REST API for an E-Banking Portal for returning list of transactions. Contains following features:
- Java 11
- Spring Boot 2
- Postgres DB
- Swagger 2 API documentation
- MrChecker for integration testing
- JMeter for performace testing
- CI/CD Jenkins pipeline configured
- Two environments (DEV and PROD)
Section describes additional setup that is needed if you are going to contribute to repository.
Import code formatter into your IDE
Download: Format_code_standards
- Download the config (attached)
- In the Intellij settings (Ctrl+Alt+S), go to Code Style
- Next to Scheme, click Manage and then Import...
- Select 'Eclipse XML Profile' and browse to the downloaded config file.
- Download the config (attached)
- Navigate to Window->Preferences
- Navigate to Java->Code Style->Formatter
- Click on Import and navigate to the downloaded config file
- Click Apply and Ok
- Install the extension Language Support for Java(TM) by Red Hat.
- File → Preferences → Settings → java.format.settings.url: Set URL (or local file path) pointing to Eclipse Formatter Profile file.
Repository uses client-side git hooks that need to be configured in each development machine separately. See Git hooks document for more details.
Git hooks installation is required.
- Application - http://localhost:8080/
- Swagger UI - http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
- Application status - http://localhost:8080/api/
To run spring app with application-{profile_name}.properties Profile. Default is "dev"
mvn -Pmock spring-boot:run
mvn -Plocal spring-boot:run
mvn -Pdev spring-boot:run
mvn -Pprod spring-boot:run
To run spring app on Dev with arguments
mvn -Pdev -Dspring-boot.run.arguments="--db.user=test --db.pass=test --jwt.sec=secret" spring-boot:run
To run jar app with arguments
java -jar ebank.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev --db.user=test --db.pass=test --jwt.sec=secret
Exchange rate service is implemented as a mocked microservice in https://github.com/lstefaniszyn/e-bank_exchange-rate repository.
EBank application can be run without exchange rate service. In this case, no currency conversion is performed.
When exchange rate service is available, EBank application will return list of transactions with amounts and currencies converted to GBP for /api/v1/transactions endpoint (com.example.ebank.services.TransactionServiceImpl.findInMonthPaginated method).
Example
Example using data from DEV DB with exchange rate service enabled.
curl --location --request GET 'localhost:8080/api/v1/transactions?date=2019-01&size=5'
[{"id":377041,"date":"2019-01-05","amount":304.2898786561228,"currency":"GBP","description":"payment CHF"},{"id":377042,"date":"2019-01-21","amount":219.8950045234303,"currency":"GBP","description":"payment CHF"},{"id":377043,"date":"2019-01-11","amount":336.1576287515951,"currency":"GBP","description":"payment CHF"},{"id":377044,"date":"2019-01-27","amount":108.30920607371392,"currency":"GBP","description":"payment CHF"},{"id":377045,"date":"2019-01-25","amount":125.46708661282963,"currency":"GBP","description":"payment CHF"}]
The way of communicating with external exchange rate API is controlled by 3 properties (example properties in application-dev.properties file):
- service.exchangerate.client - which type of client to use, possible values:
feign,resttemplate - service.exchangerate.url - URL (host and optionally port) on which exchange rate service is available (not including endpoint). See below for details.
- eureka.client.enabled - whether application should register itself in Eureka service discovery server, required for
resttemplateclient type
Properties settings:
service.exchangerate.client=resttemplate
service.exchangerate.url=http://exchange-rate-service
eureka.client.enabled=true
When client type is resttemplate, Eureka service discovery server (com.example.exchangerate.registration.RegistrationServer) should be used. This configuration is especially useful with multiple microservices.
To run Eureka registration server, use below command.
mvn spring-boot:run -DskipTests=true -Dspring.mainClass=com.example.exchangerate.registration.RegistrationServerThen run exchange rate service.
Then run EBank application as usual, for example
mvn -Pdev -DskipTests=true -Dspring-boot.run.arguments="--db.user=<user> --db.pass=<pass>" spring-boot:runRestTemplate-based client is implemented in com.example.ebank.extapi.client.ExchangeRateRestTemplateClient class.
Properties settings:
service.exchangerate.client=feign
service.exchangerate.url=http://localhost:8081
eureka.client.enabled=false
For communication with third-party APIs, Feign client can be used. To test it, run exchange rate application first.
Then run EBank application as usual, for example
mvn -Pdev -DskipTests=true -Dspring-boot.run.arguments="--db.user=<user> --db.pass=<pass>" spring-boot:runFeign-based client is implemented in com.example.ebank.extapi.client.ExchangeRateFeignClient class using com.example.ebank.extapi.client.FeignAPIClient interface for defining REST operations provided by external API.
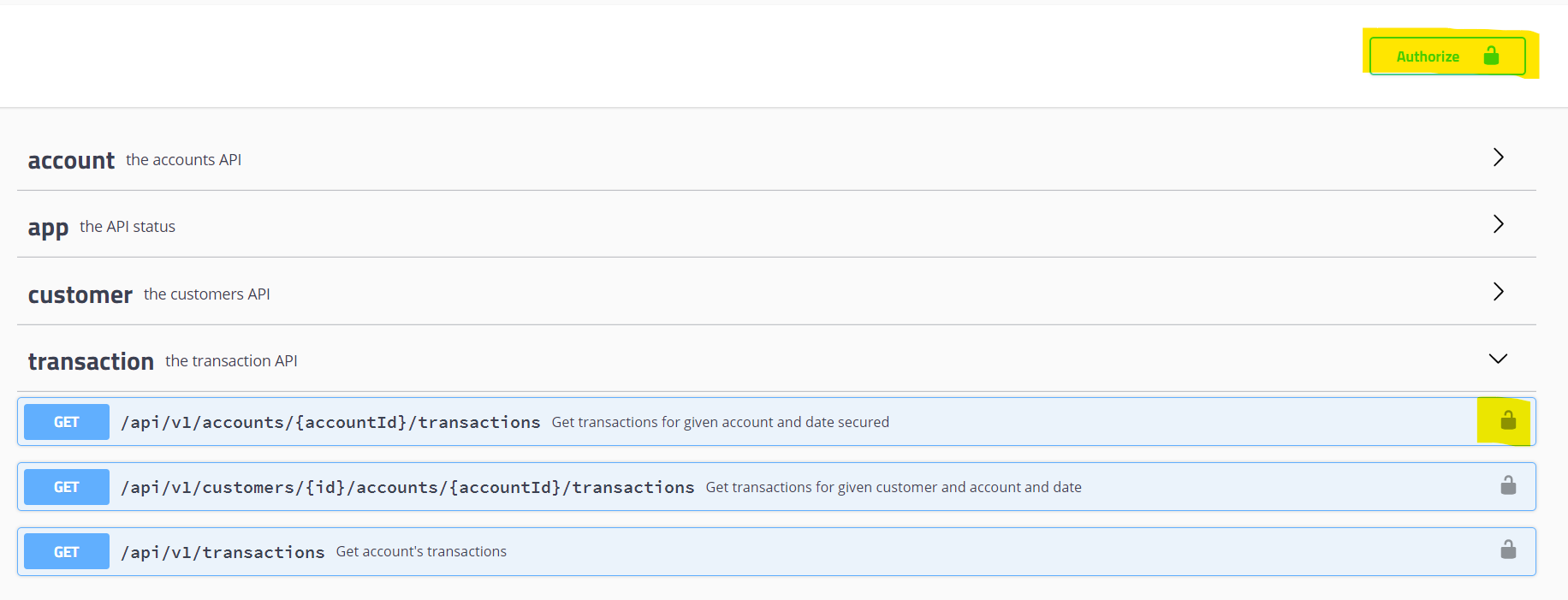
The endpoints /api and /api/v1/customers are NOT secured.
The rest resources require authorization.
To authorize add Authorization header with bearer token.
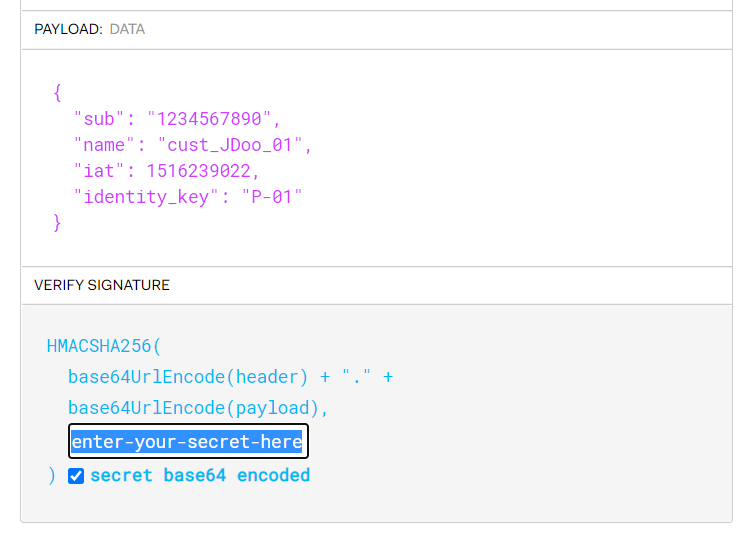
Json Web Token should contain property identity_key for specified customer, e.g.:
header: {
"alg": "HS256",
"typ": "JWT"
}
payload: {
"sub": "1234567890",
"name": "cust_JDoo_01",
"iat": 1516239022,
"identity_key": "P-01"
}
To get encoded Json Web Token use jwt.io with specific identity_key and secret.
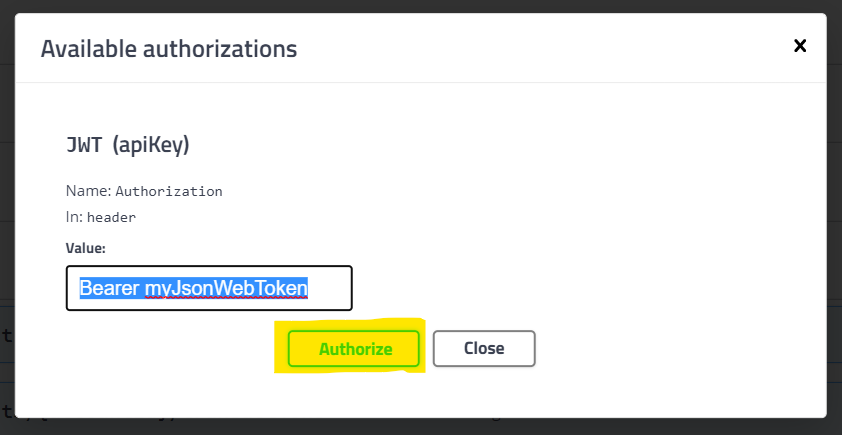
To authorize request with Swagger click on padlock icon on the top or next to the chosen endpoint
Enter bearer token and confirm with Authorize
Now all requests to the server will contain Authorization header with provided token.
kafka.host=
rabbit.hostname=
rabbit.port=
rabbit.user=
rabbit.pass=
db.host=
db.user=
db.pass=
jwt.sec=
Flyway is used as a db version control. Flyway files are located in paths:
src/main/resources/db/migration- all script connected with db schemasrc/main/resources/db/generate- scripts used to generate sample datasrc/main/resources/db/populate- scripts with simple inserting sample data
Please be aware that
/generateandpopulatescripts are mutually exclusive, you should attach at most one of them to the specific profile/generatescripts can run only on PostgreSQL, so they cannot be used with h2 database
Flyway scripts can be attached to profile by spring.flyway.locations property, e.g.:
spring.flyway.locations=classpath:db/migration,classpath:db/generate
Use mock profile while running the application or tests to switch to h2 database in memory instead of PostgreSQL.
mvn -Pmock spring-boot:run
mvn -Pmock test
The h2 db in memory is populated with mocked data. Flyway script is located in a path: src/main/resources/db/populate.
The mocked data include:
- 20 customers with subsequent ids
- 27 accounts with subsequent ids (1 or 2 account(s) per customer)
- from 24 to 30 transactions per month (for each month in period 01/2018 - 12/2019) for first 15 accounts
Currently, only basic REST endpoint integration testing is implemented. For BDD-style testing, steps definitions must be added and optionally also Cucumber integration. Details on how to do it can be found here.
There are a couple of things to be aware of when using Serenity:
-
Serenity only works with JUnit 4. Spring Boot Test starter automatically includes JUnit 5 (Jupiter), so following change needs to be done in
pom.xml:<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId> <artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency>
Also, JUnit 4 has to be included in classpath:
<dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.13</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>
There is some project to integrate Serenity with JUnit 5.
-
To integrate with latest version (4.3.1) of RestAssured, following changes in
pom.xmlare required:Include
serenity-rest-assuredintegration library<dependency> <groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId> <artifactId>serenity-rest-assured</artifactId> <version>${serenity.version}</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>
Use correct version of RestAssured:
<!-- rest-assured version working with serenity-rest (minimal: 4.2.0) --> <dependency> <groupId>io.rest-assured</groupId> <artifactId>rest-assured</artifactId> <version>${rest-assured.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- need to explicitly declare json-path (and xml-path) in correct version --> <dependency> <groupId>io.rest-assured</groupId> <artifactId>json-path</artifactId> <version>${rest-assured.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>io.rest-assured</groupId> <artifactId>xml-path</artifactId> <version>${rest-assured.version}</version> </dependency>
Use correct version of Groovy:
<properties> <groovy.version>3.0.3</groovy.version> </properties>
In order to generate Serenity report from integration tests, invoke following:
mvn clean integration-test serenity:aggregateYou can also run report generation automatically during mvn verify goal. pom.xml configuration:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>serenity-reports</id>
<phase>post-integration-test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>aggregate</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>Generated report is available under target/site/serenity folder.
For convenience and clarity, integration test cases should be created under src/test/java/com/example/ebank/integration folder structure. If you wish to include your test case in Serenity report, you can extend com.example.ebank.integration.serenity.SerenityReportBase abstract class. This class provides integration with Spring libraries, so useful annotations like @Autowired work without any additional configration needed.
To include REST requests in the report, SerenityRest class should be used instead of RestAssured. SerenityRest class is a wrapper around RestAssured, so all familiar methods are available.
Example:
SerenityRest.get(endpoint.getEndpoint());
SerenityRest.restAssuredThat(resp -> resp.statusCode(equalTo(200)));Integration tests use additional Spring profiles it-{environment}. Properties specific for integration tests are set using application-it-{environment}.properties files under src/test/resources folder. Profiles are added using Maven profiles similar to regular environment switching.
For logging, simply use com.example.ebank.utils.logger.BFLogger class and it's static methods (logInfo, logWarn, etc.)
- Enable variable update:
- management.security.enabled=false
- management.endpoint.env.post.enabled=true
- Update variable
curl -X POST localhost:8080/actuator/env -d'{"name":"info.application.name","value":"myTest"}' -H "Content-type: application/json" curl -X GET localhost:8080/actuator/env/info.application.name
curl localhost:8080/actuator/metrics/http.server.requests?tag=status:200 | python -m json.tool