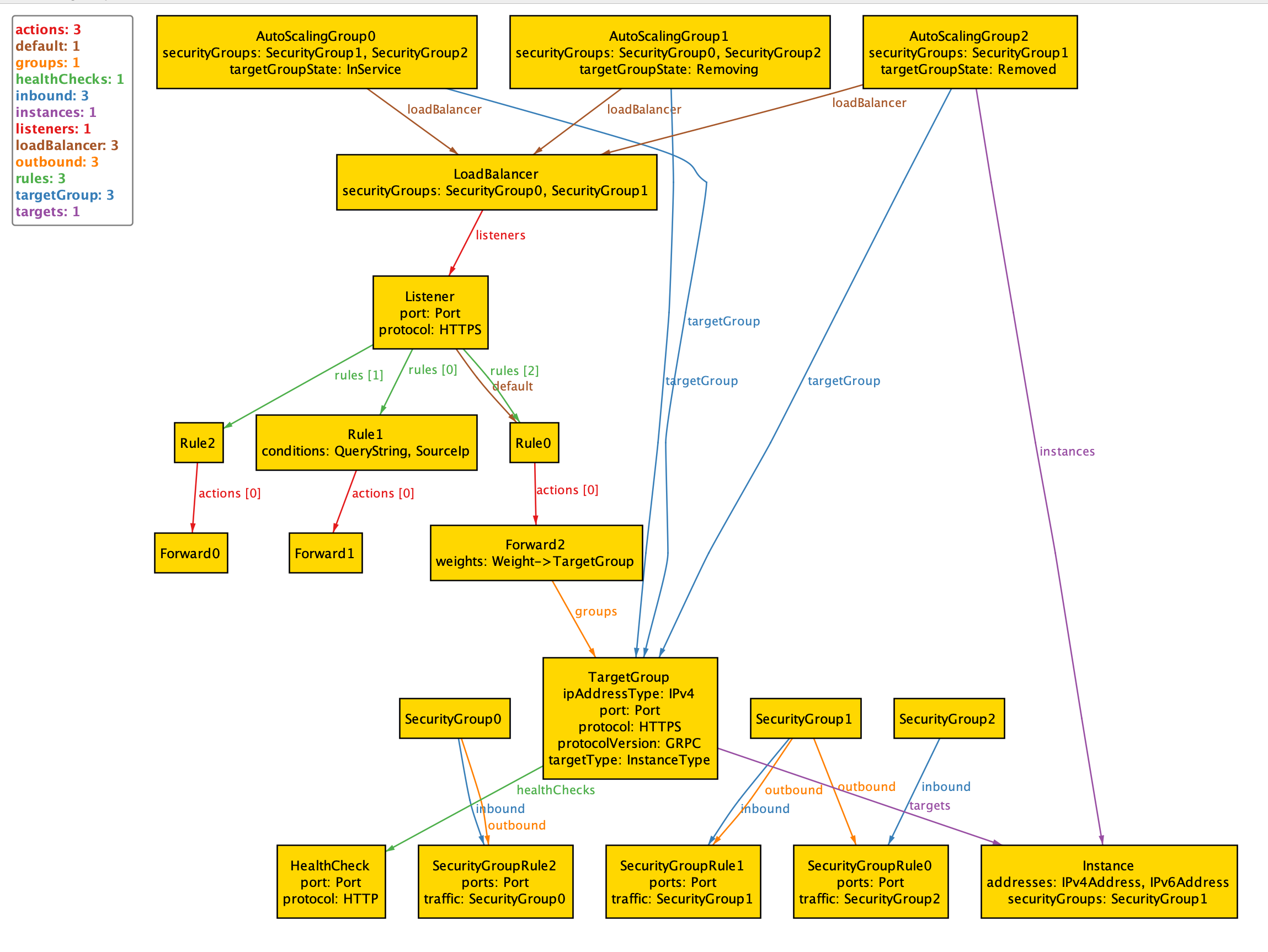
I've always found the configuration details for AWS application load balancers (ALBs) confusing.
To configure an ALB, you need to understand multiple concepts, including:
- listeners
- rules
- actions
- target groups
You also need to understand security groups, otherwise your ALB won't actually be able to serve traffic. And, if you use autoscaling groups, you'll need to understand how those relate to ALBs.
The large number of moving parts makes ALBs an excellent candidate for modeling in Alloy, which is what this repo contains. I've annotated my model with comments that are copy-pasted from the ALB docs.
Note that you can load this Markdown file directly in the Alloy Analyzer. I've also saved the theme file that I've used (it's called theme.thm) for the visualization.
Here are some common models we're going to need. Note that Alloy doesn't require us to specify them before they are used, but I decided to put them up front. Most of these should be self-explanatory.
// In the actual AWS API, duration is an integer that represents the duration in seconds
// But we don't need to model it at that level of detail here
sig Duration {}
abstract sig Protocol {}
one sig HTTP, HTTPS extends Protocol {}
sig Port {}
abstract sig IpAddressType {}
one sig IPv4, IPv6 extends IpAddressType {}
// Note that we only explicitly model the 301 and 302 codes.
sig StatusCode {}
one sig HTTP_301, HTTP_302 extends StatusCode {}
sig ContentType {}
sig HostName {}
sig Path {}
sig Query {}Before we dive in to ALBs, we're going to model security groups.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/userguide/VPC_SecurityGroups.html
sig SecurityGroup {
inbound: set SecurityGroupRule,
outbound: set SecurityGroupRule
}
sig SecurityGroupRule {
protocol: SecurityGroupProtocol,
ports: some Port,
// source for inbound, dest for outbound
// We aren't modeling prefix lists here
traffic: IPv4Address+IPv6Address+IPv4Range+IPv6Range+SecurityGroup
}
abstract sig IpAddress {}
sig IPv4Address, IPv6Address extends IpAddress {}
abstract sig IpRange {
addresses: set IpAddress
}
sig IPv4Range extends IpRange {} {
addresses in IPv4Address
}
sig IPv6Range extends IpRange {} {
addresses in IPv6Address
}
sig SecurityGroupProtocol {}
// There are other protocols, but here we're only modeling TCP
one sig TCP extends SecurityGroupProtocol {}We also create a convenience function to check for access between AWS entities. We assume both source and destination entities are associated with a collection of security groups.
// True if src is allowed to reach dest on port
pred allows[source : set SecurityGroup, dest : set SecurityGroup, port: Port] {
// inbound access allowed to dest from source
some rule : dest.inbound | {
// allows access on the port
port in rule.ports
// from the "source" security group
some source & rule.traffic
}
// outbound access allowed to dest from source
some rule : source.outbound {
// allows access on the port
port in rule.ports
some dest & rule.traffic
}
}Here's where we actually start to model the load balancer.
// A load balancer serves as the single point of contact for clients
sig LoadBalancer {
// You add one or more listeners to your load balancer.
listeners: set Listener,
securityGroups: set SecurityGroup,
} {
// The docs don't specify this, but presumably the listeners have to be on different ports
no disj l1, l2: listeners | l1.port=l2.port
// The rules for the security groups that are associated with your load balancer
// must allow traffic in both directions on both the listener and the health check ports.
// Allow inbound access to the listener
all l: Listener | some s : securityGroups | {
l.port in s.inbound.ports
}
//
// Allow the load balancer to hit the instances on their listener ports and health check ports
//
// All target groups (other than lambdas, which don't have security groups)
let grps = listeners.rules.elems.actions.elems.groups | {
all targetGroup : grps | {
// Each security group of the targets in the group must allow inbound access on the target group port
all target : targetGroup.targets | {
allows[securityGroups, target.@securityGroups, targetGroup.port]
all healthCheck : targetGroup.healthChecks |
allows[securityGroups, target.@securityGroups, healthCheck.port]
}
}
}
}
// A listener checks for connection requests from clients, using the protocol and port that
// you configure.
sig Listener {
// A listener is configured for a specific protocol and port
protocol: Protocol,
port: Port,
// The rules that you define for a listener determine how the load balancer routes requests
// to its registered targets.
// They are sorted in priority order
rules: seq Rule,
// You must define a default rule for each listener
default: Rule
} {
// Rules are unique. Even if two rules have the same values,
// they're still different rules according to Alloy
not rules.hasDups
// The default rule is evaluated last.
default in rules.last
// the default rule cannot have any conditions
// https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/application/listener-update-rules.html
no default.conditions
}
// Each rule consists of a priority, one or more actions, and one or more conditions.
// We model the priority as a sequence on the listener, rather than in the Rule sig
sig Rule {
actions: seq Action,
// conditions that need to match for the rule to fire
// not sure if any or all conditions have to match
conditions: set Condition
} {
// Each rule must include exactly one of the following actions: forward, redirect, or fixed-response
// and it must be the last action to be performed.
some s : actions.elems | {
s in Forward+Redirect+FixedResponse // one of those actions
no (actions.elems - s ) & Forward+Redirect+FixedResponse // it's the only one
s in actions.last // it's the last action
// it's not in the other acitons
no s & actions.butlast.elems
}
// Each rule can optionally include up to one of each of the following conditions: host-header, http-request-method, path-pattern, and source-ip.
lone conditions & (HostHeader+HttpRequestMethod+PathPattern+SourceIp)
// Each rule can also optionally include one or more of each of the following conditions: http-header and query-string.
// Alloy permits this by default, so nothing to specify here
}
fact "All rules are associated with a listener" {
all r : Rule | some l: Listener | r in l.rules.elems
}
sig Priority {}abstract sig Action {}
// We don't model these in detail, for more details, see:
// https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/APIReference/API_AuthenticateCognitoActionConfig.html
// https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/APIReference/API_AuthenticateOidcActionConfig.html
lone sig AuthenticateCognito, AuthenticateOidc extends Action {}
fact "authenticate actions require https listener" {
all l : Listener |
some l.rules.elems.actions.elems & (AuthenticateCognito+AuthenticateOidc) => l.protocol = HTTPS
}sig FixedResponse extends Action {
statusCode: StatusCode,
contentType: ContentType,
messageBody: MessageBody
}
sig MessageBody {}//
sig Forward extends Action {
groups: set TargetGroup,
weights: Weight->groups,
// sticky sessions are optionally configured.
// If enabled, specify a duration
// For more details on stickiness, see: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/application/sticky-sessions.html
stickiness: lone Duration
} {
// All groups get some weight
all group : groups | some weights.group
}
// Each target group weight is a value from 0 to 999
// We don't model the weights explicitly here.
sig Weight {}
//
// Redirect target: protocol://hostname:port/path?query
sig Redirect extends Action {
statusCode: HTTP_301+HTTP_302,
protocol: Protocol,
hostname: HostName,
port: Port,
path: Path,
query: Query
}// // You can specify up to three match evaluations per condition, but we don't model that explicitly here
abstract sig Condition {}
// https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/application/load-balancer-listeners.html#host-conditions
// Route based on the host name of each request
sig HostHeader extends Condition {}
// https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/application/load-balancer-listeners.html#http-header-conditions
// Route based on the HTTP headers for each request
sig HttpHeader extends Condition {}
// https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/application/load-balancer-listeners.html#http-request-method-conditions
// Route based on the HTTP request method of each request
sig HttpRequestMethod extends Condition {}
// Route based on path patterns in the request URLs.
// https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/application/load-balancer-listeners.html#path-conditions
sig PathPattern extends Condition {}
// Route based on path patterns in the request URLs.
// https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/application/load-balancer-listeners.html#query-string-conditions
sig QueryString extends Condition {}
// Route based on the source IP address of each request
// https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/application/load-balancer-listeners.html#source-ip-conditions
sig SourceIp extends Condition {}
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/application/load-balancer-target-groups.html
// Each target group routes requests to one or more registered targets, such as EC2 instances,
// using the protocol and port number that you specify.
sig TargetGroup {
protocol: Protocol,
port: Port,
targetType: TargetType,
ipAddressType: IpAddressType,
targets: set Target,
// You can configure health checks on a per target group basis.
healthChecks: set HealthCheck,
protocolVersion: ProtocolVersion
} {
// Targets have to match the type
(targetType in InstanceType) => targets in Instance
(targetType in IpType) => targets in IP
(targetType in LambdaType) => {
targets in Lambda
// For lambdas, only one target
one targets
}
// Considerations for the gRPC protocol version
(protocolVersion = GRPC) => {
// The only supported listener protocol is HTTPS.
protocol = HTTPS
// The only supported action type for listener rules is forward.
// The model already enforces this, because you can only specify a target group with a forward rule
// The only supported target types are instance and ip.
targetType in InstanceType+IpType
// You cannot use Lambda functions as targets.
// This sounds redundant with the one above
}
// Considerations for the HTTP/2 protocol version
(protocolVersion = HTTP2) => {
// The only supported listener protocol is HTTPS.
protocol = HTTPS
// The only supported action type for listener rules is forward.
// The model already enforces this, because you can only specify a target group with a forward rule
// The only supported target types are instance and ip.
targetType in InstanceType+IpType
}
}
abstract sig TargetType {}
// The targets are specified by instance ID.
one sig InstanceType extends TargetType {}
// The targets are IP addresses
// For restrictions by CIDR block, see: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/application/load-balancer-target-groups.html#target-type
one sig IpType extends TargetType {}
// The target is a Lambda function.
one sig LambdaType extends TargetType {}
// https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/application/load-balancer-target-groups.html#target-group-protocol-version
abstract sig ProtocolVersion {}
one sig HTTP1_1, HTTP2, GRPC extends ProtocolVersion {}
abstract sig Target {}
abstract sig SecurityGroupTarget extends Target {
securityGroups: set SecurityGroup
}
sig IP extends SecurityGroupTarget {
// An IP is associated with a single IP address
address: IpAddress
}
fact "addresses are unique" {
no disj ip1, ip2 : IP | ip1.address = ip2.address
}
sig Instance extends SecurityGroupTarget {
// An instance can have multiple IP addresses, must have at least one
addresses: some IpAddress
}
fact "all addresses are associated with at most one instance" {
all addr : IpAddress | lone (Instance <: addresses).addr
}
// Lambdas don't use security groups for access permissions, they use a different mechanism, see:
// https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/services-alb.html
sig Lambda extends Target {}https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/application/target-group-health-checks.html
// Health checks are performed on all targets registered to a target group that is specified in a listener rule for your load balancer.
sig HealthCheck {
protocol: Protocol,
port: Port,
// Confusingly, a "path" in the redirect actions is separate from the query: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/application/load-balancer-listeners.html#redirect-actions
// Here, the path includes the query, so we use a different model
path: HealthCheckPath,
timeout: Duration,
interval: Duration,
healthyThreshold: Count,
unhealthyThreshold: Count,
// The codes to use when checking for a successful response from a target. These are called Success codes in the console.
matcher: set StatusCode
}
sig HealthCheckPath {
path: Path,
query: lone Query
}
// Model of an integer count
sig Count {}Interestingly, you don't add an autoscaling group to a load balancer. Instead, you add a load balancer to an autoscaling group. Presumably, the ASG service is responsible for adding and removing targets to/from the load balancer's target group.
sig AutoScalingGroup {
instances: set Instance,
securityGroups: set SecurityGroup,
loadBalancer: lone LoadBalancer,
targetGroup: lone TargetGroup,
targetGroupState : TargetGroupState
} {
// All of the instances have the same security group configuration
all i : instances | securityGroups = i.@securityGroups
// if the ASG is associated with a load balancer, it is associated with a target group
some loadBalancer => some targetGroup
}
fact "instance can be in at most one ASG" {
all disj i1, i2 : Instance | no (instances.i1 & instances.i2)
}
// https://docs.aws.amazon.com/autoscaling/ec2/APIReference/API_LoadBalancerTargetGroupState.html
abstract sig TargetGroupState {}
one sig Adding, Added, InService, Removing, Removed extends TargetGroupState {}fact "no unowned entities of interest" {
all l: Listener | some listeners.l
all t: TargetGroup | some f : Forward | t in f.groups
all action : Action | some rule : Rule | action in rule.actions.elems
all h : HealthCheck | some t: TargetGroup | h in t.healthChecks
all asg : AutoScalingGroup | some asg.loadBalancer
}
// We'll focus specifically on security-group related security group rules in our outputs
fact "Only security group based security group rules" {
SecurityGroupRule.traffic in SecurityGroup
// We just won't generate any of the IP related stuff
no IP
no IpRange
}
fact "all instances are owned by ASGs" {
Instance in AutoScalingGroup.instances
}
run {
one LoadBalancer
some AutoScalingGroup.instances
some LoadBalancer.listeners
all t : TargetGroup | some t.targets
// No auth for now, to keep things simple
no AuthenticateCognito
no AuthenticateOidc
}