We here extensively benchmark 9 representative jDR approaches in three contexts:
- samples clustering from multi-omics simulated data
- ability to identify factors associated with survival or clinical annotations and metagenes associated with biological annotations (Reactome, GO, Hallmarks) in bulk multi-omics TCGA data from 10 cancer types.
- cells clustering based on scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq data from three cell lines.
The benchmarked methods are:
- iCluster
- Integrative NMF (intNMF)
- Joint and individual variation explained (JIVE)
- Multiple co-inertia analysis (MCIA)
- Multi-Omics Factor Analysis (MOFA)
- Multi-Study Factor Analysis (MSFA)
- Regularized Generalized Canonical Correlation Analysis (RGCCA)
- matrix-tri-factorization (scikit-fusion)
- tensorial Independent Component Analysis (tICA)
Please note that due to long running time, MSFA is not executed by default.
Each of the three sub-benchmarks above corresponds to a differnet Jupyter notebook in this repositiory:
Comparison in simulated data.ipynbComparison in cancer data.ipynbComparison in single-cell data.ipynb
The input data for the three notebooks are organized as follows:
- Comparison in simulated data: data simulated as part of the notebook
- Comparison in cancer data: bulk cancer data from TCGA, which was used for a previous study, available at http://acgt.cs.tau.ac.il/multi_omic_benchmark/download.html. A download script is provided to retrieve this dataset
- Comparison in single-cell data: single-cell data from Liu et al. (Nat Commun. 2019, 10(1):470) are available in
./data/folder
For running 2. also annotations from MSigDB are required and a download script is provided to retrieve them.
- Install conda from https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html
- create a new environment:
conda create -n momix -c conda-forge -c bioconda -c lcantini momix r-irkernel
If you get an error concerning the package "GenomeInfoDbData" repeat its istallation separately with:
conda install -c bioconda/label/gcc7 bioconductor-genomeinfodbdata
- Enter the conda environment:
conda activate momix. - Launch the notebook with
jupyter-notebook.
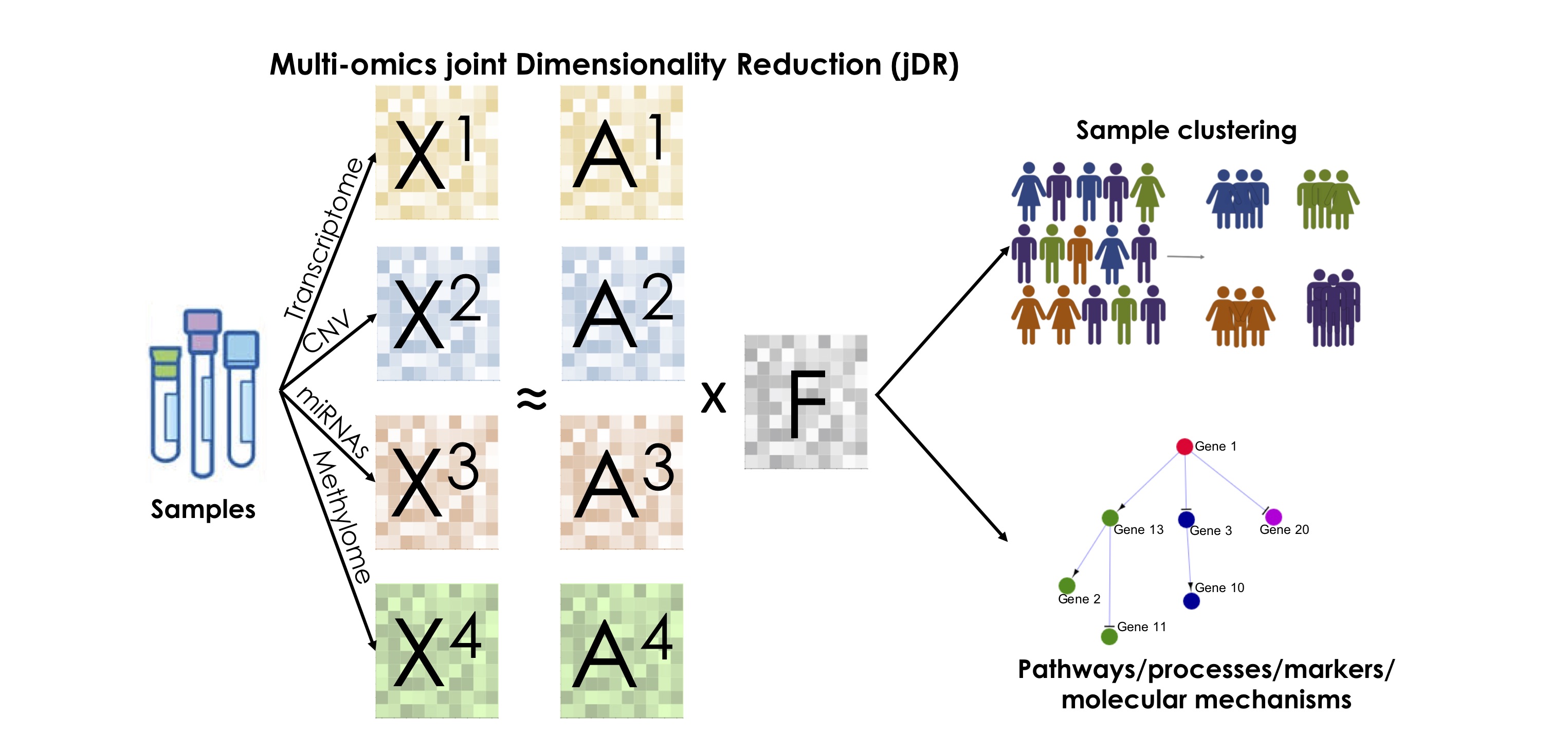
As described in the Results of our work (https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.01.14.905760v1) The jDR factorization will decompose the P omics matrices into a product of a single factor matrix F and multiple weight/projection matrices Ai, i=1...P. Starting from the factorization, (i) we can cluster samples based on the jDR output; (ii) we can describe the pathways/biological functions associated to the various factors and (iii) we can extract features representative of the various factors.
To cluster samples based on the jDR output a clustering algorithm should be applied to the factor matrix F. For example, in our notebook Comparison in simulated data.ipynb k-means clustering with consensus has been applied to the factor matrix in order to compare the clustering obtained by different jDRs.
To find the pathways associated to the various jDR factors the columns of the matrix A1 (corresponding to tyranscriptomics data) should be employed. Such columns correspond to rankings of genes and by applying Preranked GSEA the enrichment of such columns in repsect to collected pathways/biological functions (REACTOME, GO) can be tested. In our experiments, in the notebook Comparison in cancer data.ipynb we used the fgsea package to perform such test.
For each factor j, features (genes, CpGs, proteins, miRNAs) representative of such factor can be extracted. To extract such features the top contributing genes in the matrices Ai column j should be idnetified. With such aim the distribution of the weights should be studied and the fat-tail (corresponding to those features taht are more strongly contributing to factor j) should be extracted.
Of note, once features for factor j are extracted they can be used to recognise the activity of such factor on an independent dataset.
- If the inputs are bulk multi-omics data then run the 'Comparison in cancer data.ipynb' notebook changing the folder where to access the input data from
data/cancertodata/folder_new_data. - If the inputs are single-cell multi-omics data then run the 'Comparison in single-cell data.ipynb' notebook changing the folder where to access the input data from
data/single-celltodata/folder_new_data.
Add the commans to run the new algorithm in the end of the function scripts/ranfactorization.R. In this case the output of that function will have to contain the name of the new added method, the factors obtained with the method and the list of weight matrices obtained with the new method.
The preprint describing momix is available in BioRxiv https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.01.14.905760v1