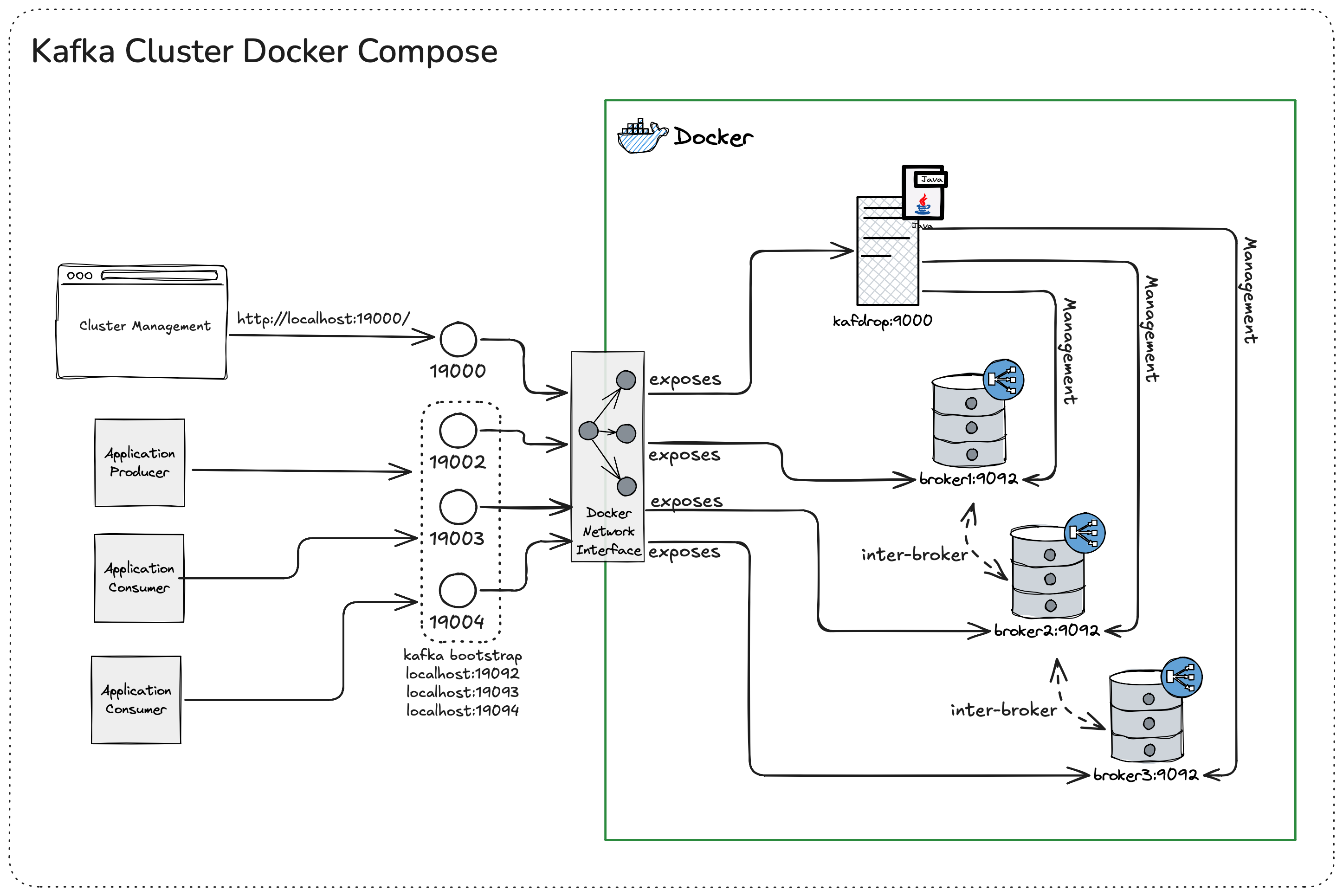
This setup provides a Kafka cluster using KRaft mode (ZooKeeper-free) with 3 brokers. Each broker is configured as both a broker and a controller, using plaintext communication and supporting automatic topic replication.
The following is an overview of the key files and directories in this repository:
.
├── docker-compose.yml
├── scripts/
├── docs/
│ ├── docker-compose-stack.png
│ ├── docker-compose-stack.json
│ └── kafdrop.png
├── .env.example
└── LICENSE.md
- docker-compose.yml: Defines the services, networks, and volumes for the Kafka cluster setup.
- scripts/: Contains scripts used for initializing and managing the Kafka brokers.
- docs/: Contains documentation and images related to the project, such as diagrams and UI screenshots.
- docker-compose-stack.png: An image file depicting the Docker Compose stack.
- docker-compose-stack.json: A JSON file for editing the Docker Compose stack diagram in Excalidraw.
- kafdrop.png: An image file related to Kafdrop, possibly a diagram or screenshot.
- .env.example: Template for environment variables, including the
KAFKA_CLUSTER_ID. - LICENSE.md: Contains the MIT License for the project.
To clone the repository, use the following command:
git clone git@github.com:luismr/kafka-cluster-docker-compose.gitBefore starting the Kafka cluster, ensure the kafka-net network is created. You can create it manually with:
docker network create kafka-netThe KAFKA_CLUSTER_ID is a crucial environment variable for setting up the Kafka cluster in KRaft mode. You can set this variable in two ways:
- Rename the
.env.examplefile to.env. - Open the
.envfile and set theKAFKA_CLUSTER_IDvariable:KAFKA_CLUSTER_ID=your-unique-cluster-id - Save the file. Docker Compose will automatically load this file and use the variable when starting the containers.
Alternatively, you can set the KAFKA_CLUSTER_ID as an environment variable in your operating system:
set KAFKA_CLUSTER_ID=your-unique-cluster-idexport KAFKA_CLUSTER_ID=your-unique-cluster-idAfter setting the environment variable, you can start the Kafka cluster with Docker Compose:
docker-compose up -d- KAFKA_KRAFT_CLUSTER_ID: Unique identifier for the Kafka cluster.
- KAFKA_NODE_ID: Unique ID for each broker.
- KAFKA_PROCESS_ROLES: Configures the broker to act as both a broker and a controller.
- KAFKA_LISTENERS: Defines the internal and external listeners for each broker.
- KAFKA_LISTENER_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_MAP: Specifies the security protocol for each listener (plaintext).
- KAFKA_INTER_BROKER_LISTENER_NAME: Specifies the listener used for inter-broker communication.
- KAFKA_CONTROLLER_LISTENER_NAMES: Specifies the listener used for controller communication.
- KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS: Advertises the listener addresses for client connections.
- KAFKA_LOG_DIRS: Directory where Kafka logs are stored.
- KAFKA_OFFSETS_TOPIC_REPLICATION_FACTOR: Sets the replication factor for the offsets topic.
- KAFKA_TRANSACTION_STATE_LOG_REPLICATION_FACTOR: Sets the replication factor for the transaction state log.
- KAFKA_TRANSACTION_STATE_LOG_MIN_ISR: Minimum in-sync replicas for the transaction state log.
To start the Kafka cluster, use the following command:
docker-compose up -dThis command will start all the services defined in the docker-compose.yml file in detached mode.
You can connect to the Kafka cluster using various client libraries. Below is an example using Python with the kafka-python library.
First, install the kafka-python library:
pip install kafka-pythonThen, use the following script to produce and consume messages:
from kafka import KafkaProducer, KafkaConsumer
# Producer
producer = KafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers=['localhost:19092', 'localhost:19093', 'localhost:19094'])
producer.send('my-topic', b'Hello, Kafka!')
producer.flush()
# Consumer
consumer = KafkaConsumer('my-topic', bootstrap_servers=['localhost:19092', 'localhost:19093', 'localhost:19094'])
for message in consumer:
print(f"Received message: {message.value.decode('utf-8')}")This example connects to the Kafka brokers running on localhost:19092, localhost:19093, and localhost:19094.
Running Kafka in standalone mode is important for testing and development purposes. It allows you to quickly set up a Kafka broker without the need for a full cluster, making it easier to test configurations, produce and consume messages, and develop applications locally.
To run Kafka in standalone mode, use the following command:
docker run -d \
--name broker \
-p 9092:9092 \
apache/kafka:latestThis project is licensed under the MIT License. For more details, please refer to the LICENSE.md file.