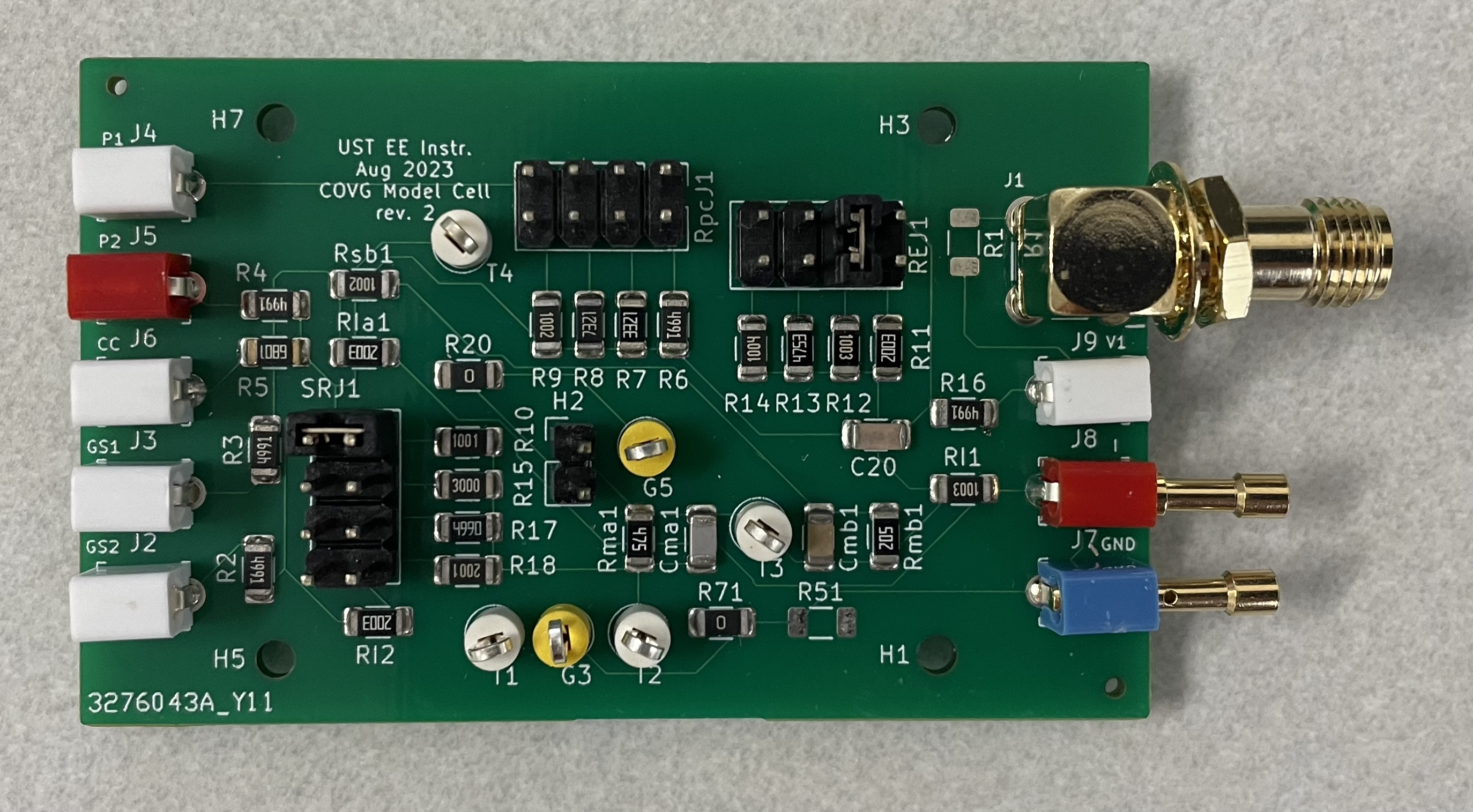
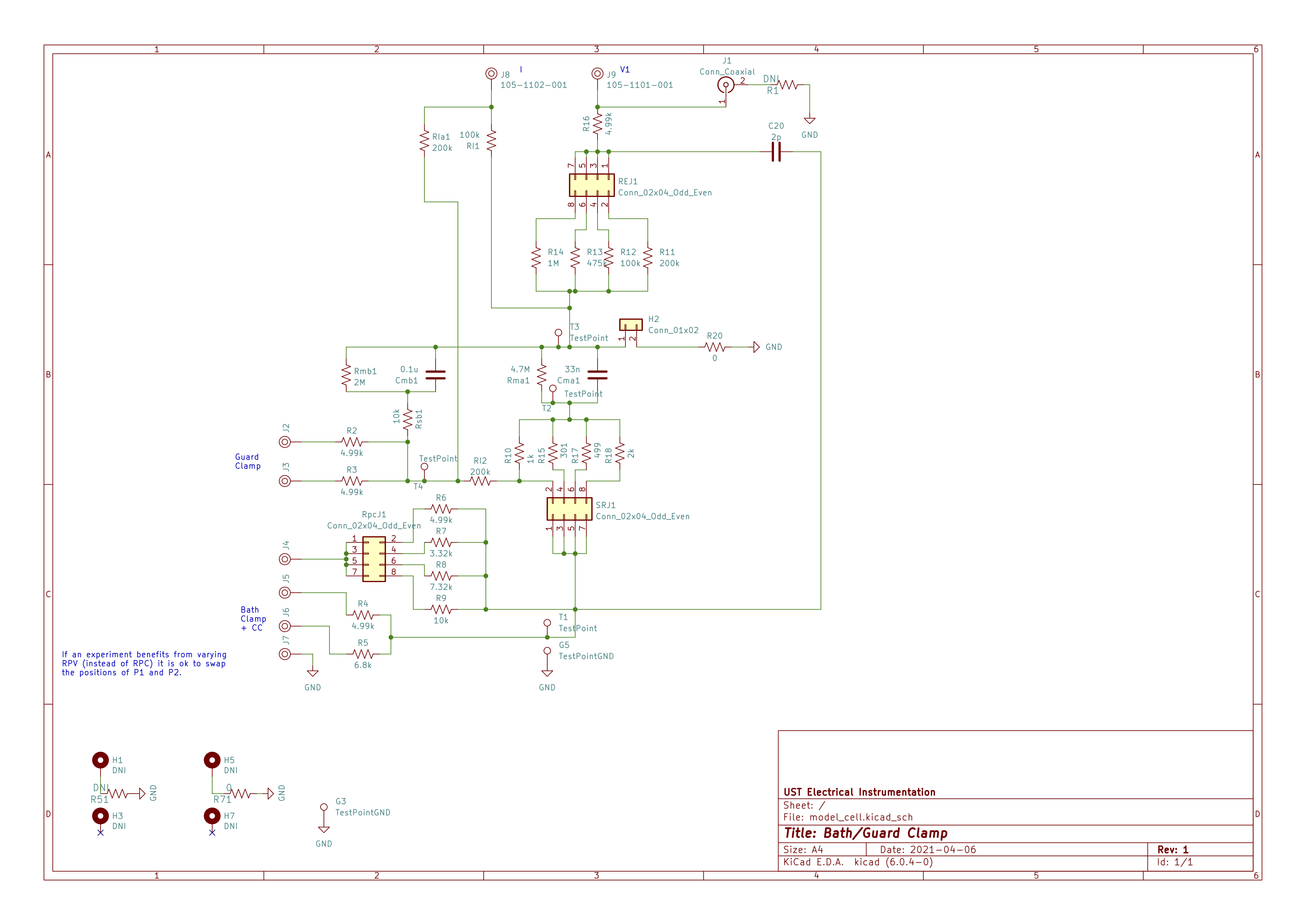
A model cell is a circuit of resistors (Rs) and capacitors (Cs) that emulates the electrical properties of a cell membrane, the solutions, and the electrodes used in an experiment.
J1 amd J9 both connect to the V1 node. C20 allows for small (2 pF) capacitive coupling from the top pool (P1, P2 after the elctrode resistance) to the microelectrode (V1).
Jumper programmable:
- Rs (SRJ1)
- V1 electrode resistance (REJ1)
- P2 electrode resistance (RpcJ1)
The board was assembled by JLCPCB using the following .
Surface mount Rs and Cs are 1206 footprint.
The test jacks are for 0.08" (2.0 mm) diameter plugs.
An example mating pin is the 3601-1-07-21-00-00-08-0.
A user's guide for this model cell is here:
This board was fabricated and assembled by JLCPCB.
Fabrication Order #: Y11-3276043A
Assembly: SMT02308141355143-3276043A
Date: 2023/08/14
The model cell is based on the schematic included in the Dagan CA-1B users manual.
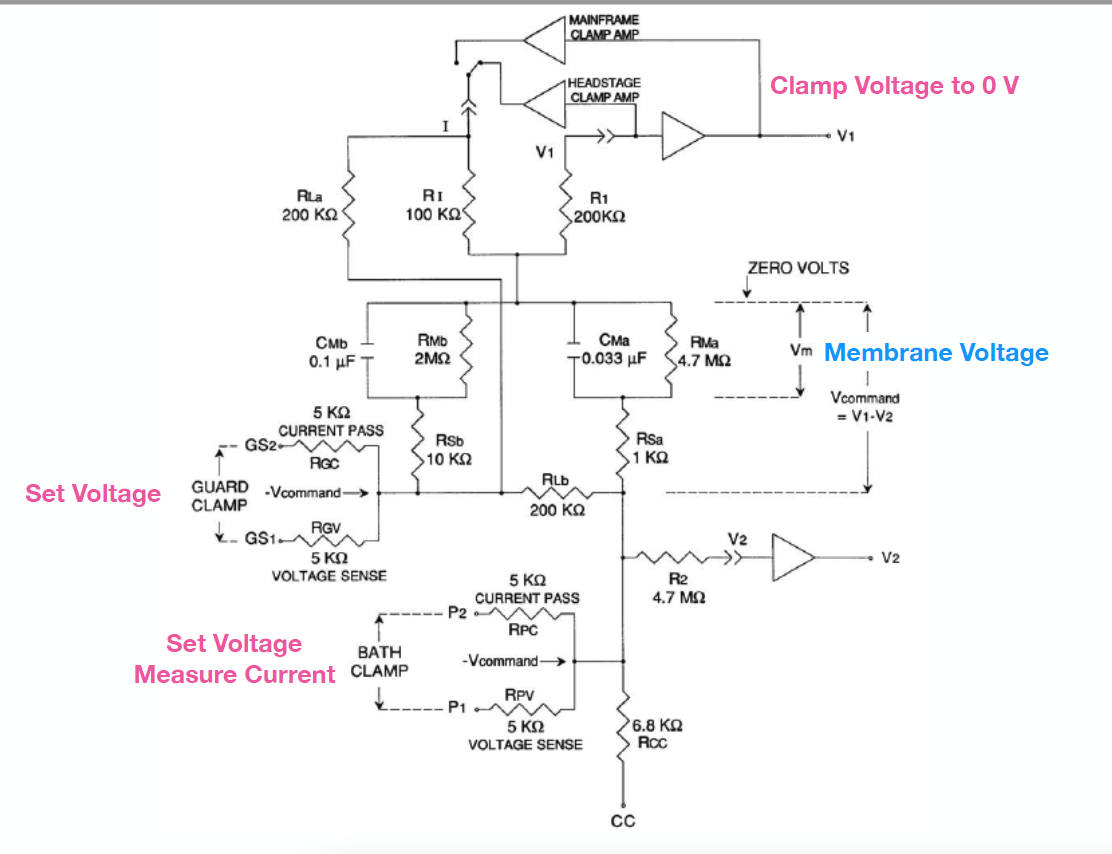
We would like to be able to test the amplifier with different values of Rs and Cs to assess the robustness to variations in these components.
Possible ideas:
- Pin headers with jumpers - this is included in both V1 and v2
- Digital potentiometer
Research reported in this repository was supported by the National Institute Of Neurological Disorders And Stroke of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number R15NS116907. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.