Team: Tim Kuffner & Lukas Hüller
Data Sources: Wikidata & Registerbekanntmachungen
This repository will be used for the course Information Integration in the summer term 2022. It is based on the codebase of bakdata and will be further developed by the project group led by Tim Kuffner and Lukas Hüller. Below you will find the documentation to set up and run the project.
- Install Poetry
- Install Docker and docker-compose
- Install Protobuf compiler (protoc). If you are using windows you can use this guide
- Install jq
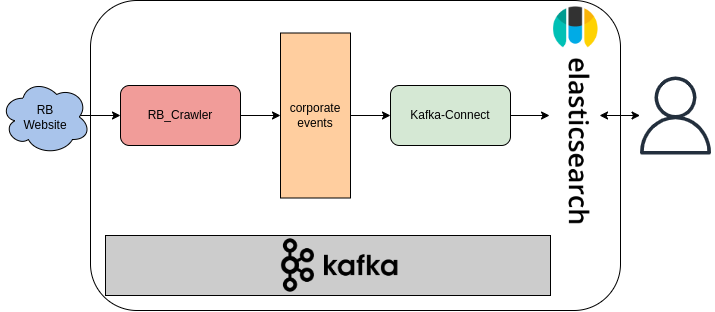
The Registerbekanntmachung website contains
announcements concerning entries made into the companies, cooperatives, and
partnerships registers within the electronic information and communication system. You can search for the announcements.
Each announcement can be requested through the link below. You only need to pass the query parameters rb_id
and land_abk. For instance, we chose the state Rheinland-Pfalz rp with an announcement id of 56267, the
new entry of the company BioNTech.
export STATE="rp"
export RB_ID="56267"
curl -X GET "https://www.handelsregisterbekanntmachungen.de/skripte/hrb.php?rb_id=$RB_ID&land_abk=$STATE"The Registerbekanntmachung crawler (rb_crawler) sends a get request to the link above with parameters (rb_id
and land_abk) passed to it and extracts the information from the response.
We use Protocol buffers to define our schema.
The crawler uses the generated model class (i.e., Corporate class) from
the protobuf schema.
We will explain furthur how you can generate this class using the protobuf compiler.
The compiler creates a Corporate class with the fields defined in the schema. The crawler fills the object fields with
the
extracted data from the website.
It then serializes the Corporate object to bytes so that Kafka can read it and produces it to the rb-announcements
topic. After that, it increments the rb_id value and sends another GET request.
This process continues until the end of the announcements is reached, and the crawler will stop automatically.
The corporate-events holds all the events (announcements) produced by the rb_crawler. Each message in a Kafka topic
consist of a key and value.
The key type of this topic is String. The key is generated by the rb_crawler. The key
is a combination of the land_abk and the rb_id. If we consider the rb_id and land_abk from the example above,
the key will look like this: rp_56267.
The value of the message contains more information like event_name, event_date, and more. Therefore, the value type
is complex and needs a schema definition.
As Wikidata provides a download of a complete, up-to-date database image in the form of a JSON, the Wikidata page does not need to be crawled.
However, since the dump is very large (~70Gb zip file, >500Gb unzipped), a preparation step must be performed on systems that do not have enough disk space to completely unzip the file.
The following command outputs the unzipped to stdout, from where we can filter the individual lines for the ID for a human. (Every person is an instance of human, so there will always be a "Q5" somewhere in the line)
lbunzip2 -c latest-all.json.bz2 | grep '"id":"Q5"' > humans.txt
Similarly, the extraction of the companies:
lbunzip2 -c latest-all.json.bz2 | grep '"id":"Q4830453"' > companys.txt
The extracted files are ~1.4Gb for the companies and ~80Gb for the humans.
With these files the WD "upserter" can then be used. It reads the files and processes them similar to the rb-crawler, but without the crawling part. There are also Protobuf objects created, which are sent to Kafka.
Kafka Connect is a tool to move large data sets into (source) and out (sink) of Kafka. Here we only use the Sink connector, which consumes data from a Kafka topic into a secondary index such as Elasticsearch.
We use the Elasticsearch Sink Connector to move the data from the three topics into the Elasticsearch.
This project uses Poetry as a build tool.
To install all the dependencies, just run poetry install.
This project uses Protobuf for serializing and deserializing objects. Just have a look at our protobuf schemas.
Furthermore, you need to generate the Python code for the model class from the proto file.
To do so run the generate-proto.sh script.
This script uses the Protobuf compiler (protoc) to generate the model classes
under the build/gen/ folder
with the names rb_announcements_pb2.py, wd_companies_pb2.py and wd_persons_pb2.py.
Use docker-compose up -d to start all the services: Zookeeper
, Kafka, Schema
Registry
, Kafka REST Proxy, Kowl,
Kafka Connect,
and Elasticsearch. Depending on your system, it takes a couple of minutes
before the services are up and running. You can use a tool
like lazydocker
to check the status of the services.
After all the services are up and running, you need to configure Kafka Connect to use the Elasticsearch sink connector. The config file is a JSON formatted file. There is a seperated config file for each connector in the folder /connect. You can find more information about the configuration properties on the official documentation page.
To start the connector, you need to push the JSON config file to Kafka. You can either use the UI dashboard in Kowl or use the bash script provided. It is possible to remove a connector by deleting it through Kowl's UI dashboard or calling the deletion API in the bash script provided.
You can start the crawler with the command below:
poetry run python rb_crawler/main.py --id $RB_ID --state $STATEThe --id option is an integer, which determines the initial event in the handelsregisterbekanntmachungen to be
crawled.
The --state option takes a string (only the ones listed above). This string defines the state where the crawler should
start from.
You can use the --help option to see the usage:
Usage: main.py [OPTIONS]
Options:
-i, --id INTEGER The rb_id to initialize the crawl from
-s, --state [bw|by|be|br|hb|hh|he|mv|ni|nw|rp|sl|sn|st|sh|th]
The state ISO code
--help Show this message and exit.
First download the cleaned Wikidata dumps (Companies and Persons) provided by us and save it in a new folder /data/ named wd_companies_dump.txt and wd_persons_dump.txt.
You can start the extractions with the command below:
poetry run python wd_upserter/wd_companies/main.py
poetry run python wd_upserter/wd_persons/main.pyKowl is a web application that helps you manage and debug your Kafka workloads effortlessly. You can create, update, and delete Kafka resources like Topics and Kafka Connect configs. You can see Kowl's dashboard in your browser under http://localhost:8080.
To query the data from Elasticsearch, you can use the query DSL of elastic. For example:
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query": {
"match": {
<field>
}
}
}
'<field> is the field you wish to search. For example:
"reference_id":"HRB 41865"
You can stop and remove all the resources by running:
docker-compose down