOG should be contained.
Before establishing communication, call the **IOTA_Init()** function to initialize the SDK. Refer to **IOTA_Init()** called by the **main()** function in the demo. For details about the parameters, see **API Reference (C)**.IOTA_Init(HW_CHAR *pcWorkPath)
void setAuthConfig(){
IOTA_ConfigSetStr(EN_IOTA_CFG_MQTT_ADDR, serverIp_);
IOTA_ConfigSetUint(EN_IOTA_CFG_MQTT_PORT, port_);
IOTA_ConfigSetStr(EN_IOTA_CFG_DEVICEID, username_);
IOTA_ConfigSetStr(EN_IOTA_CFG_DEVICESECRET, password_);
IOTA_ConfigSetUint(EN_IOTA_CFG_AUTH_MODE, EN_IOTA_CFG_AUTH_MODE_SECRET); // Secret mode
/**
* Configuration is required in certificate mode:
*
* IOTA_ConfigSetUint(EN_IOTA_CFG_AUTH_MODE, EN_IOTA_CFG_AUTH_MODE_CERT);
* IOTA_ConfigSetStr(EN_MQTT_CFG_PRIVATE_KEY_PASSWORD, "yourPassword");
* */
#ifdef _SYS_LOG
//IOTA_ConfigSetUint(EN_IOTA_CFG_LOG_LOCAL_NUMBER, LOG_LOCAL7);
IOTA_ConfigSetUint(EN_IOTA_CFG_LOG_LEVEL, LOG_INFO);
#endif
}- Obtain serverIp (EN_IOTA_CFG_MQTT_ADDR) and port (EN_IOTA_CFG_MQTT_PORT) from the IoTDA console.
- Obtain username (EN_IOTA_CFG_DEVICEID) and password (EN_IOTA_CFG_DEVICESECRET) after the device is registered.
When _SYS_LOG is defined (print a log in the system file), the facility type (EN_IOTA_CFG_LOG_LOCAL_NUMBER) and display level (EN_IOTA_CFG_LOG_LEVEL) of the log can be customized as required.
The SDK provides callback functions for you to implement service processing logic based on different events, including device authentication, device disconnection from the platform, message subscription, publication, and receiving, and command receiving. Refer to **setMyCallbacks()** called by main() function in the following demo.void setMyCallbacks(){
IOTA_SetProtocolCallback(EN_IOTA_CALLBACK_CONNECT_SUCCESS, HandleConnectSuccess);
IOTA_SetProtocolCallback(EN_IOTA_CALLBACK_CONNECT_FAILURE, HandleConnectFailure);
IOTA_SetProtocolCallback(EN_IOTA_CALLBACK_DISCONNECT_SUCCESS, HandleDisConnectSuccess);
IOTA_SetProtocolCallback(EN_IOTA_CALLBACK_DISCONNECT_FAILURE, HandleDisConnectFailure);
IOTA_SetProtocolCallback(EN_IOTA_CALLBACK_CONNECTION_LOST, HandleConnectionLost);
IOTA_SetProtocolCallback(EN_IOTA_CALLBACK_SUBSCRIBE_SUCCESS, HandleSubscribesuccess);
IOTA_SetProtocolCallback(EN_IOTA_CALLBACK_SUBSCRIBE_FAILURE, HandleSubscribeFailure);
IOTA_SetProtocolCallback(EN_IOTA_CALLBACK_PUBLISH_SUCCESS, HandlePublishSuccess);
IOTA_SetProtocolCallback(EN_IOTA_CALLBACK_PUBLISH_FAILURE, HandlePublishFailure);
IOTA_SetMessageCallback(HandleMessageDown);
IOTA_SetUserTopicMsgCallback(HandleUserTopicMessageDown);
IOTA_SetCmdCallback(HandleCommandRequest);
IOTA_SetPropSetCallback(HandlePropertiesSet);
IOTA_SetPropGetCallback(HandlePropertiesGet);
IOTA_SetEventCallback(HandleEventsDown);
IOTA_SetShadowGetCallback(HandleDeviceShadowRsp);
}- The HandleConnectSuccess function is called when a device is authenticated.
- The HandleConnectFailure function is called when a device fails to be authenticated.
- The HandleDisConnectSuccess function is called when a device proactively disconnects from the platform.
- The HandleDisConnectFailure function is called when a device fails to proactively disconnect from the platform.
- The HandleConnectionLost function is called when the connection between a device and the platform is lost.
- The HandleSubscribesuccess function is called when a message is subscribed.
- The HandleSubscribeFailure function is called when a message fails to subscribe.
- The HandlePublishSuccess function is called when device data is published.
- The HandlePublishFailure function is called when device data fails to publish.
- The HandleMessageDown function is called when a device receives the platform's transparently transmitted message (default topic), which is not parsed by the platform.
- The HandleUserTopicMessageDown function is called when a device receives the platform's transparently transmitted message (custom topic), which is not parsed by the platform.
- The HandleCommandRequest function is called when a device receives the platform's command.
- The HandlePropertiesSet function is called when a device receives the platform's request for setting device properties.
- The HandlePropertiesGet function is called when a device receives the platform's request for querying device properties.
- The HandleEventsDown function is called when a device receives the platform's notification of an event (a child device addition or deletion event or an OTA event).
- The HandleDeviceShadowRsp function is called when a device receives device shadow data.
After HW_INT IOTA_Connect() is called, the message login success is displayed. It is recommended that data be reported after a device is authenticated and sleeps for several seconds or process services via the callback function invoked when the device is authenticated.
 You can view that the gateway is online on the console.
You can view that the gateway is online on the console.
You can press Ctrl + C to stop the program. After that, you can view that the device is offline.
After a device is authenticated, a gateway can call SDK APIs to report device messages and properties. In addition, the gateway can report the command execution result, property setting result, and property query result. It is recommended that the interval for reporting data be greater than or equal to hundreds of milliseconds.-
Function for reporting a device message
HW_INT IOTA_MessageReport(HW_CHAR *object_device_id, HW_CHAR *name, HW_CHAR *id, HW_CHAR *content)The data reported via this function is not parsed by the platform. It can be forwarded to other services or pushed to the application server. object_device_id indicates the device to report messages. name indicates the message name. id indicates the message ID. content indicates the content to report. topicParas indicates the parameters of a custom topic. If this parameter is set to NULL, the default topic of the platform is used to report data. Refer to the Test_MessageReport function in the demo. For details about the parameters, see API Reference (C).
void Test_MessageReport() { //default topic // int messageId = IOTA_MessageReport(NULL, "data123", "123", "hello", NULL);
//user topic int messageId = IOTA_MessageReport(NULL, "data123", "123", "hello", "devMsg"); if (messageId != 0) { PrintfLog(EN_LOG_LEVEL_ERROR, "device_demo: Test_MessageReport() failed, messageId %d\n", messageId); } }
- **Function for reporting device properties**
`HW_INT IOTA_PropertiesReport(ST_IOTA_SERVICE_DATA_INFO pServiceData[], HW_INT serviceNum)`
The data reported via this function is parsed by the platform and the data in the structure must be the same as the properties defined in the product model. **ST_IOTA_SERVICE_DATA_INFO** indicates a structure array. A gateway can report multiple services at the same time. **serviceNum** indicates the number of services to report. Refer to the **Test_propertiesReport** function in the demo. For details about the parameters, see **API Reference (C)**.
```c
void Test_propertiesReport() {
int serviceNum = 2; // Number of services to be reported by a gateway
ST_IOTA_SERVICE_DATA_INFO services[serviceNum];
//---------------the data of service1-------------------------------
char *service1 = "{\"Load\":\"5\",\"ImbA_strVal\":\"6\"}";
// services[0].event_time = GetEventTimesStamp(); //you need to free the services[0].event_time
services[0].event_time = NULL;
services[0].service_id = "parameter";
services[0].properties = service1;
//---------------the data of service2-------------------------------
char *service2 = "{\"PhV_phsA\":\"4\",\"PhV_phsB\":9}";
// services[1].event_time = GetEventTimesStamp(); //you need to free the services[1].event_time
services[0].event_time = NULL;
services[1].service_id = "analog";
services[1].properties = service2;
int messageId = IOTA_PropertiesReport(services, serviceNum);
if(messageId != 0) {
PrintfLog(EN_LOG_LEVEL_ERROR, "device_demo: Test_batchPropertiesReport() failed, messageId %d\n", messageId);
}
}
- A device receives a message (transparently transmitted message).
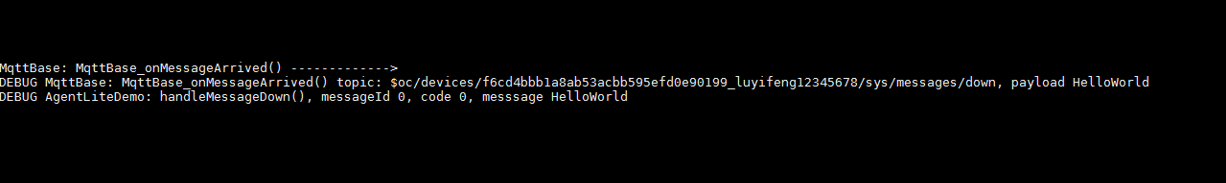 After receiving a message, the device processes it via a callback function. For details, see the HandleMessageDown function in the demo. (Set the callback function in advance for processing the platform's messages.)
After receiving a message, the device processes it via a callback function. For details, see the HandleMessageDown function in the demo. (Set the callback function in advance for processing the platform's messages.) - A device receives the platform's command as defined in the product model.
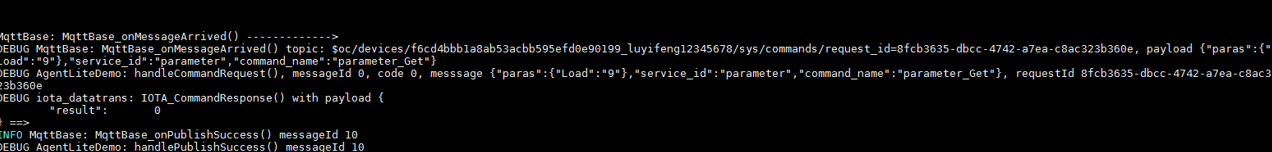
- A device receives the platform's request for setting device properties.
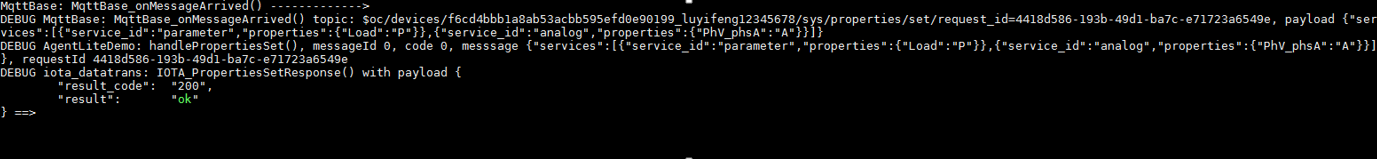 After receiving the platform's request for setting device properties, call the IOTA_PropertiesSetResponse function to report the response. For details, see the HandlePropertiesSet function in the demo. (Set the callback function in advance.)
After receiving the platform's request for setting device properties, call the IOTA_PropertiesSetResponse function to report the response. For details, see the HandlePropertiesSet function in the demo. (Set the callback function in advance.) - A device receives the platform's request for querying device properties.
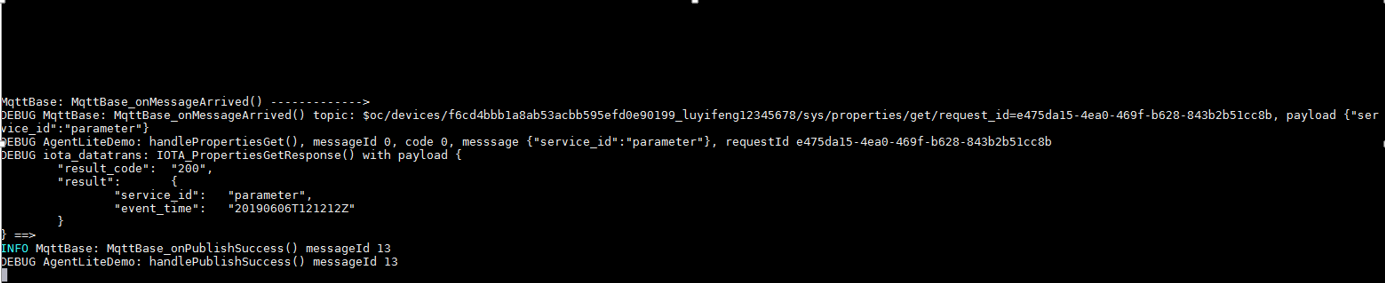 After receiving the platform's request for querying device properties, call the IOTA_PropertiesGetResponse function to report the device's response. For details, see the HandlePropertiesGet function in the demo. (Set the callback function in advance.)
After receiving the platform's request for querying device properties, call the IOTA_PropertiesGetResponse function to report the device's response. For details, see the HandlePropertiesGet function in the demo. (Set the callback function in advance.) - The platform notifies a gateway of child device addition.
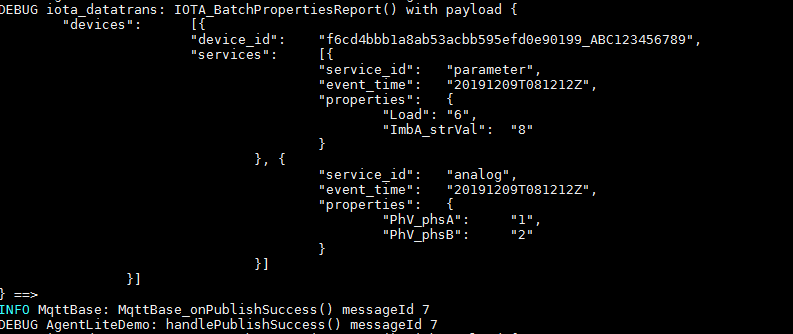
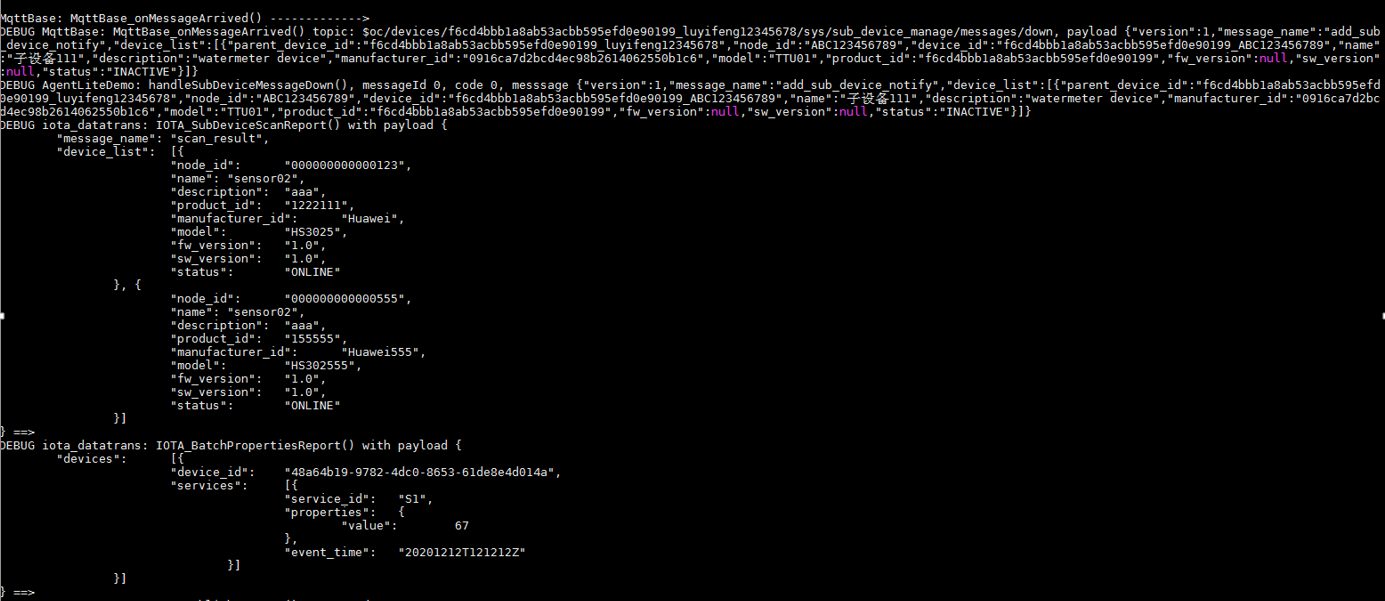 After receiving the notification, call the IOTA_BatchPropertiesReport function to report child device data (view the reported data on the console). For details, see the HandlePropertiesGet function in the demo. (Set the callback function in advance.)
After receiving the notification, call the IOTA_BatchPropertiesReport function to report child device data (view the reported data on the console). For details, see the HandlePropertiesGet function in the demo. (Set the callback function in advance.) - The platform notifies a gateway of child device deletion.
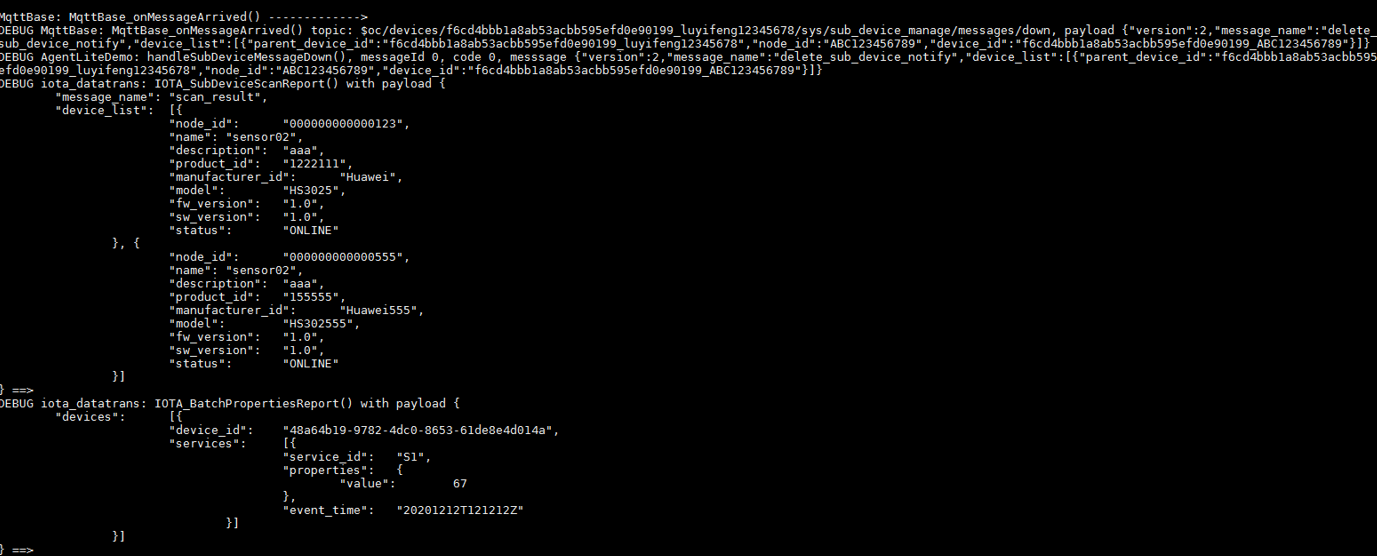
HW_INT IOTA_BatchPropertiesReport(ST_IOTA_DEVICE_DATA_INFO pDeviceData[], HW_INT deviceNum, HW_INT serviceLenList[])
The data reported via this function is parsed by the platform. The data in the structure must be the same as that defined in the product model. ST_IOTA_DEVICE_DATA_INFO indicates a structure array. Multiple child devices can report data at the same time and each child device can report multiple services. deviceNum indicates the number of child devices to report data. serviceLenList indicates the number of services reported by a child device. Refer to the Test_batchPropertiesReport function in the demo. For details about parameters, see API Reference (C).
```c
void Test_BatchPropertiesReport() {
int deviceNum = 1; // Number of child devices to report data
ST_IOTA_DEVICE_DATA_INFO devices[deviceNum]; // Array hosting the structure of data to be reported by child devices
int serviceList[deviceNum]; // Number of services to be reported by each child device
serviceList[0] = 2; // **device1** needs to report two services.
// serviceList[1] = 1; // **device2** needs to report one service.
char *device1_service1 = "{\"Load\":\"1\",\"ImbA_strVal\":\"3\"}"; // Properties to be reported by **service1** (in JSON format)
char *device1_service2 = "{\"PhV_phsA\":\"2\",\"PhV_phsB\":\"4\"}";// Properties to be reported by **service2** (in JSON format)
devices[0].device_id = subDeviceId;
devices[0].services[0].event_time = "20191209T081212Z";
devices[0].services[0].service_id = "parameter";
devices[0].services[0].properties = device1_service1;
devices[0].services[1].event_time = "20191209T081212Z";
devices[0].services[1].service_id = "analog";
devices[0].services[1].properties = device1_service2;
// char *device2_service1 = "{\"AA\":\"2\",\"BB\":\"4\"}";
// devices[1].device_id = "subDevices22222";
// devices[1].services[0].event_time = "d2s1";
// devices[1].services[0].service_id = "device2_service11111111";
// devices[1].services[0].properties = device2_service1;
int messageId = IOTA_BatchPropertiesReport(devices, deviceNum, serviceList);
if(messageId != 0) {
printfLog(EN_LOG_LEVEL_ERROR, "device_demo: Test_BatchPropertiesReport() failed, messageId %d\n", messageId);
}
}
-
Topic Customization
For details, see API Reference (C) in the home directory.
-
OTA Upgrades
For details, see API Reference (C) in the home directory.
-
Device Shadow Query
For details, see API Reference (C) in the home directory.
To generate a .so file, modify the **Makefile**. You can open the file using Notepad and upload it to the Linux environment. Alternatively, you can directly run the **vim Makefile** to modify the file using in the Linux environment, press **i** to edit the file, and then run **wq!** to save the modification.