This code allows users to do computations using Truncated Power Series Algebra (TPSA) and/or Differential Algebra (DA). A Python wrapper of this lib is hosted in a separate repository.
For TPSA and DA, please refer to chapter 8 in Lecture Notes on Special Topics in Accelerator Physics by Prof. Alex Chao and chapter 2 in Modern Map Methods in Particle Beam Physics by Prof. Martin Berz.
This code is developed based on Dr. Lingyun Yang's tpsa codes in C++ . His codes (tpsa.cpp and tpsa.h) are included in this repository. They are untouched, except for a few functions that are commented off and replaced by functions in tpsa_extend.cc.
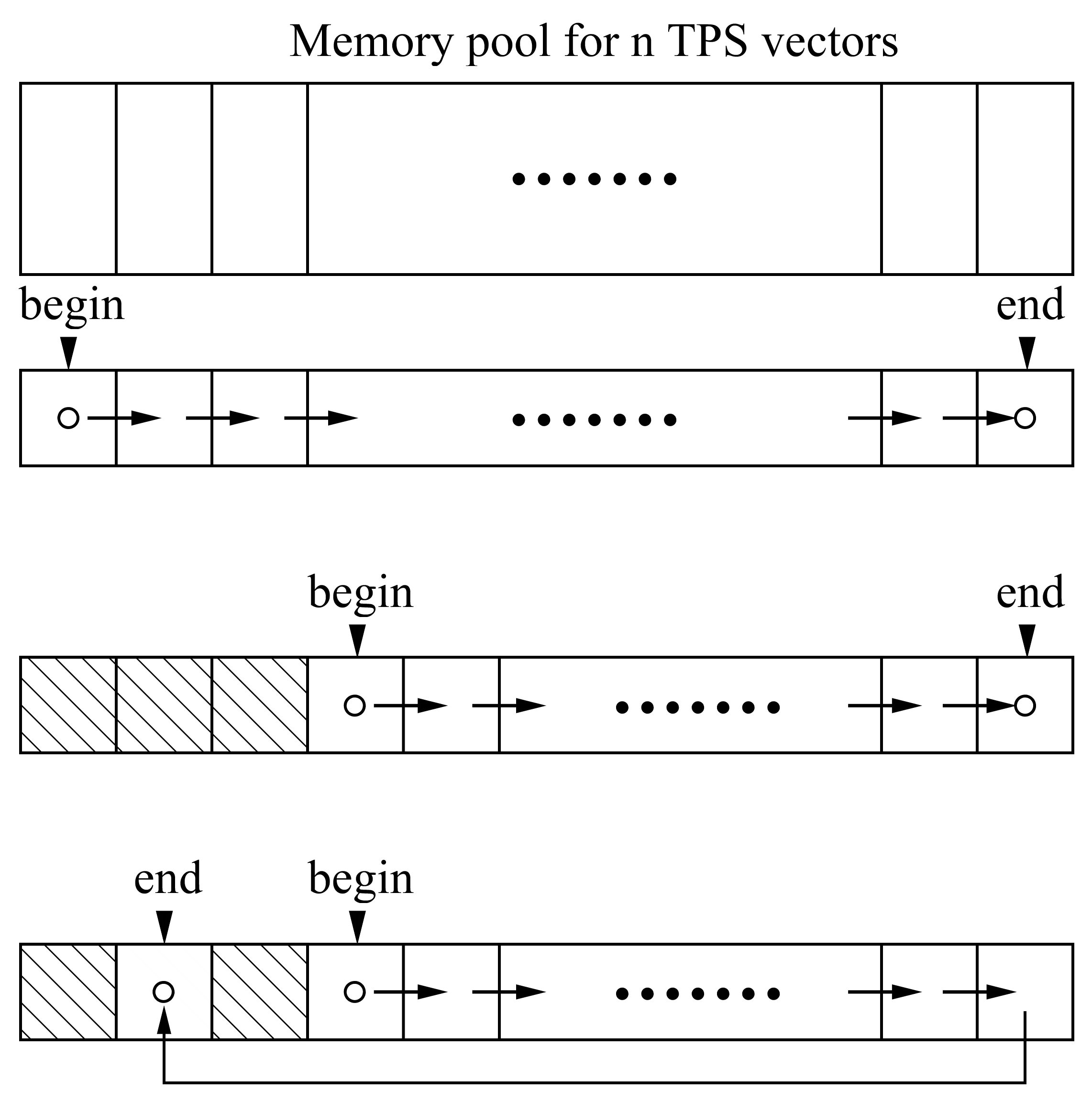
The major change is the memory management. The current memory management works in the following way. Before any TPSA/DA calculation, one needs to reserve the memory for
A new data type DAVector is created as a wrapper of the TPS vector. The following mathematical operator and functions are overloaded for DAVector, so that a variable of DAVector type can be used as a intrinsic type in calculations.
Math operator overloaded: (DA - DA vector, CD - complex DA vector)
| Left hand | Operator | Right hand |
|---|---|---|
| DA/CD | + | DA/CD |
| double | + | DA/CD |
| DA/CD | + | double |
| + | DA/CD | |
| DA/CD | - | DA/CD |
| DA/CD | - | double |
| double | - | DA/CD |
| - | DA/CD | |
| DA/CD | * | DA/CD |
| DA/CD | * | double |
| double | * | DA/CD |
| DA/CD | / | DA/CD |
| DA/CD | / | double |
| double | / | DA/CD |
| DA/CD | = | DA/CD |
| DA/CD | = | double |
| DA/CD | += | DA/CD |
| DA/CD | += | double |
| DA/CD | -= | DA/CD |
| DA/CD | -= | double |
| DA/CD | *= | DA/CD |
| DA/CD | *= | double |
| DA/CD | /= | DA/CD |
| DA/CD | /= | double |
Math functions overloaded:
- sqrt
- exp
- log
- sin
- cos
- tan
- asin
- acos
- atan
- sinh
- cosh
- tanh
- pow
- abs
- erf (DA only)
Some test results for efficiency are presented in the following. They are done in a Windows 10 desktop with Intel Xeon (R) E5-1620 processor at 3.60 GHz. Table 1 shows the time cost for composition of one DA/TPS vector of six bases with six DA/TPS vectors. First column shows the order of the vectors, second column the number of terms in each vector, third column the time using the DA data type with revised memory management, and the fourth column the time using the original code. Table 2 shows the time of composition of six DA vectors, each having six bases, with the other group of six DA vectors. The composition in group cost less time if compared with separate compositions.
Table 1. Time (in second) of composition
| Order | No. of terms | DA | TPSA |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 28 | ||
| 4 | 210 | ||
| 6 | 924 | ||
| 8 | 3003 | ||
| 10 | 8008 |
Table 2. Time (in second) of group composition
| Order | DA |
|---|---|
| 2 | |
| 4 | |
| 6 | |
| 8 | |
| 10 |
More information is available at doc/doxygen/html/index.html.
You will need a C++ compiler that supports C++ 11 standard. There are three ways to use the code as follows:
-
Download the source files. Include "tpsa_extend.h" and "da.h" in your project and compile.
-
The code is developed using Code::Blocks IDE. There are two C::B profiles under the cbp directory: tpsa_lib.cbp and tpsa_dll.cbp for static library and dynamic library respectively. The cbp files are tested in Windows 10 with gcc compiler.
-
You can also use cmake to compile the code into both a static library and a dynamic library. This has been tested in Ubuntu 16.04 and in Ubuntu 18.04 (WSL2).
cmake .makeHere is an example of compiling the code under Ubuntu 16.04.
Assume I have cloned the codes to the following folder:
$HOME/tpsa
Inside the above folder, run:
cmake .The Makefile will be generated.
Then run:
makeBoth the static lib and the shared lib of tpsa will be generated. You can find the following two files:
libtpsa.a and libtpsaso.so
Now you can use any of them to compile your file. Here let us compile the examples/examples.cc using libtpsa.a.
gcc examples/examples.cc -o tpsa_exp -I ./include/ -L. -ltpsa -lstdc++ -lm -std=c++11You can also use libtpsaso.so.
gcc examples/examples.cc -o tpsa_exp -std=c++11 -Iinclude -L. -ltpsaso -lstdc++ -lmThe executable file tpsa_exp will be generated.
To run the tpsa_exp file, tell the OS where to find the libtpsaso.so:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:$HOME/tpsaRun the executable:
./tpsa_exp
Thanks to Dr. Lingyun Yang for providing his tpsa code.
Contact the author by hezhang.AT.jlab.org.