A python based GUI built using Dear PyGui Python GUI Framework to add multiple tasks and link them together to create and balance an assembly line by assigning tasks to various workstations to achieve the desired output rate with the smallest number of workstations according to the longest or shortest work element rule.
This helps create well-balanced workloads for each workstation and minimizes bottlenecks.
-
Make sure you have Python 3.9 installed and working
-
Clone the repo:
git clone https://github.com/RahulShagri/Interactive-Assembly-Line-Balancer.git
- Install prerequisites using pip, preferably in a virtual environment:
pip install -r requirements.txt
-
Run the assembly_line_balancer.py file to start the application
-
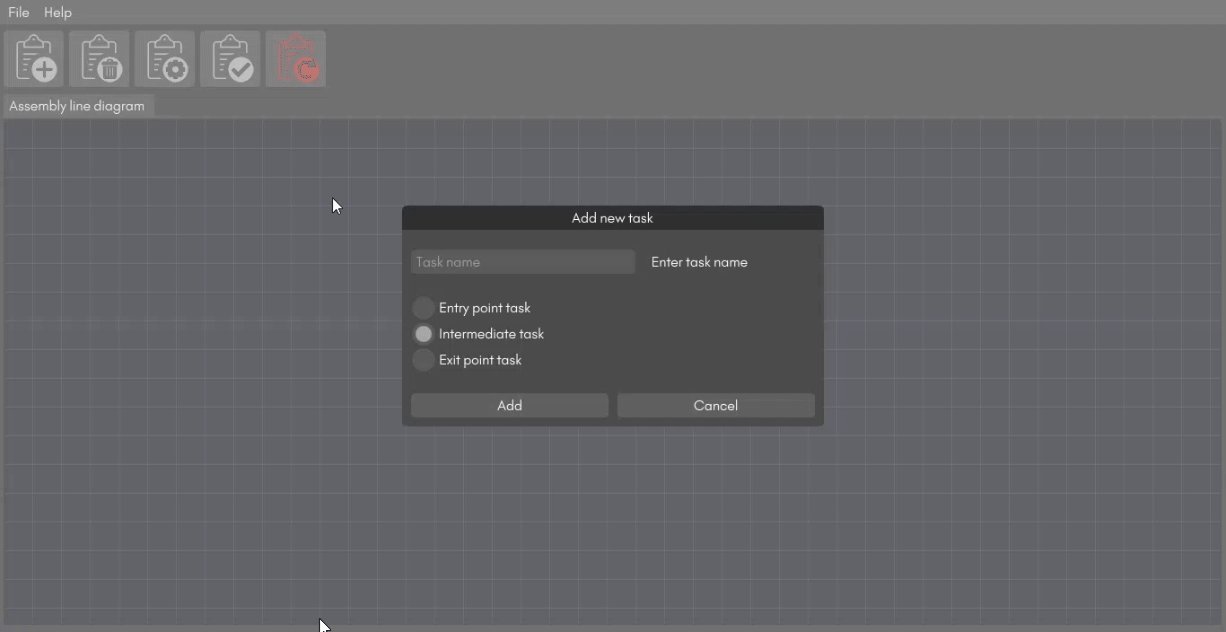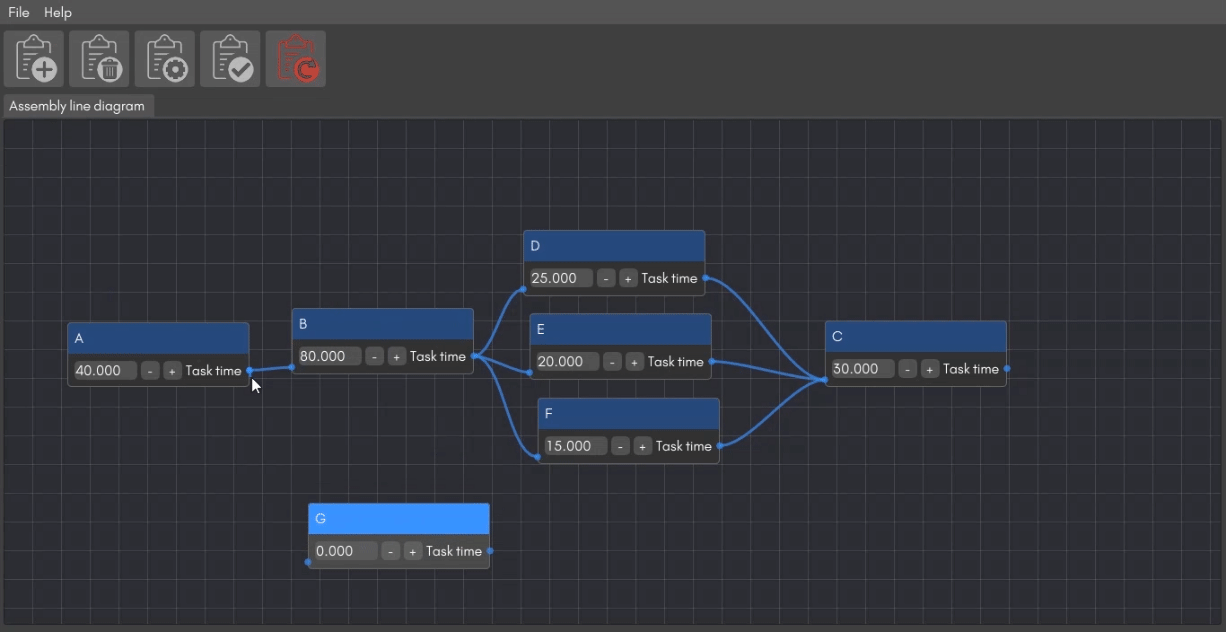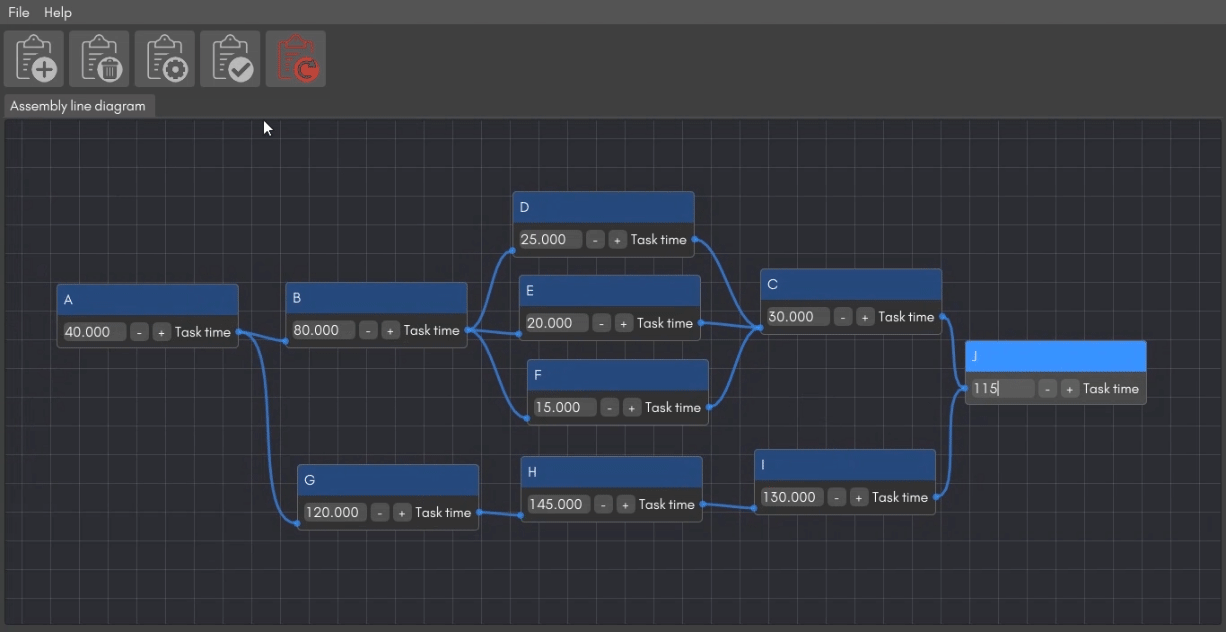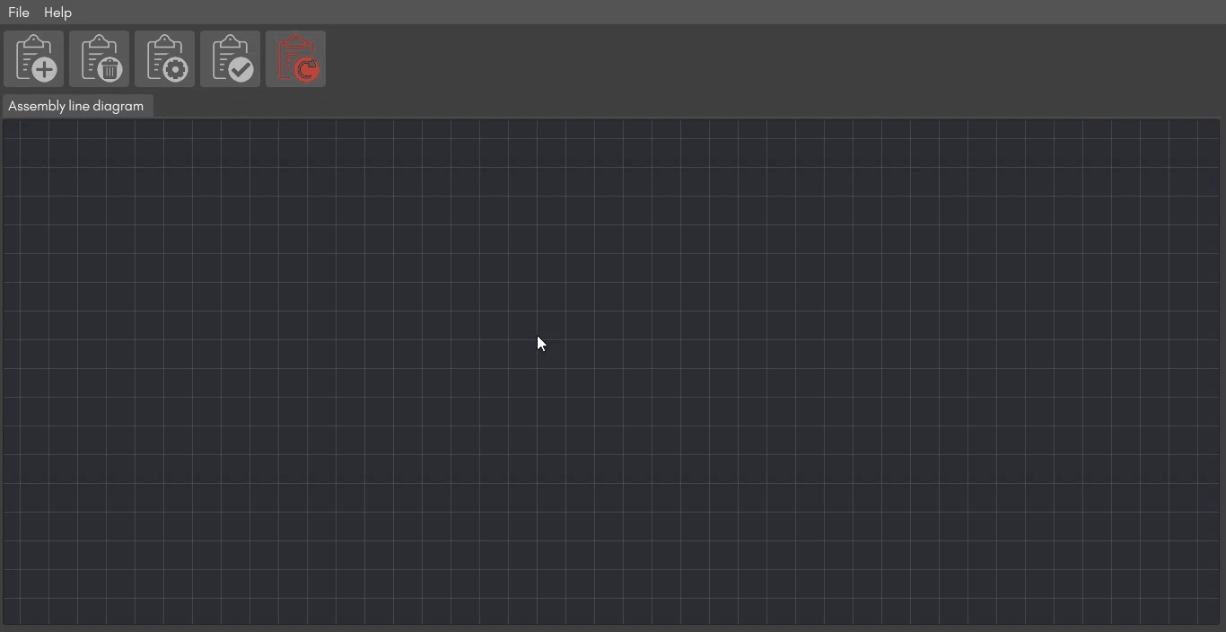
Click on the "Add a new task" button to add a new task. Assign a unique name to the task and set the type
-
Adjust the task time and link each task in the line to each other to complete the assembly line. You can choose to delete or update any of the task details at any point
-
Click on the Finalize button to open up the precedence table. This table lists all the different tasks that have added, any immediate predecessors detected, and their respective tasks times
-
Make sure you do not see any errors on the top of the window. If you do, please resolve it before proceeding
-
Set the cycle time (or leave blank if you want the cycle time to be equal to the maximum task time in the line). Check the total time for producing one unit of product, and the minimum theoretical number of tasks
-
Select an appropriate priority rule and click on the Calculate button
-
In the Solution window, you can see that all the tasks have been assigned a workstation according to the priority rule you selected
-
In the results box below, you can view the actual number of workstations, efficiency of the line if these stations were introduced, and the balance delay
-
If you wish to save the assembly line, you can go to File > Save assembly line. Similarly, you can open an assembly line by going to File > Open assembly line*
*Due to the limitations of the GUI framework being used, the tasks are added one over each other after the assembly line is opened. You need to drag all the tasks to their respective places for a better view of the line.
[Note: The software does not convert any units. The user should take care of the units.]