🔎 coco is an interactive command line interface for creating conventional commits.
This is a port to Rust ⚡ of the original (and slower)
lucas-labs/coco-js, that was implemented using node.js.
This implementation, being written in Rust, is faster, more efficient and has implemented several improvements over the original implementation.
You can download the latest binary for your platform from the releases page.
Then drop the binary in your PATH and you're good to go.
You can also install coco from source using cargo:
$ cargo install rs-cocoIf you have binstall installed, you can install coco with:
$ cargo binstall rs-cocoDrop the coco binary somewhere in your PATH:
$ coco --version
rs-coco vx.y.zThen you can use coco to create conventional commits by running it in your repository:
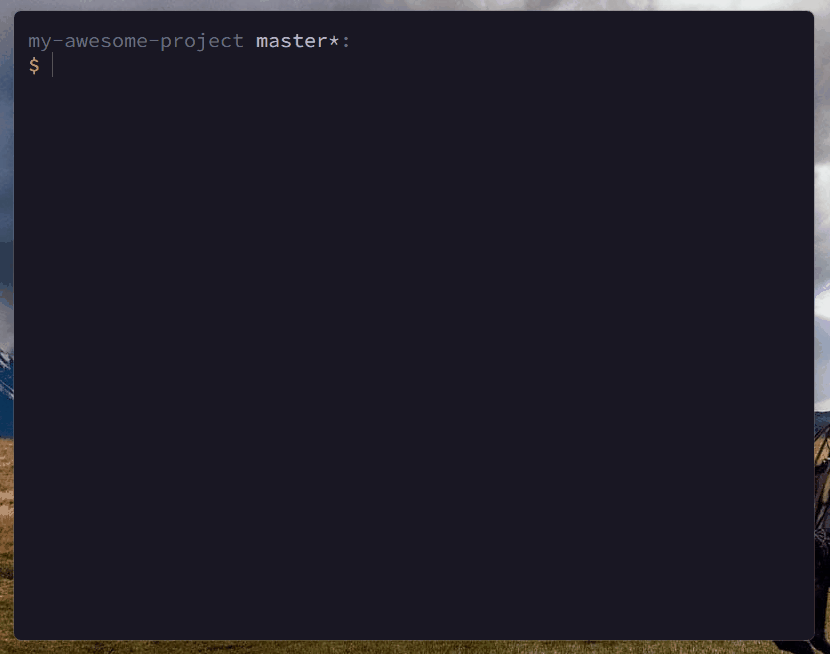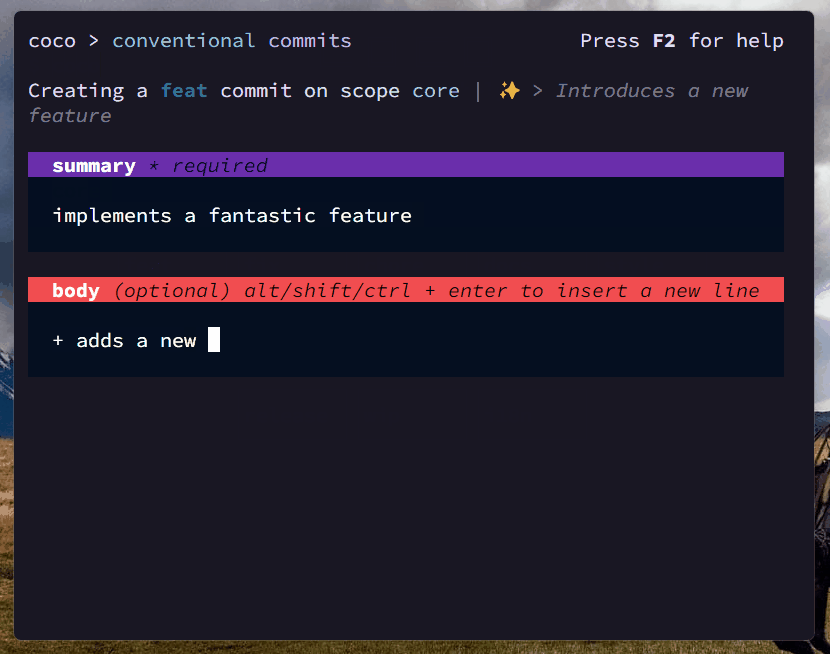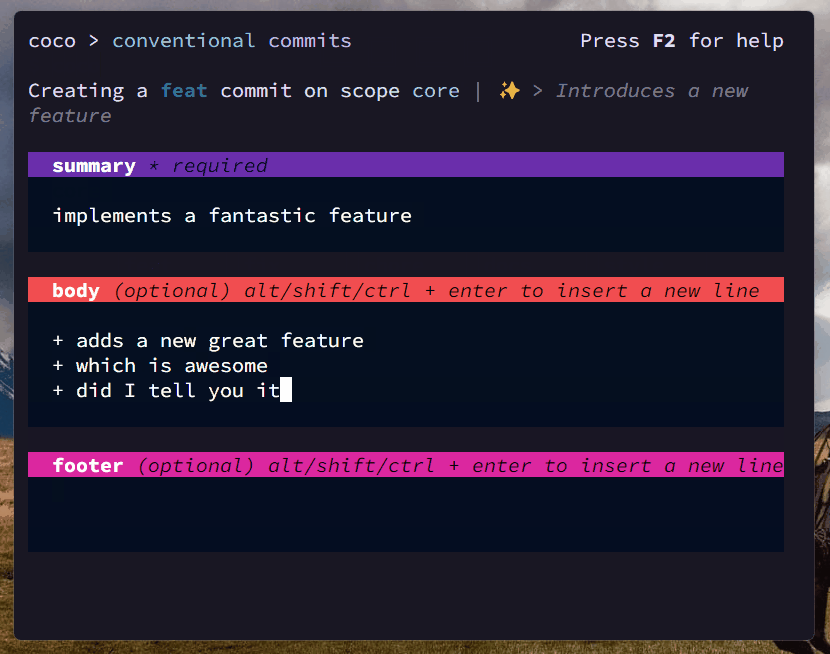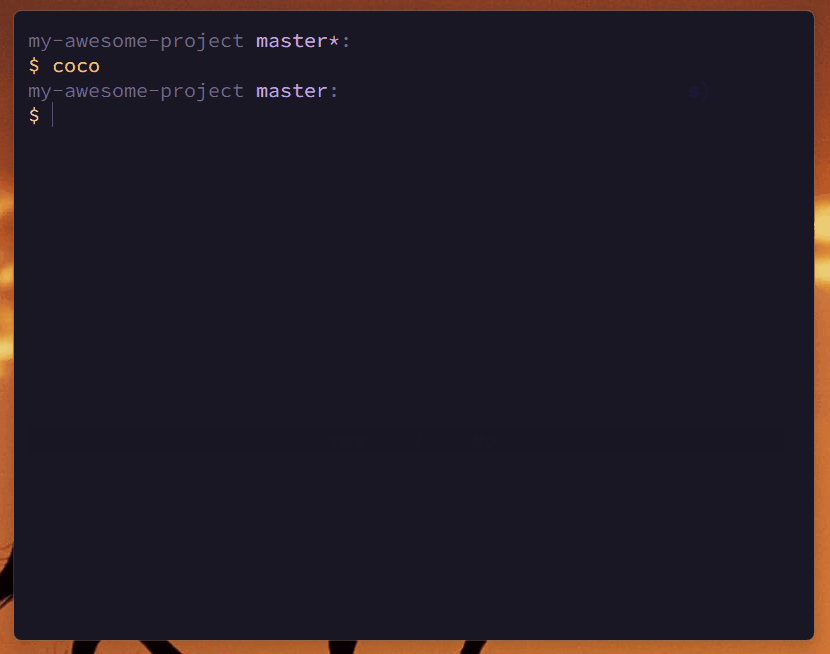
$ coco
# and follow the steps 😊coco can be configured by creating a coco.yaml, coco.yml or .cocorc file in your project's
root (per repository config) or in your users home directory (global config). The file should be a
valid YAML.
See the coco.yml file from this
repository for an example configuration.
Note
Config is totally optional. If no config is provided, coco will use default values.
An array of commit types. Each type should be an object with the following properties:
name- The name of the typedesc- The description of the typeemoji- The emoji to be used for the type ifuseEmojiis set totrue
types:
- name: feat
desc: A new feature
emoji: 🎉
- name: fix
desc: A bug fix
emoji: 🐛An array of commit scopes.
scopes:
- api
- uiIf provided, instead of asking you to type the scope, coco will prompt you to select one from the
list.
Whether to use emojis in the summary. If set to true, the emoji property of the type will be
used to create the commit message.
useEmoji: trueProvided useEmoji is true, an example of a commit message would be:
feat(api): ✨ add new endpoint
Whether to ask for the scope of the commit. IF set to true, the user will be prompted to enter or
select a scope (depending if scope list was provided by user config or not). If set to false, the
scope will be omitted from the commit message and the cli won't ask for it.
askScope: trueWhether to ask for the body of the commit. If set to true, the user will be prompted to enter the
body of the commit. If set to false, the body will be omitted from the commit message and the cli
won't ask for it.
askBody: trueWhether to ask for the footer of the commit. If set to true, the user will be prompted to enter
the footer of the commit. If set to false, the footer will be omitted from the commit message and
the cli won't ask for it.
askFooter: trueWhether to ask for the breaking change of the commit. If set to true, the user will be prompted to
specify if the commit is a breaking change. If set to false, the breaking change information will
be omitted from the commit message and the cli won't ask for it.
askBreakingChange: trueDefines the maximum length of the commit summary (the "title" of the commit). The summary textarea will be limited to this length.
The default value is 72.
maxSummaryLength: 72You can also customize the colors of the CLI by providing a theme object.
Check the coco.yml file to a full list
of the available theme configuration tokens with their default values.
theme:
logo:fg:1: blue
logo:fg:2: light-magenta
...# override the default commit types
types:
- name: feat
desc: A new feature
emoji: 🎉
- name: fix
desc: A bug fix
emoji: 🐛
# set of scopes to choose from
scopes:
- api
- ui
useEmoji: true # default
askScope: true # default
askBody: true # default
askFooter: true # default
askBreakingChange: true # default