ESP-IDF Eclipse Plugin brings developers an easy-to-use Eclipse-based development environment for developing ESP32 based IoT applications. It provides better tooling capabilities, which simplifies and enhances standard Eclipse CDT for developing and debugging ESP32 IoT applications. It offers advanced editing, compiling, flashing and debugging features with the addition of Installing the tools, SDK configuration and CMake editors.
The plug-in runs on Windows, macOS and GNU/Linux.
Note: It supports ESP-IDF CMake based projects (4.x and above)
- Installing Prerequisites
- Installing IDF Eclipse Plugin
- Installing ESP-IDF Tools
- Creating a new Project
- Configuring Launch Target
- Compiling the Project
- Flashing the Project
- Viewing Serial Output
- Configuring the Project using sdkconfig Editor
- CMake Editor
- Debugging the Project
- ESP-IDF Application Size Analysis Editor
- ESP-IDF Terminal
- Configuring Build Environment Variables
- Configuring Core Build Toolchain
- Configuring CMake Toolchain
- Configuring the flash arguments
- Installing IDF Eclipse Plugin from Eclipse Market Place
- Installing IDF Eclipse Plugin using local archive
- Upgrading IDF Eclipse Plugin
- Importing an existing IDF Project
- Importing an existing Debug launch configuration
- Troubleshooting Guide
- How to raise bugs
- FAQ
- Java 8 Update 212 and above : Download and install Java SE from here
- Python 3.5 and above : Download and install Python from here
- Eclipse 2018-12 CDT and above : Download and install Eclipse CDT package from here
- Git : Get the latest git from here
- ESP-IDF 4.0 and above : Clone the ESP-IDF repo from here
Note: Make sure Java, Python and Git are available on the system environment PATH.
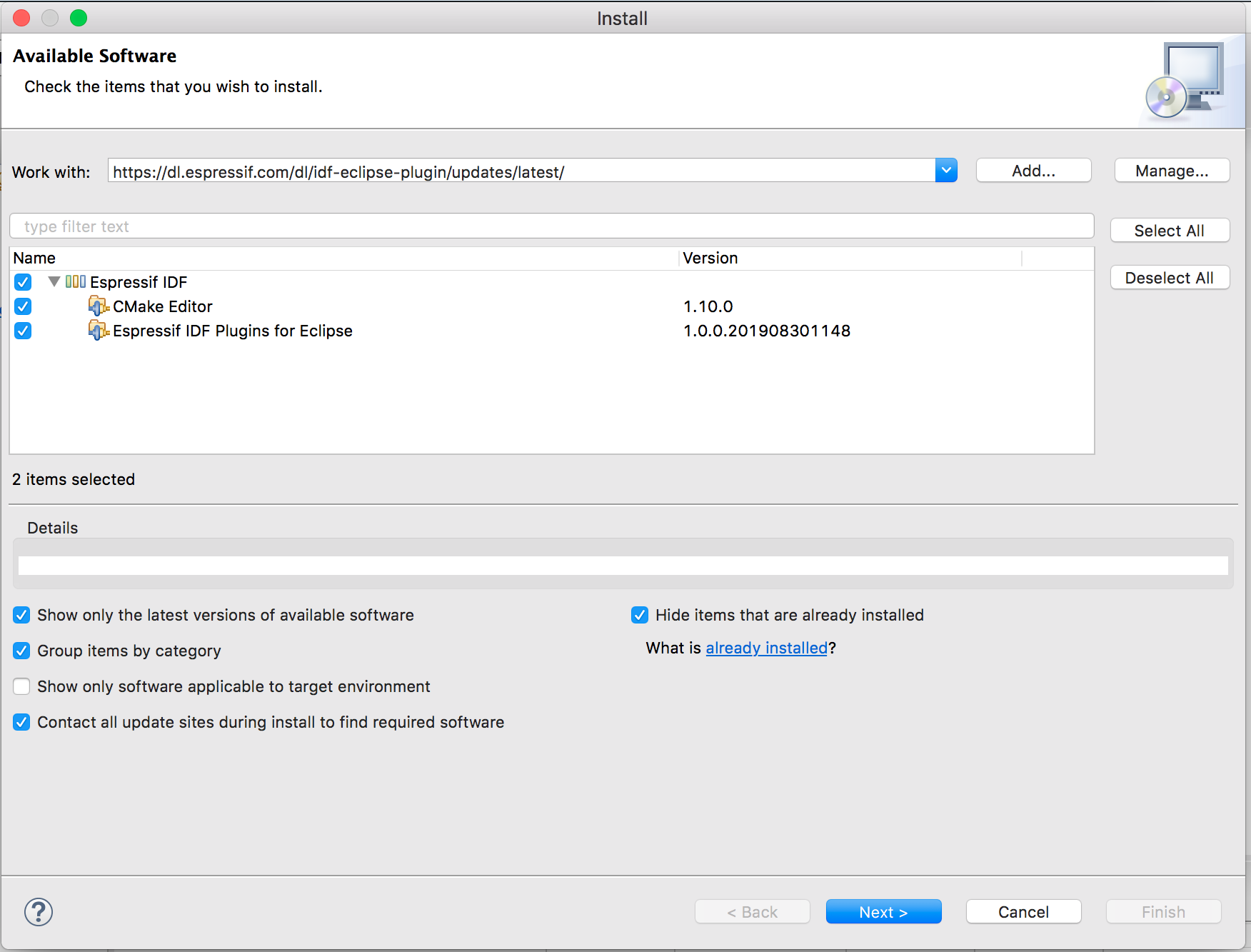
You can install the IDF Eclipse plugin into an existing Eclipse CDT installation using the update site URL. You first need to add the release repository URL as follows:
- Go to
Help->Install New Software - Click
Add… - Enter
Locationof the repository https://dl.espressif.com/dl/idf-eclipse-plugin/updates/latest/ - Enter
NameasEspressif IDF Plugin for Eclipse - Click
Ok - Select
Espressif IDFfrom the list and proceed with the installation
Note: Though screenshots are captured from
macOS, installation instructions are applicable forWindows,LinuxandmacOS.
ESP-IDF requires some prerequisite tools to be installed so you can build firmware for the ESP32. The prerequisite tools include Python, Git, cross-compilers, menuconfig tool, CMake and Ninja build tools.
For this getting started guide, follow the instructions below.
- Navigate to
Help>ESP-IDF Tools Manager>Install Tools - Provide the
ESP-IDF Directorypath - Provide
GitandPythonexecutable locations if they are not auto-detected. - Click on
Install Toolsto proceed with the installation process. Check the Console for the installation details. - Installation might take a while if you're doing it for the first time since it has to download and install xtensa-esp32-elf, esp32ulp-elf, cmake, openocd-esp32 and ninja tools.
Note: Make sure you run this step even if you've already installed the required tools, since it sets the IDF_PATH, PATH, OPENOCD_SCRIPTS and IDF_PYTHON_ENV_PATH to the Eclipse CDT build environment based on the idf_tools.py export command.
ESP-IDF Directory selection dialog:
- Make sure you are in
C/C++ Perspective - Go to
File>New>Espressif IDF Project(If you don't see this, please reset the perspective fromWindow>Perspective>Reset Perspective..) - Provide the
Project name - Click
Finish
Note: You will see a lot of unresolved inclusion errors in the editor and those will be resolved only after the build.
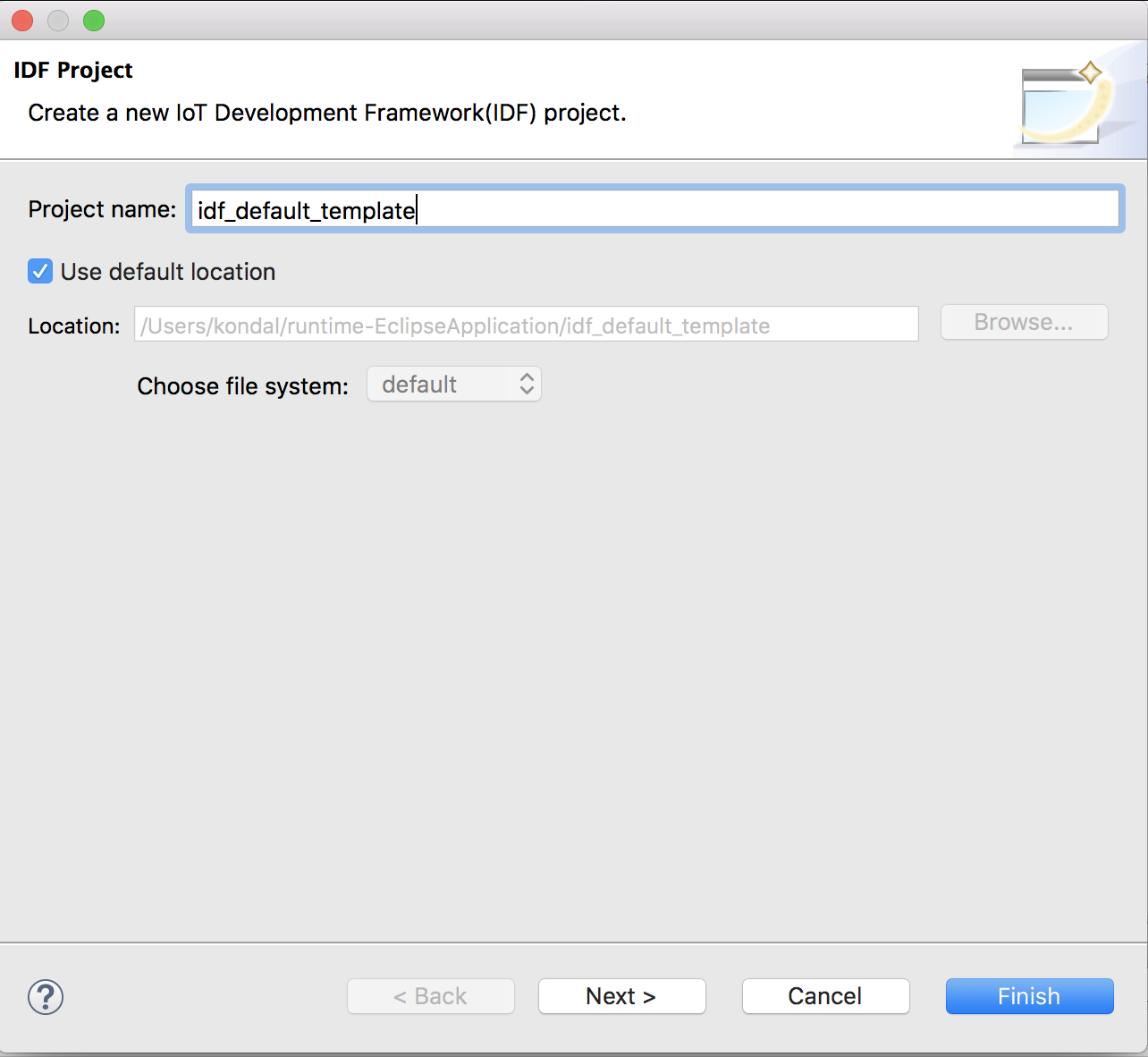
- Make sure you're in
C/C++ Perspective - Go to
File>New>Espressif IDF Project(If you don't see this, please reset the perspective fromWindow>Perspective>Reset Perspective..) - Provide the
Project name - Click
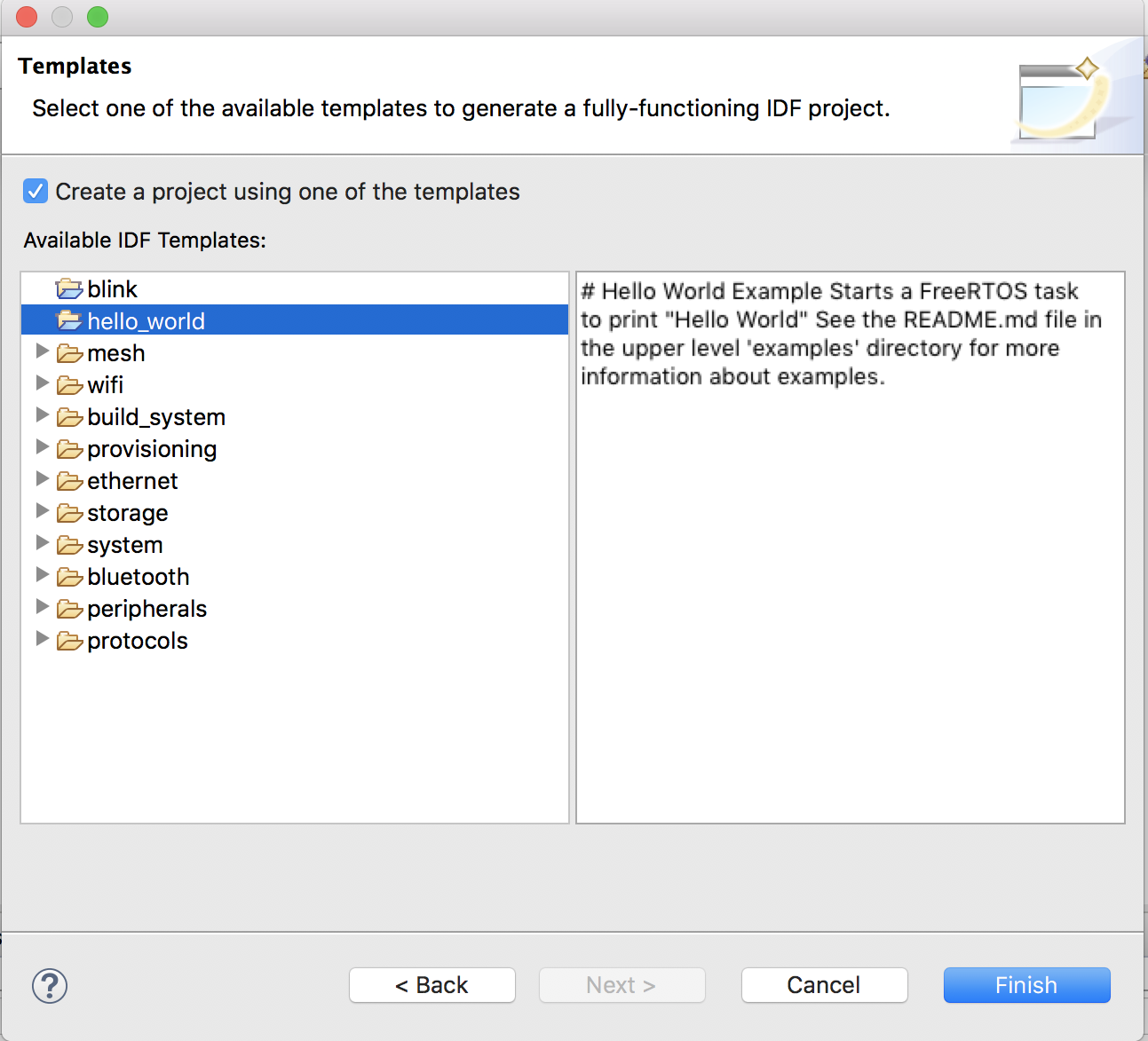
Next - Check
Create a project using one of the templates - Select the required template from the tree
- Click
Finish
Note: You will see a lot of unresolved inclusion errors in the editor and those will be resolved only after the build.
Next, we need to tell CDT to use the toolchain for our project so that all the headers will be indexed and resolved. This is accomplished through the Launch Bar, the new widget set you see on the far left of the toolbar. This will be shown only when you have a project in the project explorer.
- Click on the third dropdown
- Select
New Launch Target - Select
ESP Target - Provide properties for the target where you would like to launch the application. Enter a
Namefor the target and select theSerial Portyour ESP device is connected to on your machine.
- Select a project from the Project Explorer
- Select
Runfrom the first drop-down, which is calledLaunch Mode - Select your application from the second drop-down, which is called
Launch Configuration(Auto-detected) - Select target from the third drop-down, which is called
Launch Target - Now click on the
Buildbutton widget which you see on the far left of the toolbar
ESP-IDF has a tool called idf.py which is a wrapper around make flash command with some handy operations. Flash operation can be initiated with just a click of a launch button(second button from the left) and it's auto-configured to flash the application with the default flash command i.e, idf.py -p PORT flash.
To provide the customized flash arguments, please follow this link for further instructions.
To see the serial output in Eclipse, we need to configure the ESP-IDF Serial Monitor to connect to the serial port.
- Click on the
Open a Terminalicon from the toolbar - Choose
ESP-IDF Serial Monitorfrom the terminal drop-down - Select
Serial Portfor your board if it's not detected. Baud Rate and Serial Port settings are auto-configured by default. - Click on
OKto launch the terminal, which will listen to the USB port
IDF plugin will allow you to configure sdkconfig without leaving the Eclipse environment.
Project configuration is held in a single file called sdkconfig in the root directory of the project. This configuration file can be modified using SDK Configuration Editor
To launch the SDK Configuration editor:
- Navigate to
sdkconfigfile - Double click on the file to launch the SDK configuration editor
- Use
Ctrl+SorCommand+Sbased on the OS environment to save the changes. You can also use EclipseSavebutton from the toolbar - To revert the sdkconfig editor changes, you can either close the editor without saving them or you can right click on the
sdkconfigfile and selectLoad sdkconfigmenu option to revert the changes from the editor.
CMake Editor Plug-in is integrated with IDF Plugin for editing CMake files such as CMakeLists.txt. It provides syntax coloring, CMake command content assist, and code templates.
CMake editor preferences can be controlled using Eclipse > Preferences > CMakeEd
Please refer to JTAG Debugging guide
Predefined debug launch configuration files can be found here. These can be used for reference.
Please refer to Importing Debug Launch Configuration section for importing the existing configuration files into Eclipse. Make sure to modify the debug launch configuraton project specific settings after importing.
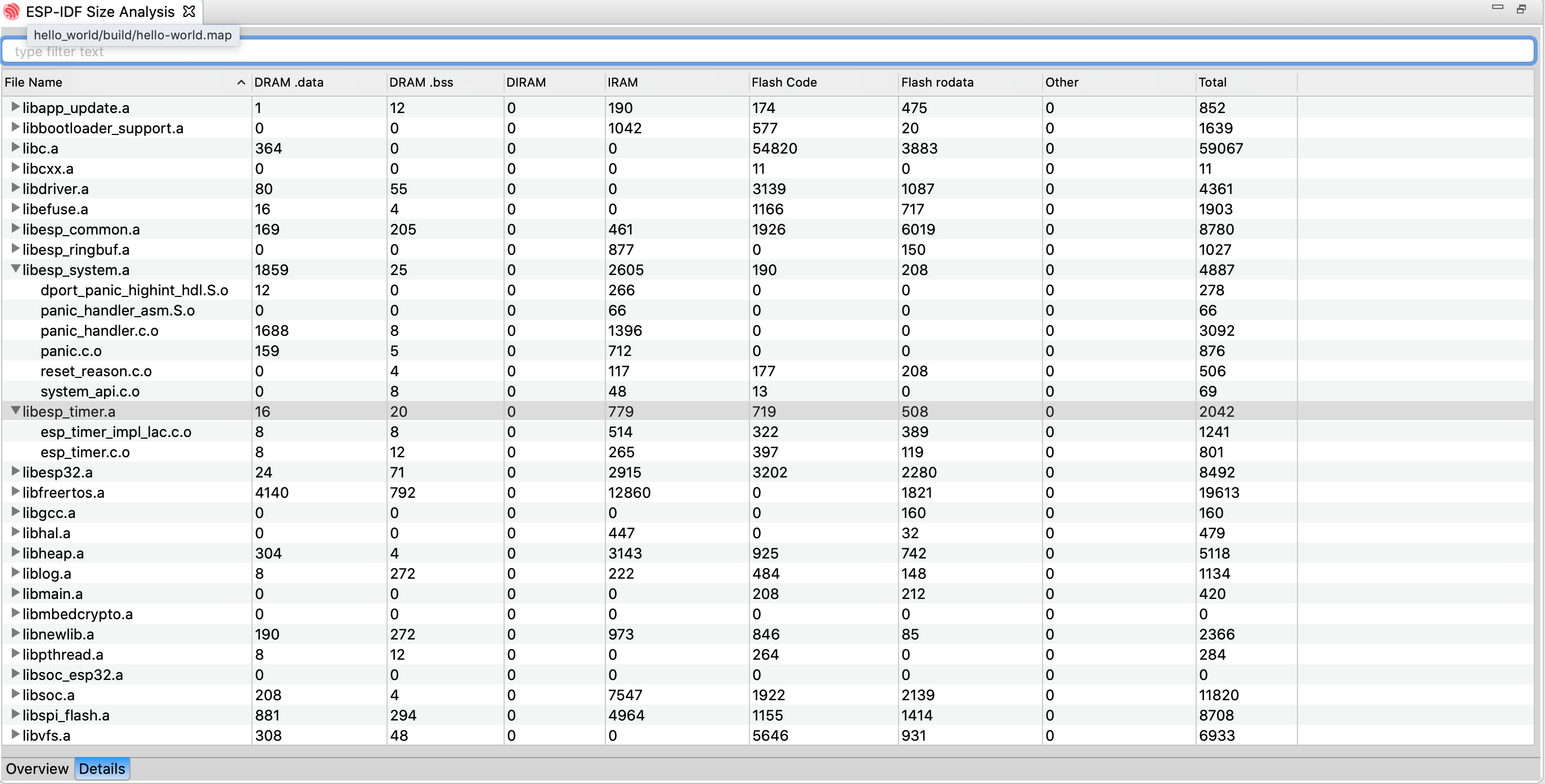
Application Size Analysis editor provides a way to analyze the static memory footprint of your application. It has two sections - Overview and Details. The Overview section provides a summary of the application memory usage and the Details section will have in-depth details about components and per-symbol level memory information.
Details table viewer also provides you with searching and sorting capabilities on various columns.
To launch the Application Size Analysis editor:
- Right-click on the project
- Select
ESP-IDF: Application Size Analysismenu option to launch the editor
Application Size Analysis - Overview
Application Size Analysis - Details
This would launch a local terminal with all the environment variables which are set under Preferences > C/C++ > Build > Environment. The default working directory would be either the currently selected project or IDF_PATH if there is no project selected.
The terminal PATH is also configured with esptool, espcoredump, partition_table, and app_update component paths so that it will be handy to access them directly from the ESP-IDF terminal.
To launch the ESP-IDF Terminal:
- Click on the
Open a Terminalicon from the toolbar - Choose
ESP-IDF Terminalfrom the terminal drop-down and clickOKto launch a terminal
Eclipse auto configures the required environment variables in the Preferences > C/C++ Build > Environment section if IDF Tools are installed using Help > ESP-IDF Tools Manager > Install Tools menu option.
Required environment variables:
- IDF_PATH
- PATH
- OPENOCD_SCRIPTS
- IDF_PYTHON_ENV_PATH
If the required environment variables are not configured for any reason, please follow the step by step instructions below.
- Click on the
Environmentpreference page underC/C++ Build. - Click “Add…” again, and enter name
IDF_PATH. The value should be the full path where ESP-IDF is installed. - Similarly we shoud configure OPENOCD_SCRIPTS, IDF_PYTHON_ENV_PATH and PATH environment variables
This is how they should look:
/Users/user-name/esp/esp-idf
/Users/user-name/.espressif/tools/openocd-esp32/v0.10.0-esp32-20190313/openocd-esp32/share/openocd/scripts
/Users/user-name/.espressif/python_env/idf4.0_py3.7_env
/Users/user-name/.espressif/tools/xtensa-esp32-elf/esp32-2019r1-8.2.0/xtensa-esp32-elf/bin:/Users/user-name/.espressif/tools/esp32ulp-elf/2.28.51.20170517/esp32ulp-elf-binutils/bin:/Users/user-name/.espressif/tools/cmake/3.13.4/CMake.app/Contents/bin:/Users/user-name/.espressif/tools/openocd-esp32/v0.10.0-esp32-20190313/openocd-esp32/bin:/Users/user-name/.espressif/tools/ninja/1.9.0/:/Users/user-name/.espressif/python_env/idf4.0_py3.7_env/bin:/Users/user-name/esp/esp-idf/tools:$PATH
In the above path, the last segment $PATH needs to be replaced with the system environment PATH based on the operating system.
For example, to get the system environment PATH.
- In macOS,
$echo $PATH - In Windows,
$echo %PATH%
We need to tell Eclipse CDT what core build toolchain and CMake toolchain need to be used to build the project. However, this will be auto-detected if you've installed the tools using the Help > ESP-IDF Tools Manager > Install Tools option from the Eclipse.
If these toolchains are not detected for any reason, please follow the step by step instructions below to add a new toolchain.
- Open Eclipse Preferences
- Navigate to
C/C++ -> “Core Build Toolchainspreference page - Click on
Add..from the User defined Toolchians tables - Select
GCCas a toolchain type - Click on
Next> - Provide the GCC Toolchain Settings:
Compiler: /Users/user-name/esp/xtensa-esp32-elf/bin/xtensa-esp32-elf-gcc, Operating System: esp32, CPU Architecture: xtensa
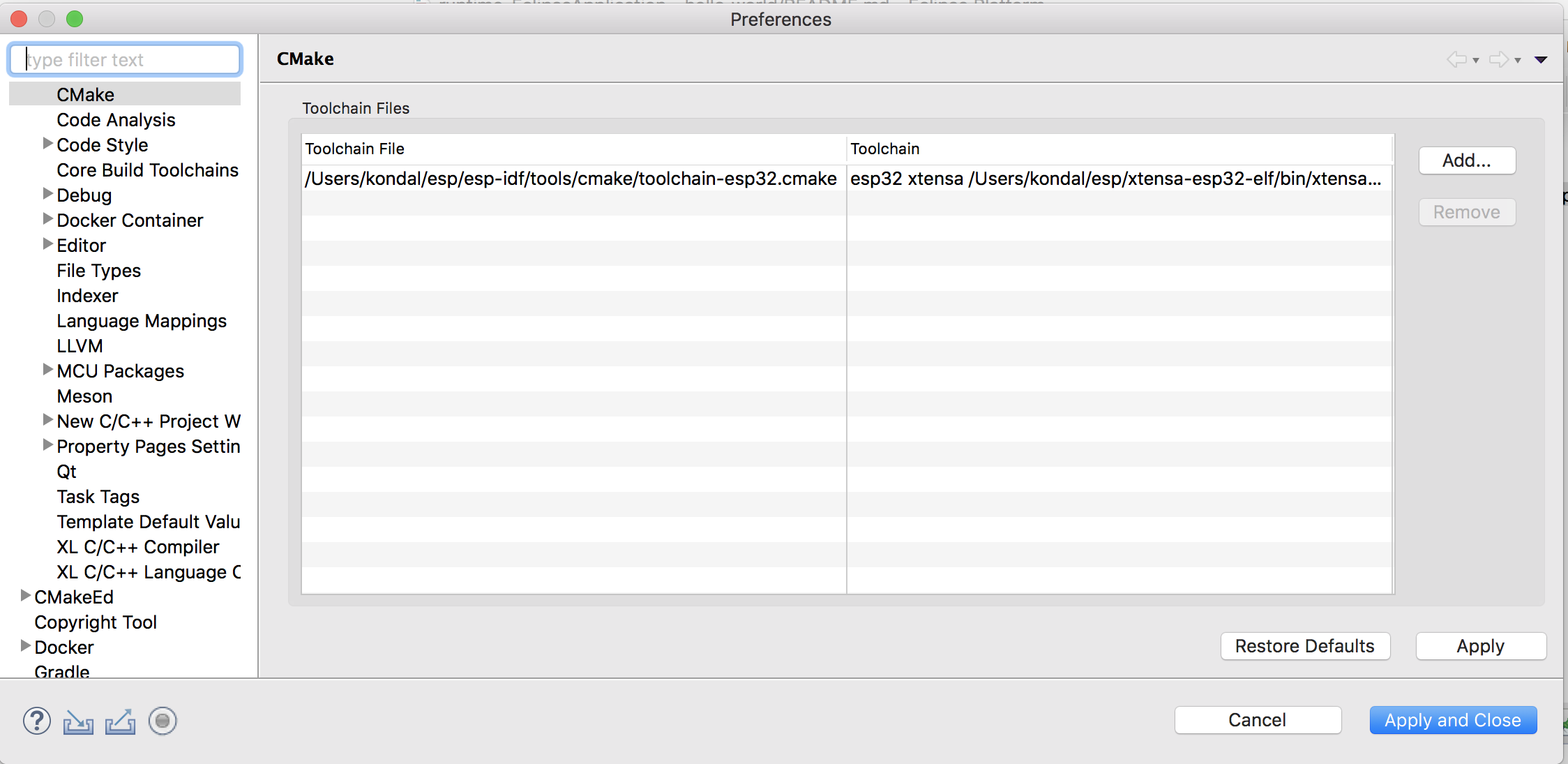
We now need to tell CDT which toolchain to use when building the project. This will pass the required arguments to CMake when generating the Ninja files.
- Navigate to “C/C++ -> “CMake” preference page
- Click
Add..and this will launch the New CMake Toolchain configuration dialog - Browse CMake toolchain
Path. Example:/Users/user-name/esp/esp-idf/tools/cmake/toolchain-esp32.cmake - Select GCC Xtensa Toolchain compiler from the drop-down list. Example:
esp32 xtensa /Users/user-name/esp/xtensa-esp32-elf/bin/xtensa-esp32-elf-gcc
NOTE: Eclipse CDT has a bug in saving the toolchain preferences, hence it's recommended to restart Eclipse before we move further configuring the launch target.
To provide the customized launch configuration and flash arguments, please follow the step by step instructions below.
- Click on the
Launch Configurationedit button - Switch to the
Maintab - Specify the
Locationwhere this application has to run. Sinceidf.pyis a python file, will configure the python system path. Example:${system_path:python} - Specify
Working directoryof the application. Example:${workspace_loc:/hello_world} - In additional arguments, provide a flashing command which will run in the specified working directory
- Flash command looks like this:
/Users/user-name/esp/esp-idf/tools/idf.py -p /dev/cu.SLAB_USBtoUART flash - Click OK to save the settings
- Click on the
Launchicon to flash the application to the selected board
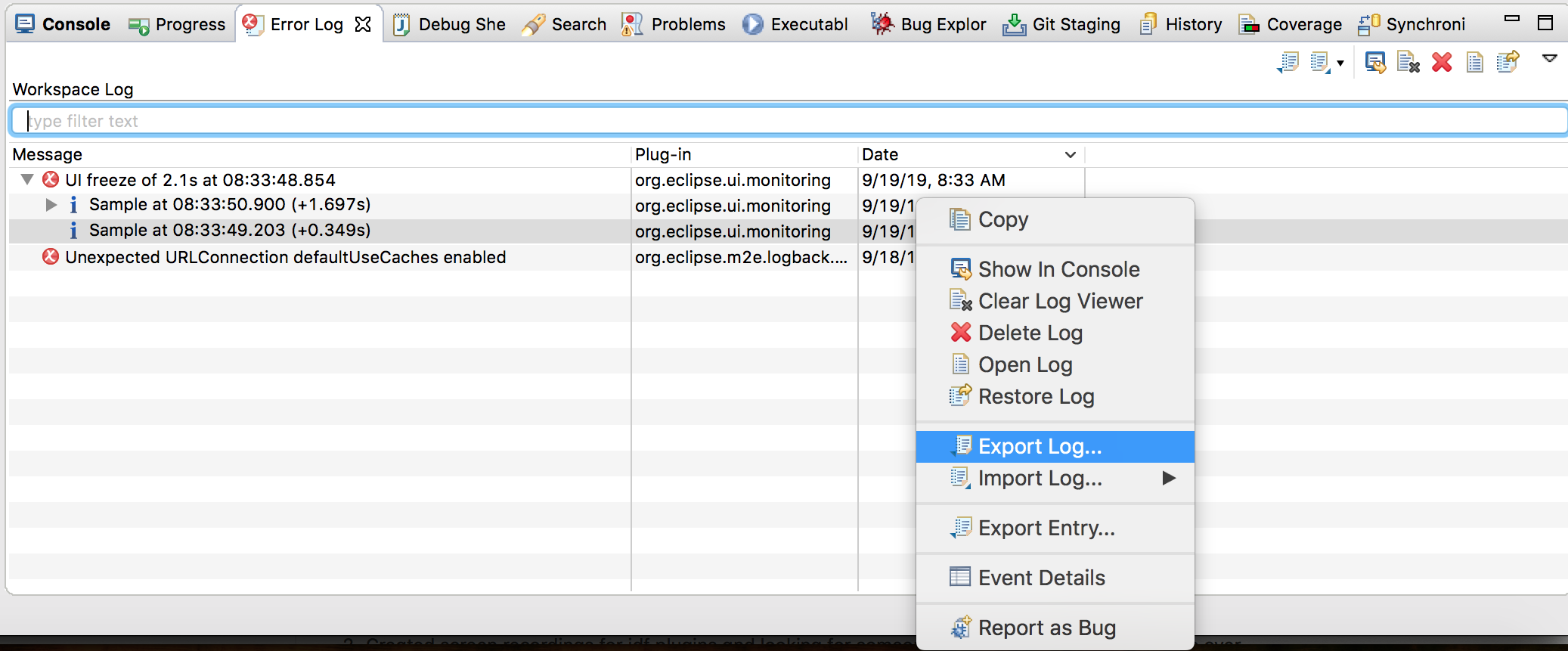
The Error Log view captures all the warnings and errors logged by plug-ins. The underlying log file is a .log file stored in the .metadata subdirectory of the workspace.
The Error Log view is available in Window > Show View > Error Log .
To export the current log view content into a file, press the Export Log toolbar button or select Export Log... from the context menu. Then, enter a file name.
Always provide an error log when reporting an issue.
The Console View provides all the warnings and errors related to the current running process or build. To access the console view.
From the menu bar, Window > Show View > Console.
Go to Preferences > C/C++ > Build > Logging
The Espressif IDF Tools Console is part of Console view, this will be opened only during the installation of IDF tools from the Eclipse.
If you encounter any issue while installing the IDF tools using Help > ESP-IDF Tools Manager > Install tools, please check the Espressif IDF Tools Console to see the errors reported.
If this is not active, it can be switched by clicking on the Display Selected Console icon from the console view.
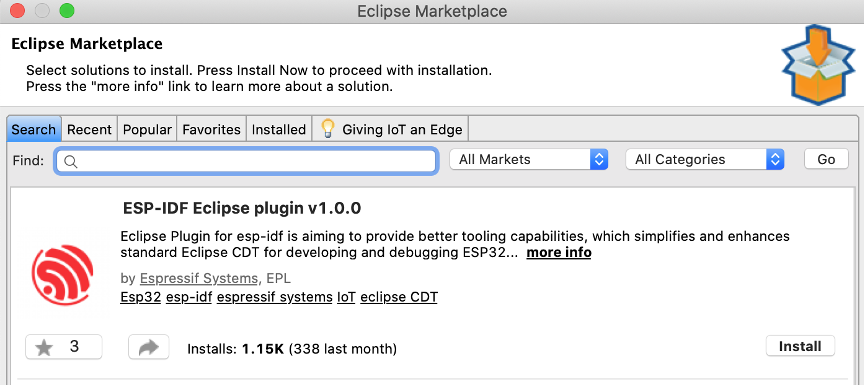
Please follow the steps below to install IDF Eclipse Plugin from the Eclipse Market Place.
- In Eclipse, choose
Help->Eclipse Market Place... - Enter
ESP-IDF Eclipse Pluginin the search box to find the plugin - Click on
Installto follow the installation instructions. - Restart the Eclipse
- Download the latest update site archive for IDF Eclipse Plugin here - https://github.com/espressif/idf-eclipse-plugin/releases
- In Eclipse, choose
Help->Install New Software - Click
Add…button - Select
Archivefrom Add repository dialog and select the filecom.espressif.idf.update-vxxxxxxx.zip - Click
Add - Select
Espressif IDFfrom the list and proceed with the installation - Restart the Eclipse
If you are installing IDF Eclipse Plugin into your Eclipse for the first time, you first need to add the new release's repository as follows:
- Window > Preferences > Install/Update > Available Software Sites
- Click
Add - Enter the URL of the new repository https://dl.espressif.com/dl/idf-eclipse-plugin/updates/latest/
- Click
Ok
If you've already installed IDF Eclipse Plugin using update site URL, you can get the latest changes using below
- Help > Check for Updates
- If updates are found, select
Espressif IDF Plugins for Eclipseand deselect all other items - Click
Nextto proceed with the installation
- Make sure you're in
C/C++ Perspective. - Right click in the Project Explorer
- Select
Import..Menu - Select
Existing IDF ProjectfromEspressifimport wizard menu list - Click
Next - Click on
Browse...to choose an existing project location directory - Provide
Project nameif you wish you have a different name - Click
Finishto import the selected project into eclipse workspace as a CMake project
To import an existing launch configuration into Eclipse:
- Select
Import...from theFilemenu - In the Import dialog box, expand the
Run/Debuggroup and selectLaunch Configurations - Click on
Next - Click on
Browse...to select the required location in the local file system - Select the folder containing the launch files and then click OK
- Select the checkboxes for the required folder and launch file
- If you are replacing an existing configuration with the same name then select
Overwrite existing launch configurations without warning - Click on
Finish
Please raise the issues here https://github.com/espressif/idf-eclipse-plugin/issues with the complete environment details and log.
Please refer to https://github.com/espressif/idf-eclipse-plugin/blob/master/FAQ.md#FAQ