Over the next few days, we will get you acclimated with using Angular. Angular is a massive framework, so obviously we won't get through all of it, but by the end of the next few lessons, you will be proficient enough to get started!
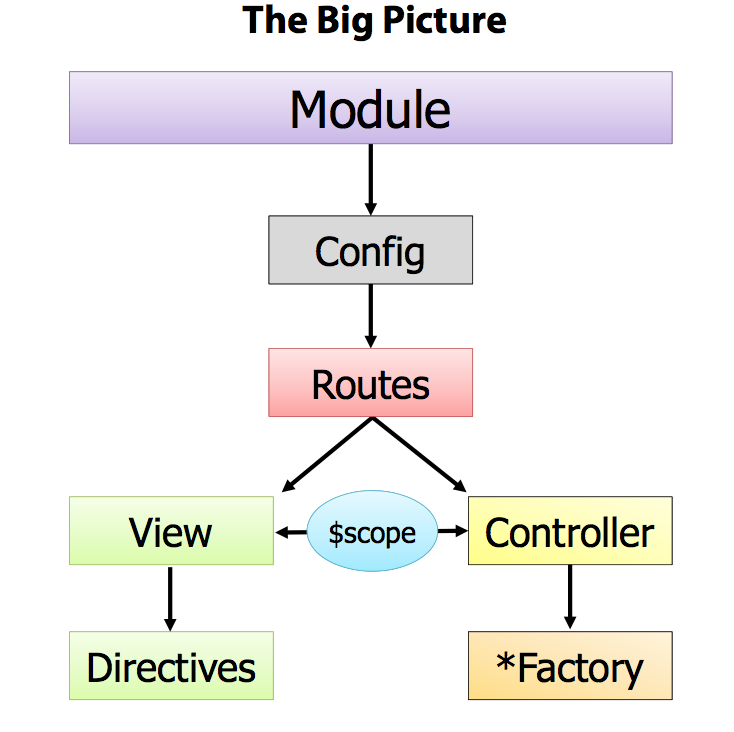
Angular is a client-side structural framework that was developed by Google. It leverages javascript to give our HTML a fresh batch of steriods. How, you ask?
-
Data-Binding
We've used templating engines like Handlebars to bind data to templates with javascript before, but now, our template will be written in html and live in the DOM. Angular's template engine binds the data to our template AFTER the DOM has loaded, not before. This allows us to do some nifty tricks like use two-way data-binding.
-
Custom HTML tags
Angular has a feature called Directives that lets us create custom HTML tags to do our bidding. Our dreams of typing <max-rules></max-rules> into our HTML markup have finally come true.
- Bake-in functionality in our HTML tags
Angular let's you write form validation and functionality right into the html tags of forms. Also, the days of writing jQuery event handlers whenever you want to do something dynamic client-side have passed.
We are going to dive into Angular Views. Later we will see how views fit into the Angular architecture.
- Learn the most common Angular Directives.
- Use Angular Filters in views.
- Show how Angular enables two-way Data Binding with Expressions.
- Validate Forms.
- Introduce the concept of ViewModel, $scope.
Just Views for now.
We have included a bower.json file with angular listed as a dependency. Please run bower install to download angular into our repository.
Let's create an Angular Single Page Application (SPA).
- Load Angular js in the page.
- Set the ng-app directive on the html or body tag. This marks it as a Angular application.
- Bind data using the ng-model directives and displays data using an angular expression
{{ }}
Create a directives1.html file and add the below. Then open in a browser.
<!-- 1. ng-app -->
<html ng-app>
<head>
<!-- 2. angular javascript -->
<script type="text/javascript" src='bower_components/angular/angular.js'>
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>First Angular View<h1>
<!-- 3. ng-model -->
<input type='text' ng-model='name' placeholder="Enter name"></input>
<!-- 4. {{ Data Binding Expresssion}} -->
<p> Name's value is: {{name}}</p>
</body>
</html>Wow, we didn't have to write any javascript. No event handling code!!
- The ng-app directive tells the angular.js that this is an angular app.
- Include the Angular javascript.
- The ng-model directive is used to create a property in this view's ViewModel.
- Data Binding Expression will output the value of the property/attribute.
Each Angular View has a ViewModel that can be accessed via the scope syntax. It's a container of attributes. We can think that it's just an object literal with properties.
We'll see later how scope fits into the Angular architecture.
HTML Element attributes or tags provided by Angular that "teaches HTML new tricks".
Are contained in Views, HTML pages. These are Angular specific HTML Elements attributes and tags that enhance or extend HTML.
- They typically start with ng-. But can start with data-ng- to be compatible with HTML validators.
Are contained in Views. These are somewhat like a javascript eval in that they can execute javascript.
The syntax for an expression is {{ ... }} where ... is any javascript expression.
Some Expressions:
{{ 3 + 11 }}
{{ "Mr " + name }}- Templates consist of the raw HTML and Angular directives.
- Views are generated from a Templates in Angular. This is what is shown in the browser.
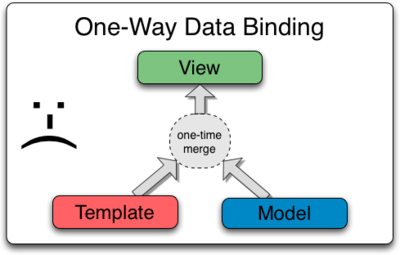
#####Data Binding in Classical Template Systems Most templating systems bind data in only one direction: they merge template and model components together into a view. After the merge occurs, changes to the model or related sections of the view are NOT automatically reflected in the view. Worse, any changes that the user makes to the view are not reflected in the model. This means that the developer has to write code that constantly syncs the view with the model and the model with the view.
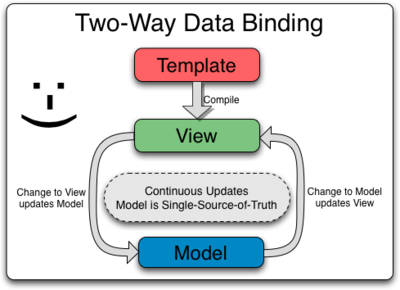
#####Data Binding in Angular Templates
Angular templates work differently. First the template (which is the uncompiled HTML along with any additional markup or directives) is compiled on the browser. The compilation step produces a live view. Any changes to the view are immediately reflected in the model, and any changes in the model are propagated to the view. The model is the single-source-of-truth for the application state, greatly simplifying the programming model for the developer. You can think of the view as simply an instant projection of your model.
Because the view is just a projection of the model, the controller is completely separated from the view and unaware of it. This makes testing a snap because it is easy to test your controller in isolation without the view and the related DOM/browser dependency.
Previously, we used an control oriented approach to handling changes to elements, controls (input fields, ...), on the page. We attached javascript handlers that would process these change events.
With automatic data binding that Angular provides there is no need for all this code. We just bind to the data we're interested in and all places that use that data in the page will change.
Create a template file, directives_email_age.html, that is like the above but it will add input fields for email and age that have bindings to attributes. Show these attributes using expressions.
Let's use the HTML validators and use data-ng- directives.
Create a file directives2.html.
<html data-ng-app>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript" src='bower_components/angular/angular.js'> </script>
</head>
<!-- initialize name attribute to the value 'James' -->
<body data-ng-init="name='James'">
<!-- Bind hide to isHidden -->
<div data-ng-hide="isHidden">
<input type='text' data-ng-model="name" placeholder="Enter name"/>
<p> Name's value is: {{name}}</p>
</div>
<!-- Toggle the isHidden property between true and false -->
Hide: <input type='checkbox' data-ng-model="isHidden"/>
<br/>
<!-- Set the name property to Mortimer -->
<button data-ng-click="name='Mortimer'">Change Name</button>
<script type='text/javascript' src='js/angular.js'></script>
</body>
</html>Now we see a couple of new directives.
- ng-hide - Shows or hides the HTML element depending on the value of the isHidden attribute.
- ng-init - Evaluates expression,
name='James', in the current scope. Creates and initializes the name attribute. - ng-click - Evaluates the expression,
name='Mortimer`. Changes the name attribute's value to 'Mortimer'
In the Chrome debugger notice how the div surrounding the input field gets the class ng-hide when one clicks the checkbox.
Create a file directives3.html.
<html data-ng-app>
<head>
<title>More on Directives</title>
<link href="css/styles.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css">
<script type='text/javascript' src='bower_components/angular/angular.js'></script>
</head>
<!-- Set the initial model property, data. -->
<body data-ng-init="data={name:'James', isVisible: true, loggedIn: false, status: 'red'}">
<div data-ng-switch on="data.loggedIn">
<div data-ng-switch-when="true">
Welcome {{data.name}}
</div>
<div data-ng-switch-default data-ng-class="data.status">Login</div>
</div>
<br/>
<div data-ng-show="data.isVisible">
Name: <input type='text' data-ng-model="data.name" />
{{ data.name }}
</div>
</body>
</html>This will create an object literal, data, that is seen in the view. The data.name is shown if you are logged in. Otherwise show a red login.
Change the data object literal so that:
- Input fields are hidden.
- User is logged in.
This will create an Array of people that contains an object literal for each person. This will emulate an Array that we get from an API using Ajax.
We want to iterate over this people Array and repeat some markup that will show each person.
Create a file directives_repeat.html.
<html ng-app>
<head>
<script type='text/javascript' src='bower_components/angular/angular.js'></script>
</head>
<body>
<div ng-init="people=[{name: 'Tom', city:'Groton'}, {name: 'Mike',
city: 'Tewksbury'}, {name: 'Joe', city: 'Derry'}, {name: 'Ed',city:'Portland'}]">
<h3>Iterating through data with ng-repeat</h3>
<ul>
<li ng-repeat="person in people">{{person.name}} lives in {{person.city}}</li>
</ul>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>City</th>
</tr>
<tr ng-repeat="person in people">
<td>{{ person.name }}</td>
<td>{{ person.city}}</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</body>
</html>- ng-repeat - Add ng-repeat directive to the HTML element you want to repeat. Once for each member of a collection.
Here we are repeating a list element and a table row for each person in the people Array.
Create a list of songs, songs have a title, artist, duration, released (boolean) and price. Show only the songs that are released unless you check a box to show all songs.
Filters can be used to format data, convert it to json, limit the number of items to show, upcase or lower case a string or order data in a collection.
Create directives_orderby.html.
<html ng-app>
<head>
<script type='text/javascript' src='bower_components/angular/angular.js'></script>
</head>
<body ng-init="customers=[{joined: '2000-12-02', name:'John', city:'Chandler', orderTotal: 9.9956}, {joined: '1965-01-25',name:'Zed', city:'Las Vegas', orderTotal: 19.99},{joined: '1944-06-15',name:'Tina', city:'New York', orderTotal:44.99}, {joined: '1995-03-28',name:'Dave', city:'Seattle', orderTotal:101.50}]">
<h3>Customers</h3>
Filter: <input type="text" ng-model="customerFilter.name"/>
<br/>
<br/>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>City</th>
<th>Order Total</th>
<th>Joined</th>
</tr>
<tr ng-repeat="cust in customers | orderBy:'name'">
<td>{{ cust.name }}</td>
<td>{{ cust.city}}</td>
<td>{{ cust.orderTotal | currency }}</td>
<td>{{ cust.joined | date}}</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>-
Order By the name property.
<tr ng-repeat="cust in customers | orderBy:'name'"> -
Can chain filters
<tr ng-repeat="cust in customers | orderBy:'name' | orderBy:'city' "> -
Filter by the name property.
Filter: <input type="text" ng-model="customerFilter.name"/> ... <tr ng-repeat="cust in customers | filter: customerFilter | orderBy:'name'">
Create directives_last.html.
<html ng-app>
<head>
<script type='text/javascript' src='bower_components/angular/angular.js'></script>
</head>
<body ng-init="customers=[{joined: '2000-12-02', name:'John', city:'Chandler', orderTotal: 9.9956}, {joined: '1965-01-25',name:'Zed', city:'Las Vegas', orderTotal: 19.99},{joined: '1944-06-15',name:'Tina', city:'New York', orderTotal:44.99}, {joined: '1995-03-28',name:'Dave', city:'Seattle', orderTotal:101.50}]">
<h3>Customers</h3>
Filter: <input type="text" ng-model="customerFilter.name"/>
<br/>
<br/>
<table>
<tr>
<th ng-click="sortBy='name';reverse=!reverse">Name</th>
<th ng-click="sortBy='city';reverse=!reverse">City</th>
<th ng-click="sortBy='orderTotal';reverse=!reverse">Order Total</th>
<th ng-click="sortBy='joined';reverse=!reverse">Joined</th>
</tr>
<tr ng-repeat="cust in customers | filter: customerFilter | orderBy:sortBy:reverse">
<!-- <tr ng-repeat="cust in customers"> -->
<td>{{ cust.name }}</td>
<td>{{ cust.city}}</td>
<td>{{ cust.orderTotal | currency }}</td>
<td>{{ cust.joined | date}}</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>- Create a model customFilter.name that will use the contents of the input field as a filter.
- Create click handlers for each column.
- Each click handler will:
- Set the sortBy property used in the orderBy filter.
- Toggle the reverse property used in the orderBy filter.
Create a set of songs, like in the last Lab. And use each of the Angular filters to display these songs.